What is the American version of ICD 10 for fetal death?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of O36.4 - other international versions of ICD-10 O36.4 may differ. Applicable To. Maternal care for intrauterine fetal death NOS. Maternal care for intrauterine fetal death after completion of 20 weeks of gestation. Maternal care for late fetal death. Maternal care for missed delivery.
What is the ICD 10 code for continuing pregnancy after intrauterine death?
ICD-10: This coding issue will be addressed in ICD-10 where you will have a code for "Continuing pregnancy after intrauterine death of one fetus or more." Specifically, these codes are: O31.20 -- Continuing pregnancy after intrauterine death of one fetus or more, unspecified trimester
What is the ICD 10 code for missed abortion?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O02.1. Missed abortion. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code Maternity Dx (12-55 years) Female Dx. O02.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 9 code for fetal loss and retention?
Answer: The ICD-9 coding staff weighed in on this one and said that fetal loss is fetal loss even if retained. So you should use 651.3 ( Twin pregnancy with fetal loss and retention of one fetus [0,1,3] ).
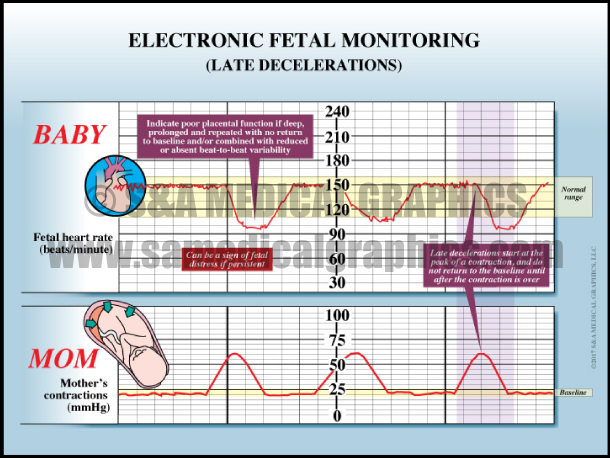
What is the ICD-10 for fetal demise?
4.
Is fetal demise the same as stillbirth?
Stillbirth is a common term for death of a fetus after 20 weeks. It is also called intrauterine fetal death or demise. Causes of stillbirth may include the following: Mother with diabetes or high blood pressure.
What is a fetal demise?
A death that occurs prior to 20 weeks' gestation is usually classified as a spontaneous abortion; those occurring after 20 weeks constitute a fetal demise or stillbirth. Many states use a fetal weight of 350 g or more to define a fetal demise.
What is the ICD 10 code for stillborn?
P95ICD-10 code P95 for Stillbirth is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period .
What is it called when a baby dies after birth?
A neonatal death (also called a newborn death) is when a baby dies during the first 28 days of life. Most neonatal deaths happen in the first week after birth. Neonatal death is different from stillbirth. A stillbirth is when the baby dies at any time between 20 weeks of pregnancy and the due date of birth.
What is the difference between stillbirth and stillborn?
What Is Stillbirth? Stillbirth is the delivery, after the 20th week of pregnancy, of a baby who has died. Loss of a baby before the 20th week of pregnancy is called a miscarriage. A baby is stillborn in about 1 in 200 pregnancies.
What causes fetal demise?
The primary fetal demise causes include: Post-term pregnancy (passing 42 weeks of gestation) Serious maternal infections (e.g., malaria, cytomegalovirus, listeriosis, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, or HIV) Chronic maternal disorders (e.g., diabetes, high blood pressure, or obesity)
What is the difference between stillbirth and IUFD?
Early intrauterine fetal death (IUFD) was defined as intrauterine death < 20 weeks, late IUFD was death at 20–23 weeks and stillbirth was death ≥ 24 weeks.
How common is fetal demise?
Second trimester intrauterine fetal death is typically recognized as a demise after 20 weeks of gestation or a fetal weight of more than 500 grams. It affects about 1 in 100 pregnancies each year in the United States, and the rate has declined by more than 25% in the last 15 years.
What is the CPT code for fetal demise?
365300: Intrauterine Fetal Demise/Stillborn Profile (Extended) | Labcorp.
When is it considered stillbirth?
In the United States, a miscarriage is usually defined as loss of a baby before the 20th week of pregnancy, and a stillbirth is loss of a baby at or after 20 weeks of pregnancy. Stillbirth is further classified as either early, late, or term.
What is the ICD 10 code for missed abortion?
O02.1ICD-10-CM Code for Missed abortion O02. 1.
What is the difference between fetal demise and miscarriage?
The U.S. medical community most often defines miscarriage (also called spontaneous abortion) as the spontaneous loss of a nonviable, intrauterine pregnancy before 20 weeks gestational age (GA), while stillbirth (also called fetal death and intrauterine fetal demise) describes this event at ≥ 20 weeks GA.
What causes fetal demise?
The primary fetal demise causes include: Post-term pregnancy (passing 42 weeks of gestation) Serious maternal infections (e.g., malaria, cytomegalovirus, listeriosis, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, or HIV) Chronic maternal disorders (e.g., diabetes, high blood pressure, or obesity)
What is the difference between fetal death and neonatal death?
Neonatal mortality The number of deaths from birth to under age 28 days. Perinatal mortality There are two definitions of perinatal mortality: The number of deaths of infants under age 7 days, plus fetal deaths that occur at 28 weeks or more of completed gestation.
How common is fetal demise?
Second trimester intrauterine fetal death is typically recognized as a demise after 20 weeks of gestation or a fetal weight of more than 500 grams. It affects about 1 in 100 pregnancies each year in the United States, and the rate has declined by more than 25% in the last 15 years.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for alcohol intoxication with complication
- 2. icd 9 code for non healing ulcer of foot
- 3. what is icd 10 code used for?
- 4. icd 10 code for external cause for doing stunts on scooter
- 5. icd 9 code for severe coagulopathy
- 6. icd 10 code for history cin2 for medicare high risk
- 7. icd-10 code for screening for pelvic
- 8. icd 10 cm code for abscess repacking
- 9. icd 10 code for diabetes mellitus, type i, with diabetic nephrosis.
- 10. icd code for medication given or taken in errors