What is the CPT code for a thickened endometrium?
Thickened endometrium For a thickened endometrium you would use code 621.30 for a thickened endometrium found by use of an ultrasound you would use code 793.5
What is the latest version of ICD 10 for Tia?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I77.9 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I77.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 I77.9 may differ. transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes ( G45.-)
Is intima-media thickness a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis?
Intima-media thickness is an important atherosclerotic risk marker. However, this increase is not synonymous with subclinical atherosclerosis, but is related to it.
What is a normal intima-media thickness for a carotid artery?
An article from the e-journal of the ESC Council for Cardiology Practice. Intima-media thickness values of more than 0.9 mm (ESC) or over the 75th percentile (ASE) should be considered abnormal. Carotid artery ultrasound scan is the method of choice and results are reliable provided certain standards are followed.
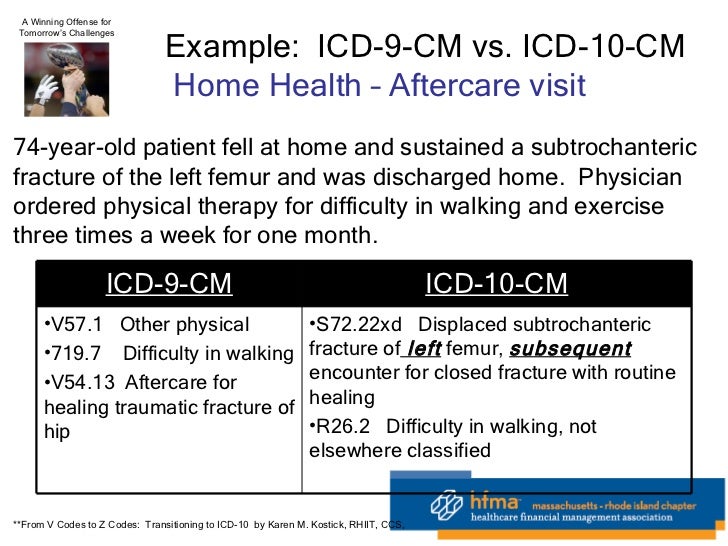
How do I find ICD-9 codes?
ICD9Data.com takes the current ICD-9-CM and HCPCS medical billing codes and adds 5.3+ million links between them. Combine that with a Google-powered search engine, drill-down navigation system and instant coding notes and it's easier than ever to quickly find the medical coding information you need.
What are ICD-9 10 and CPT codes?
In a concise statement, ICD-9 is the code used to describe the condition or disease being treated, also known as the diagnosis. CPT is the code used to describe the treatment and diagnostic services provided for that diagnosis.
What is the ICD-9 code for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
ICD-9 code 425.11 for Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -OTHER FORMS OF HEART DISEASE (420-429).
Is ICD-9 still used in 2020?
Easier comparison of mortality and morbidity data Currently, the U.S. is the only industrialized nation still utilizing ICD-9-CM codes for morbidity data, though we have already transitioned to ICD-10 for mortality.
What is an ICD-9 10 code?
ICD-9-CM is the official system of assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. The ICD-9 was used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates until 1999, when use of ICD-10 for mortality coding started.
How many ICD-9 codes are there?
13,000 codesThe current ICD-9-CM system consists of ∼13,000 codes and is running out of numbers.
What is the ICD-10 code for I42 9?
9: Cardiomyopathy, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
ICD-10 code I42. 2 for Other hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is the diagnosis code for left ventricular hypertrophy?
I51. 7 - Cardiomegaly. ICD-10-CM.
Why are ICD-9 codes no longer used?
Why the move from ICD-9 codes to ICD-10 codes? The transition for medical providers and all insurance plan payers is a significant one since the 18,000 ICD-9 codes are to be replaced by 140,000 ICD-10 codes. ICD-10 replaces ICD-9 and reflects advances in medicine and medical technology over the past 30 years.
When was ICD-9 discontinued?
No updates have been made to ICD-9 since October 1, 2013, as the code set is no longer being maintained.
Why did ICD-9 change to ICD-10?
ICD-9 follows an outdated 1970's medical coding system which fails to capture detailed health care data and is inconsistent with current medical practice. By transitioning to ICD-10, providers will have: Improved operational processes by classifying detail within codes to accurately process payments and reimbursements.
What is the IMT in a carotid artery?
Intima-media thickness (IMT) is a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis (asymptomatic organ damage) and should be evaluated in every asymptomatic adult or hypertensive patient at moderate risk for cardiovascular disease. Intima-media thickness values of more than 0.9 mm (ESC) or over the 75th percentile (ASE) should be considered abnormal. A carotid artery ultrasound scan is the method of choice, and results are reliable, provided certain standards are followed.
Where is IMT measured?
IMT measurement at a distance of at least 5 mm below the distal end of CCA (IMT could also be measured at the carotid bifurcation and internal carotid artery bulb, but the values should be given separately).
What is B-mode ultrasonography?
B-mode ultrasonography is a noninvasive, safe, easily performed, reproducible, sensitive, relatively inexpensive and widely available method for detection of early stages of atherosclerosis and is accepted as one of the best methods for evaluation of arterial wall structure.#N#IMT is defined as a double-line pattern visualised by echo 2D on both walls of the common carotid artery (CCA) in a longitudinal view. Two parallel lines (leading edges of two anatomical boundaries) form it: lumen-intima and media-adventitia interfaces – Fig. 1.
What is IMT measurement?
What: IMT measurement is advised in a search for target organ damage; asymptomatic vascular damage could be detected with ultrasound scanning of carotid arteries searching for vascular hypertrophy or asymptomatic atherosclerosis. Damage is defined as the presence of IMT >0.9 mm or plaque. The other markers of asymptomatic vascular (target organ) damage are: pulse pressure ≥ 60 mmHg, carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity > 10 m/s and ankle-brachial index < 0.9.
What causes IMT to increase?
Indeed, increase in IMT is also the result of nonatherosclerotic processes such as smooth muscle cell hyperplasia and fibrocellular hypertrophy leading to medial hypertrophy and compensatory arterial remodeling. Therefore This process may be an adaptive response to changes in flow, wall tension, or lumen diameter.
Is IMT a subclinical marker?
Intima-media thickness is accepted as a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis and IMT screening can help the clinician to reclassify a substantial proportion of intermediate cardiovascular risk patients into a lower or higher risk category. In order to implement IMT screening in our daily practice, however, we should be aware of the standards of measurement, as they are described here.
Is IMT a routine measure?
Vascular ultrasound (IMT measurement) is not recommended for routine measurement in clinical practice for risk assessment for a first atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease event. (8) Serial studies of IMT to assess progression or regression in individual patients are not recommended.

Background
I – What to Evaluate and in Which Patients – Guidelines
- Screening for multisite artery diseases is important in asymptomatic adults at moderate cardiovascular risk, as well as in hypertensive patients. (2, 3) The clinician searches for evidence of asymptomatic organ damage, which can further determine cardiovascular risk and lead to reclassification of intermediate risk patients into low or high risk categories. (4-6)
II – Intima-Media Thickness Measurement
- Examination of the carotid wall gives every clinician an opportunity to evaluate subclinical alterations in wall structure that precede and predict future cardiovascular clinical events. B-mode ultrasonography is a noninvasive, safe, easily performed, reproducible, sensitive, relatively inexpensive and widely available method for detection of early stages of atherosclerosis and is …
III - Challenges and Current Recommendations For IMT Measurement
- One of the main problems in interpreting IMT results from clinical trials is the differences in measurement methodology. These discrepancies can refer to either one or more of these parameters: the precise definition of the investigated carotid segment, the use of mean or maximal IMT, the measurement of near and far wall or only far wall IMT, the insonation at a sing…
IV – Normal Versus Abnormal Values
- Normal IMT values and reference ranges are age- and sex-dependent – there is a significant steady increase in IMT with advancing age in all carotid segments (16-18) and significantly higher IMT values in men than in women – Table 1. Table 1. Normal IMT values – median (P50), 25th and 75th percentile (P) IMT values for men and women at different age categories, separately fo…
Conclusions
- Intima-media thickness is accepted as a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis and IMT screening can help the clinician to reclassify a substantial proportion of intermediate cardiovascular risk patients into a lower or higher risk category. In order to implement IMT screening in our daily practice, however, we should be aware of the standards of measurement, as they are described …
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2017 icd 10 code for bilateral cystic breast
- 2. icd 10 code for vascular depletion
- 3. icd 10 code for coma scale, eyes open, to sound
- 4. icd 10 code for metastatic breast cancer left side
- 5. 2016 icd 10 code for compression fracture c2
- 6. icd 10 code for history of presyncope
- 7. icd 10 code for b. type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic nephropathy
- 8. icd 10 code for lytic metastases
- 9. icd 10 code for thrombotic disorder
- 10. icd 10 code for r14.0