How do you diagnose an adrenal adenoma?
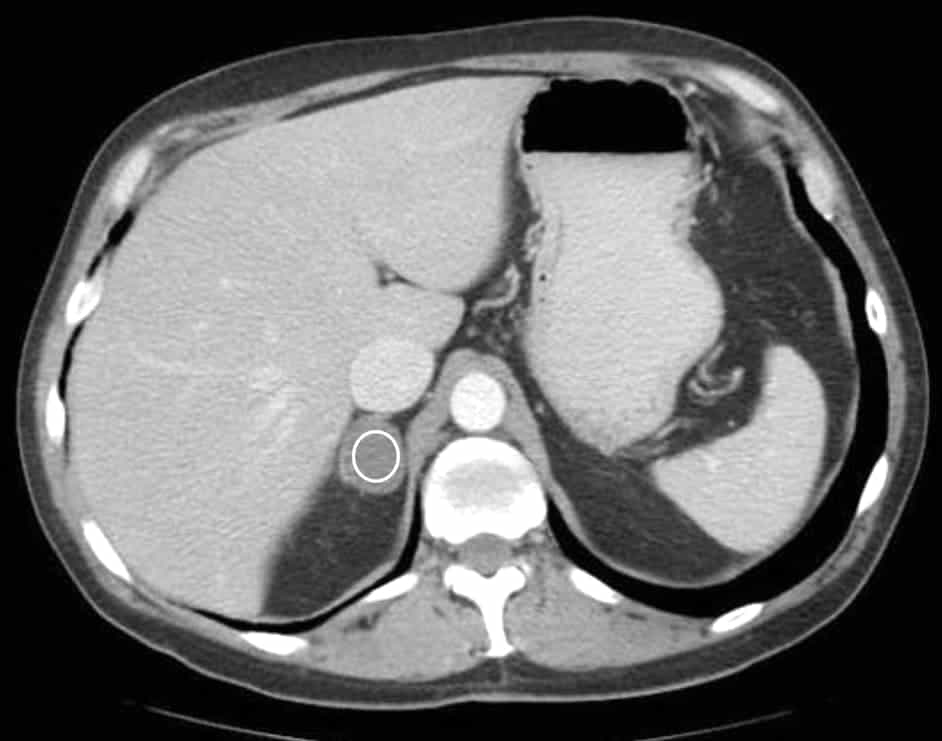
[9] [8] In addition to a complete physical exam and medical history, the following imaging tests are usually necessary to diagnose an adenoma of the adrenal gland: computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan), and/or positron emission tomography (PET scan).
What is the ICD 10 adenocarcinoma?
Adenocarcinoma; Adenocarcinoma ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index. The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index is designed to allow medical coders to look up various medical terms and connect them with the appropriate ICD codes. There are 35 terms under the parent term 'Adenocarcinoma' in the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index.
What are the symptoms of an enlarged adrenal gland?
The symptoms of Cushing’s disease are related to the overproduction of cortisol, and include:
- A lump of fat between the shoulders ( buffalo hump)
- Diabetes
- Excess body hair
- Facial swelling (sometime called moon face)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Obesity
- Sexual dysfunction
- Weakness (loss of strength)
What are the treatments for adrenal gland disorders?
Treatment for adrenal disorders in which tumors manifest either on the glands themselves or on the pituitary gland typically involves some sort of surgery. The operation may be minimally invasive depending on the size or severity of the tumors.
What is the ICD-10 code for adrenal adenoma?
D35. 00 - Benign neoplasm of unspecified adrenal gland. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for left adrenal adenoma?
Benign neoplasm of unspecified adrenal gland D35. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D35. 00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a functional adrenal adenoma?
Functioning (active) adrenal adenomas secrete excess adrenal gland hormones and may cause symptoms that require treatment. Nonfunctioning (inactive) adrenal adenomas don't produce excess adrenal hormones. Most adrenal adenomas are nonfunctioning. They don't cause symptoms or require treatment.
What is the ICD-10 code for right adrenal mass?
ICD-10-CM Code for Benign neoplasm of right adrenal gland D35. 01.
What is an adenoma?
Listen to pronunciation. (A-deh-NOH-muh) A tumor that is not cancer. It starts in gland-like cells of the epithelial tissue (thin layer of tissue that covers organs, glands, and other structures within the body).
What is the ICD-10 code for right adrenal Myelolipoma?
D17.79The alphabetic index in ICD-10 directs you from 'myelolipoma' to 'lipoma', which classifies to D17. Since the adrenal glands are retroperitoneal, D17. 79 is the most correct code, in my opinion.
Where is adrenal adenoma located?
You have two adrenal glands, one located above each kidney. Each gland contains two tissue types: the cortex and the medulla. Benign adrenal tumors that develop in the cortex are also called adrenal adenomas. Those that develop in the medulla are also called pheochromocytomas (fee-o-kroe-moe-sy-TOE-muhs).
What causes adenomas to form?
Gene mutations (changes): Genetic conditions like multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) make adenomas more likely. These types of gene mutations are hereditary (inherited from your biological parents). Genetic diseases: Some adenoma causes, such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), run in families.
How common are adrenal adenoma?
About two to four new cases per 1 million people are diagnosed in this country each year. Overproduction of cortisol may be caused by: A benign tumor on the adrenal gland called an adenoma.
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral adrenal nodules?
Disorder of adrenal gland, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E27. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for pituitary adenoma?
Acromegaly - Pituitary tumor - Pituitary Adenoma (ICD-10 : E22) - Indigomedconnect.
What is an adrenal mass?
An adrenal mass is an abnormal growth that develops in the adrenal gland. It's unclear why these masses form. They can develop in anyone of any age, but they are more common in older individuals.!
What percent of adrenal adenomas are functional?
Differential diagnosis Overall, benign, non-functioning adrenal adenomas account for about 80% of adrenal incidentalomas. Of the tumours that are functional, 5% are pheochromocytomas, 5% cortisol-producing and 1% aldosterone-producing. Adenomas that produce sex hormones are very rare.
Is adrenal adenoma serious?
ANSWER: Adrenal adenomas are one of several types of nodules that develop on the adrenal glands. They are common, and they usually don't pose a health threat or require treatment.
Do adrenal adenomas need to be removed?
Most adrenal tumors are noncancerous (benign). You may need surgery (adrenalectomy) to remove an adrenal gland if the tumor is producing excess hormones or is large in size (more than 2 inches or 4 to 5 centimeters). If you have a cancerous tumor, you also may need an adrenalectomy.
How is adrenal adenoma treated?
For functional tumors, you typically get surgery. You can usually have laparoscopic surgery, where the adrenal gland and tumor are removed through small openings made in your body. But if there's a chance it's cancer, you'll likely need open surgery.
Known As
Adrenal mass is also known as abnormality of cortisol-binding globulin, adrenal cyst, adrenal gland cytomegaly, adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal hypertrophy or hyperplasia, adrenal necrosis, adrenocortical hyperplasia, adrenomedullary hyperplasia, aldosteronism and nodular hyperplasia, adrenal cortex, aldosteronism with nodular hyperplasia of adrenal cortex, cortisol binding globulin abnormality, cortisol binding globulin high, cortisol binding globulin low, enlarged adrenal gland, hyperaldosteronism w nodular hyperplasia of adrenal cortex, hyperaldosteronism with nodular hyperplasia of adrenal cortex, macronodular adrenal hyperplasia, mass of adrenal gland, micronodular adrenal hyperplasia, nodular adrenal cortex, pigmented micronodular adrenal hyperplasia, pseudohypoaldosteronism, pseudoprimary aldosteronism, and salt-losing congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Adrenal Mass Definition and Symptoms
Adrenal mass is a benign, non-cancerous growth of the adrenal gland. Symptoms include excess facial hair, irregular periods, deepening of the voice, decrease in sex drivee, early puberty, and an enlargement of the penis.
What is the ICd 10 code for malignant neoplasm of adrenal gland?
194.0 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of malignant neoplasm of adrenal gland. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
How to treat functional adrenal adenomas?
Functional adrenal adenomas are typically treated with surgery. Removal of the affected adrenal gland usually resolves other medical conditions that may be present as a result of elevated adrenal hormones (i.e. primary aldosteronism, Cushing's syndrome ).
What causes adrenal adenomas?
In these cases, affected people usually have multiple adenomas and other characteristic features of the condition that are all caused by changes ( mutations) in a gene. MEN1 is caused by mutations in the MEN1 gene, while FAP is caused by mutations in the AP C gene. [7] [8] [9]
What is the condition where the adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone?
Primary aldosteronism (also called Conn syndrome) is a condition in which the adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone. This hormone is responsible for balancing the levels of sodium and potassium in the blood.
What is an adenomas?
Adenomas of the adrenal gland are non-cancerous (benign) tumors on the adrenal gland. Most do not cause any signs or symptoms and rarely require treatment. However, some may become "active" or "functioning" which means they produce hormones, often in excess of what the adrenal glands typically produce. High levels of these hormones can lead ...
What is the best test for adrenal gland adenoma?
In addition to a complete physical exam and medical history, the following imaging tests are usually necessary to diagnose an adenoma of the adrenal gland: computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan), and/or positron emission tomography (PET scan). Some people may also need a biopsy of the tumor to confirm the diagnosis. Laboratory tests that evaluate the levels of certain hormones in the blood or urine can be used to determine if the adrenal adenoma is functional or nonfunctional. [2]
What are the symptoms of adenomas?
Symptoms of this condition may include high blood pressure, fatigue, headache, muscle weakness, numbness and paralysis that comes and goes. [5] Benign cortisol-secreting adenomas can also produce small amounts of androgens (steroid hormones, such as testosterone), although androgen levels in the blood are usually not elevated. [3] . ...
What are the effects of androgens on masculine traits?
Excess amounts of androgens can cause an increase in masculine characteristics (virilization) such as increased facial and body hair (hirsutism); deepening of the voice; increased muscularity; and other characteristics. [6] Last updated: 11/24/2014.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for staging left breast cancer
- 2. icd-10 code for sle
- 3. icd 10 code for concerning mass
- 4. icd 10 code for bilateral breast lumpectomies
- 5. icd 10 code for withdrawal from benzodiazepines
- 6. icd-10-cm code for history of respiratory bacterial infection
- 7. icd-10 code for eeg
- 8. icd 10 code for heterotopic ossification elbow post op
- 9. icd 10 cm code for calculus of gallbladder
- 10. icd 10 code for ckd4