What is the ICD 10 code for esophagus with tracheo-esophageal fistula?
Atresia of esophagus with tracheo-esophageal fistula 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Q39.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Q39.1 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for esophageal abscess without fistula?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Q39.0. Atresia of esophagus without fistula. Q39.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the difference between tracheoesophageal fistula and esophagal atresia?
The trachea is for air, the esophagus is for food. If the esophagus and trachea form abnormally or don’t divide completely, an esophageal atresia and/or tracheoesophageal fistula can occur. While EA can appear alone, most forms of EA also include TEF. What is esophageal atresia?
Is esophageal atresia the same as TEF?
While EA can appear alone, most forms of EA also include TEF. What is esophageal atresia? An esophageal atresia occurs when the esophagus is formed in two segments, and the baby is born with their esophagus not attached to their stomach.
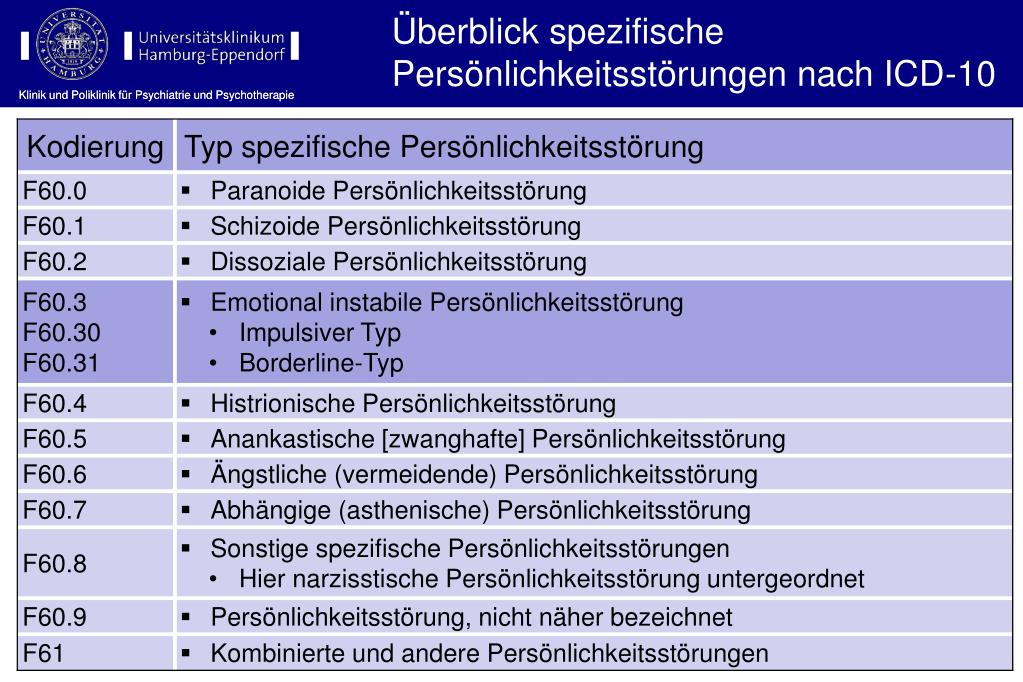
What is the ICD 10 code for tracheoesophageal fistula?
Tracheo-esophageal fistula following tracheostomy J95. 04 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J95. 04 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for esophageal atresia?
1 for Atresia of esophagus with tracheo-esophageal fistula is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
Is esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula the same?
TE fistula is an abnormal connection between the esophagus and the trachea. Esophageal atresia happens when the esophagus has 2 segments. These parts don't connect to each other. Your child's healthcare provider will often spot symptoms of these issues soon after your baby is born.
What is distal tracheoesophageal fistula?
Collapse Section. Esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula (EA/TEF) is a condition resulting from abnormal development before birth of the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach (the esophagus ).
What does TEF mean in medical terms?
EA often occurs in association with a tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF), which is an abnormal passage or connection (fistula) between the esophagus (usually the lower) and the trachea (windpipe).
What is the ICD-10 code for difficulty swallowing?
Code R13. 10 is the diagnosis code used for Dysphagia, Unspecified. It is a disorder characterized by difficulty in swallowing. It may be observed in patients with stroke, motor neuron disorders, cancer of the throat or mouth, head and neck injuries, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
When is EA TEF diagnosis?
If your baby has TEF alone, it may be weeks or months after birth before TEF is diagnosed as the cause of symptoms. Symptoms of EA only: Your baby is not swallowing their saliva, is drooling a lot or has foamy mucus in their mouth or nose. Most often, EA alone is diagnosed before birth or right after birth.
What are the types of esophageal atresia?
There are four types of esophageal atresia: Type A, Type B, Type C and Type D.Type A is when the upper and lower parts of the esophagus do not connect and have closed ends. ... Type B is very rare. ... Type C is the most common type. ... Type D is the rarest and most severe.
What are the 5 types of tracheoesophageal fistula?
Type A = pure esophageal atresia; type B = esophageal atresia with proximal tracheoesophageal fistula; type C = esophageal atresia with distal tracheoesophageal fistula; type D = esophageal atresia with proximal and distal tracheoesophageal fistula; type E = H-type tracheoesophageal fistula without esophageal atresia.
Which of the following forms of tracheoesophageal fistula and esophageal atresia is most common?
Type C esophageal atresia is the most prevalent at 84% and involves a proximal EA with distal tracheoesophageal fistula. Type D is esophageal atresia with both a proximal and distal TEF. It is rare at 3%. Type E esophageal atresia is just an isolated tracheoesophageal fistula without associated esophageal atresia.
How many types of tracheoesophageal fistula are there?
Esophageal atresia is closely related to tracheo-esophageal fistula and can be divided into1: type A: isolated esophageal atresia (8%) type B: proximal fistula with distal atresia (1%) type C: proximal atresia with distal fistula (85%)
How do you say esophageal atresia?
0:261:12How to Pronounce "Esophageal Atresia" - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipEsophageal atresia esophageal atresia.MoreEsophageal atresia esophageal atresia.
What is esophageal atresia?
Esophageal atresia is a birth defect in which part of a baby's esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach) does not develop properly. Esophageal atresia is a birth defect of the swallowing tube (esophagus) that connects the mouth to the stomach.
What is the ICD-10 code for respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure, unspecified, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia. J96. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.
What is the ICD-10 code for Tracheomalacia?
ICD-10 code Q32. 0 for Congenital tracheomalacia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
What is the ICD-10 code for aspiration pneumonia?
ICD-10 Code for Pneumonitis due to inhalation of food and vomit- J69. 0- Codify by AAPC.
What is the name of the condition where the esophagus is not attached to the stomach?
An esophageal atresia occurs when the esophagus is formed in two segments, and the baby is born with their esophagus not attached to their stomach. The upper part connects the mouth/throat to a blind pouch (proximal end), and the lower part connects the stomach to a blind pouch (distal end). In infants with esophageal atresia, the two ends ...
How long does it take for a baby to heal from esophageal atresia?
If a leak occurs, it will generally heal in a week or two. Additional surgery is not usually necessary.
What is a small camera inserted into the windpipe?
In a bronchoscopy, a small camera is inserted into the windpipe to look for fistulas that are small, hidden, or not obvious from prior tests. If your child has tracheoesophageal fistula and esophageal atresia, the surgeon may decide to place a gastrostomy tube that can be used to feed your child and “burb” the stomach of excess air. ...
How long does it take for a TE fistula to show up?
Babies with a TE fistula — but not EA — may take several weeks to diagnose because TE fistula symptoms generally only appear as mild coughing or respiratory problems. Other tracheoesophageal fistula symptoms and/or esophageal atresia symptoms can include: Frothy, white bubbles from the mouth. Vomiting.
What happens if the esophagus and trachea don't divide completely?
If the esophagus and trachea form abnormally or don’t divide completely, an esophageal atresia and/or tracheoesophageal fistula can occur. While EA can appear alone, most forms of EA also include TEF.
How do you know if you have esophageal atresia?
The most common esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula symptoms include: Difficulty breathing. Coughing or choking when swallowing or attempting to feed.
What is the EA?
Esophageal atresia (EA) and tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) are rare conditions that develop before birth. They often occur together and affect the development of the esophagus, trachea or both. These conditions can be life-threatening and must be treated shortly after birth. During normal prenatal development, ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. each unique icd-10-cm diagnosis code may be reported more than once for an encounter
- 2. icd-10 code for biliary obstruction
- 3. icd 10 code for 852.2
- 4. icd 10 code for twin delivery
- 5. icd 10 code for cerebrospinal fluid leak
- 6. icd-10-cm code for cad involving coronary bypass graft native artery without angina
- 7. icd 10 code for expressive aphasia syndrome
- 8. icd 9 code for staphylococcus
- 9. icd 10 cm code for hemolysis
- 10. icd-10 code for rule out chest pain