What is the ICD 10 code for hemangioma?
Hemangioma of other sites. D18.09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM D18.09 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D18.09 - other international versions of ICD-10 D18.09 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for lymphangioma?
D18 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D18. Hemangioma and lymphangioma, any site 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. Type 1 Excludes benign neoplasm of glomus jugulare (D35.6) blue or pigmented nevus (D22.-) nevus NOS (D22.-) vascular nevus (Q82.5) Hemangioma and lymphangioma, any site.
What is a hemangioma tumor?
Hemangioma. Extremely common benign tumor, occurring most commonly in infancy and childhood, made up of newly formed blood vessels, and resulting from malformation of angioblastic tissue of fetal life; can occur anywhere in the body but is most frequently noticed in the skin and subcutaneous tissues.
What is the ICD 10 code for intracranial hemorrhage?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D18.02. Hemangioma of intracranial structures. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. D18.02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for hemangioma?
ICD-10 code D18. 0 for Hemangioma is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Neoplasms .
What is a hemangioma tumor?
A hemangioma (he-man-jee-O-muh) is a bright red birthmark that shows up at birth or in the first or second week of life. It looks like a rubbery bump and is made up of extra blood vessels in the skin. A hemangioma can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly appears on the face, scalp, chest or back.
What is the ICD-10 code for spinal mass?
Malignant neoplasm of spinal cord C72. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C72. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for a cavernous hemangioma?
02.
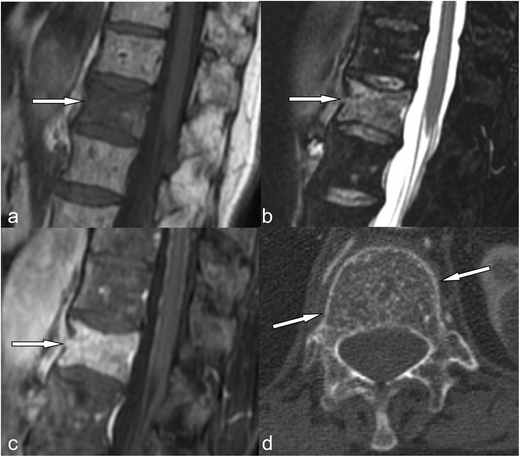
What is hemangioma in the vertebral body?
Spinal hemangiomas are benign tumors that are most commonly seen in the mid-back (thoracic) and lower back (lumbar). Hemangiomas most often appear in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. They are very common and occur in approximately 10 percent of the world's population.
What is an atypical hemangioma of the spine?
Rarely, vertebral hemangiomas can exhibit extraosseous expansion with resulting compression of the spinal cord. Such lesions are termed aggressive or atypical vertebral hemangiomas (AVH) and account for less than 1% of spinal hemangiomas.
What is G95 89?
89 - Other specified diseases of spinal cord.
What is the ICD-10 code for spinal cord compression?
ICD-10 Code for Unspecified cord compression- G95. 20- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for degenerative disc disease?
ICD-10 code M51. 36 for Other intervertebral disc degeneration, lumbar region is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Dorsopathies .
What is the ICD 10 code for a cavernous hemangioma in intracranial structures?
02.
What is the ICD 10 code for Cavernoma?
Q28. 3 - Other malformations of cerebral vessels | ICD-10-CM.
What ICD-10-CM code is used for spinal meningitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Meningitis, unspecified G03. 9.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
Is morphology included in the category and codes?
In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a benign vascular neoplasm characterized by the formation of capillary-sized or
A benign vascular neoplasm characterized by the formation of capillary-sized or cavernous vascular channels. A hemangioma characterized by the presence of cavernous vascular spaces. A vascular anomaly due to proliferation of blood vessels that forms a tumor-like mass.
What is a benign skin lesion?
The majority of cases are congenital. A benign skin lesion consisting of dense, usually elevated masses of dilated blood vessels. A benign tumor of the blood vessels that appears on skin. A benign vascular neoplasm characterized by the formation of capillary-sized or cavernous vascular channels.
Is morphology included in the category and codes?
In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code prophyalactic for premri
- 2. icd 10 code for ibd
- 3. icd 10 cm code for left index finger avulsion laceration
- 4. icd 10 code for presence of nexplanon
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for left adrenal adenoma
- 6. icd 9 code for removal of warts
- 7. icd 10 code for liver cancer with hepatatis c
- 8. icd 10 cm code for dropped razor on toe yesterday
- 9. icd 9 code for right upper lobe pneumonia
- 10. icd 10 code for r/o lung tb