What causes calcification of the uterus?
- Preterm birth
- Low birth weight
- Low Apgar score
- Postpartum hemorrhage
- Placental abruption
- Fetal distress
- Stillbirth
What causes calcification of fibroids?
Sometimes this condition is caused by scarring from IUDs or from previous surgeries. Hyaline degeneration that supplies its own blood supply can lead up to calcification formation. The calcification that forms on the wall can be thin, however can grow into fibroid like tumors or cysts. It can also spread to other parts of the uterus.
Can uterine fibroids be cured?
You may need a combination of therapies. In moderate to severe cases where symptoms are bothersome, worsening, or not improved with medication, fibroids may be treated with surgery or ultrasound therapy. Surgery may involve removing just the fibroids or your entire uterus.
How to reduce uterine fibroid pain?
What can you do to reduce fibroid pain?
- Easing the pain at home. Fibroids can cause pain that interferes with daily life. ...
- Medication. A person can take medication to help ease fibroid pain. ...
- Surgery. When fibroids cause pain, and medication does not work, a person may consider surgery. ...
- Other symptoms of fibroids
- Diagnosis. ...
- Causes. ...
- When to see a doctor. ...
- Summary. ...
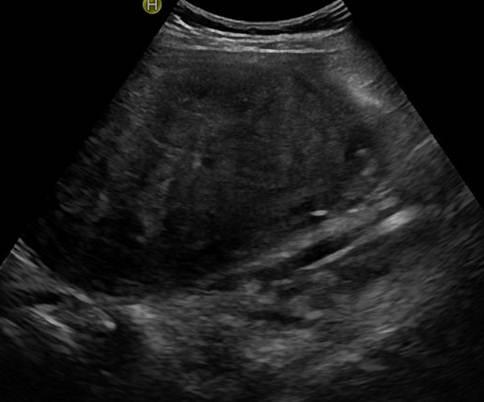
What is the ICD-10 code for calcified uterine fibroid?
Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D25. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis code for uterine fibroids?
D25. 9 - Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What are the classification of fibroids?
There are four main types of fibroids: Intramural fibroids. Subserosal fibroids. Pedunculated fibroids.
What is the ICD-10 code for submucosal fibroid?
D25. 0 - Submucous leiomyoma of uterus | ICD-10-CM.
What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. Also called leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs) or myomas, uterine fibroids aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer.
What does pedunculated fibroid mean?
Pedunculated fibroids are benign (noncancerous) growths in the uterus. These fibroids are attached to the uterine wall by a stalk-like growth called a peduncle. The main difference between pedunculated fibroids and other fibroids is the peduncle. These fibroids can grow both inside and outside the uterus.
What are the four types of fibroids?
According to their position within the uterine wall, uterine fibroids are classified in four different types:Subserosal Fibroids. Subserosal Fibroids are located near the outer layer or serosa of the uterus. ... Submucosal Fibroids. ... Intramural Fibroids. ... Pedunculated Fibroids.
What is the most common type of uterine fibroid?
Subserosal fibroids: These are the most common fibroids. They can push outside of the uterus into the pelvis. Subserosal fibroids can grow large at times and sometimes have a stalk that attaches to the uterus (pedunculated fibroid).
What is a Type 2 uterine fibroid?
A broad definition is that submucosal fibroids are those that distort the endometrial cavity; however, submucosal fibroids can be further subdivided into three subtypes: Type 0, pedunculated fibroids without any intramural extension; Type I, sessile with less than 50% intramural extension; and Type II, sessile with ...
What is a submucosal fibroid?
Submucosal fibroids are a type of uterine fibroid that grow in the uterine cavity, just under the surface of the endometrium (uterine lining). 2. Submucosal fibroids are the least common type of uterine fibroids, but they typically cause the most problems.
What is an intramural fibroid?
An intramural fibroid is a noncancerous tumor that grows between the muscles of the uterus. There are several types of intramural fibroids: anterior intramural fibroid, located in the front of the uterus. posterior intramural fibroid, located in the back of the uterus.
What is the ICD-10 code for myomectomy?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98. 891 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z98.
What is the ICd 9 code for uterine fibroids?
If you have no symptoms, you may not even need treatment. nih: national institute of child health and human development. ICD-9-CM Coding Information. 218.9 is only applicable to female patients.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
ICD-9-CM 218.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 218.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What is a fibrous tumor?
Uterine fibroids are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women of childbearing age . Fibroids are made of muscle cells and other tissues that grow in and around the wall of the uterus, or womb. The cause of fibroids is unknown. Risk factors include being african-american or being overweight.
What is the definition of fibromyoma?
Fibromyoma (M8890/0) - see also Neoplasm, connective tissue, benign. uterus (corpus) (see also Leiomyoma, uterus) 218.9. in pregnancy or childbirth 654.1. affecting fetus or newborn 763.89. causing obstructed labor 660.2. affecting fetus or newborn 763.1.
What is the ICd 10 code for uterus?
621.8 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other specified disorders of uterus, not elsewhere classified. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
How many women develop fibroids?
Many people develop uterine fibroids in their lifetimes. In fact, approximately 33 percent of women develop fibroids before age 50. If you’ve been diagnosed with this common condition, you’re not alone. Depending on your symptoms, treatment could help you find relief and meet your goals.
What happens to fibroid cells?
When this happens, the cells in the fibroid begin to degenerate, or die, in order to bring the fibroid back to a sustainable size. During this degeneration process, calcium deposits build up on top of the remaining fibroid tissue — we call fibroids “calcified” after this process is complete.
Can fibroids cause constipation?
After calcification, fibroids can cause new or increased symptoms. For example, a large calci fied fibroid can put pressure on the bladder or bowel, causing symptoms like frequent urination or constipation. In addition, calcified fibroids may act like regular fibroids, causing abdominal pain, pressure, or other unpleasant symptoms.
Do you need to know about fibroids?
Before you can decide on a treatment for uterine fibroids, however, you need to know how fibroids affect you specifically — it’s helpful to know the location and size of the fibroids as well as whether or not they are calcified, since these details may influence treatment decisions. To successfully navigate this process, ...
Can fibroid calcification affect your life?
However, if symptoms of fibro id calcification are negatively affecting your life, you don’t have to face the situation alone — a fibroid specialist at USA Fibroid Centers can provide valuable support and guidance. Fibroid Symptom Checker.
What does it mean when a woman's fibroid is calcified?
When a woman’s fibroid (s) calcify, it indicated the end stages of degeneration and she may experience less pain or abnormal periods than during the growth and degeneration periods. When the calcified fibroid is large, it may put pressure on the bladder and bowel causing the need for frequent urination, incontinence issues, constipation, ...
What is calcified fibroid?
What is a calcified fibroid? A calcified fibroid is when a fibroid has reached the final stage of degeneration, or cell death and calcium deposits develop on the remaining fibroid tissue. Fibroids are benign tumors that grow in or on the uterine walls.
Why are fibroids different from calcified fibroids?
Calcified fibroids are different only because they typically have become larger than the blood supply that was attributed to the growth. Now that the blood supply has been compromised the tumor degenerates and may become smaller.
What is the first step in a fibroids treatment plan?
The first step in any treatment plan should be a thorough diagnostic assessment including a detailed conversation about the symptoms, a pelvic exam, and imaging tests, if necessary. The symptoms common to fibroids can also be caused by other conditions such as uterine polyps, polycystic ovary syndrome, or endometriosis.
Can calcification cause miscarriage?
Calcified fibroids can also cause complications in pregnancy including miscarriage, premature placenta detachment, or breech positioning.
What is the code for uterine fibroids?
Hysterectomy —Uterus removal is the only certain way to cure uterine fibroids. For a hysterectomy performed via the abdomen, look to code range 58150-58240. For a hysterectomy by vaginal approach, select a code from 58260-58294.
What is the ICd 9 code for fibroid?
Most fibroids grow within the uterus wall. These are known as intramural fibroids and are reported using 218.1 Intramural leiomyoma of uterus (interstitial leiomyoma of uterus). Whereas submucosal fibroids (218.0 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus) grow into the uterine cavity; and subserosal fibroids (218.2 Subserous leiomyoma of uterus) grow outside of the uterus.#N#Other fibroids grow on stalks from the uterus’ surface or in the uterus’ cavity (they might look like mushrooms). These are called pedunculated fibroids and are reported with 218.9 Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified. You should also report 218.9 if the provider does not specify the location of the uterine fibroid.
What is the procedure code for a vaginal hysterectomy?
58550 Laparoscopy, surgical, with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less; 58552 Laparoscopy, surgical, with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less; with removal of tube (s) and/or ovary (s) 58553 Laparoscopy, surgical, with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus greater than 250 g;
Where do submucosal fibroids grow?
Whereas submucosal fibroids (218.0 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus) grow into the uterine cavity; and subserosal fibroids (218.2 Subserous leiomyoma of uterus) grow outside of the uterus. Other fibroids grow on stalks from the uterus’ surface or in the uterus’ cavity (they might look like mushrooms).
What test is used to confirm fibroids?
The physician may perform imaging tests to confirm fibroids. These tests might include: Ultrasound —The ultrasound probe can be placed on the abdomen or inside the vagina. For pelvic exam, report 76856 Ultrasound, pelvic (nonobstetric), real time image documentation; complete.
Can fibroids displace fallopian tubes?
Fibroids may also displace the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Because fibroids are almost always benign, it is rare (less than one in 1,000 cases) for a cancerous fibroid (leiomyosarcoma) to occur. No one knows for sure what causes fibroids.
Can a doctor check for fibroids?
The physician may also perform hysteroscopy to confirm fibroids. The doctor passes a long, thin scope with a light through the vagina and cervix into the uterus; no incision is needed. The doctor can look inside the uterus for fibroids and other problems, such as polyps.
What is a fibrous tumor?
Uterine fibroids are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women of childbearing age . Fibroids are made of muscle cells and other tissues that grow in and around the wall of the uterus, or womb. The cause of fibroids is unknown. Risk factors include being african-american or being overweight.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
Can fibroids cause infertility?
most women with fibroids can get pregnant naturally. For those who cannot, infertility treatments may help. Treatment for uterine fibroids includes medicines that can slow or stop their growth, or surgery.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the cpt code for icd placement
- 2. icd 10 code for tracheostomy
- 3. icd 10 cm code for neonatal jaundice
- 4. icd 10 code for cerebellar infarct
- 5. icd 9 code for cellulitis of leg without abscess
- 6. icd 10 cm code for viable birth single live birth
- 7. icd-10 code for subgaleal hematoma in adults
- 8. icd 10 cm code for foley catheter removal
- 9. icd 9 code for colonic inertia
- 10. find icd 10 code for corneal abrasion left eye