What is renal insufficiency ICD 10?
The patient is diagnosed as having acute renal insufficiency due to dehydration with decreased urinary output and was admitted for IV hydration. What diagnosis codes should we assign? A: The ICD-10-CM codes that would be most appropriate for this case are: ICD-10-CM code N28.9 is reported to capture the acute renal insufficiency.
Is chronic kidney disease stage 5 ICD 10 curable?
N18.5 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Chronic kidney disease, stage 5 . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 . ICD-10 code N18.5 is based on the following Tabular structure:
What is the ICD 10 for chronic renal insufficiency?
- ICD-10-CM Codes › N00-N99 Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease › . (2018). Retrieved August 17, 2018, from www.icd10data.com: https://www.icd10data.com/ICD10CM/Codes/N00-N99/N17-N19
- International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10)-WHO Version. (2016). ...
- Yu, B. N. ...
What is post renal obstruction?
Postrenal failure is a type of acute renal failure that occurs as a result of obstruction to urine outflow. This obstruction to urine outflow can occur anywhere after, or 'post-,' the kidneys. This...
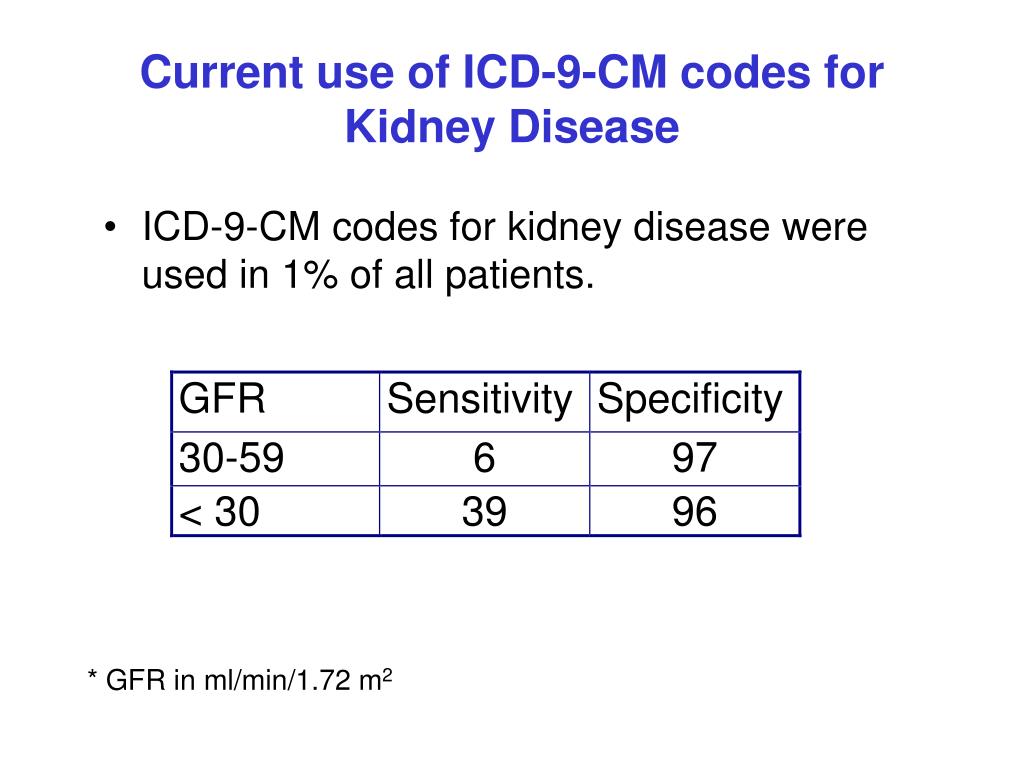
What is the ICD-10 code for renal calculi?
ICD-10 code N20. 0 for Calculus of kidney is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the ICD-10 code for left renal calculi?
N20. 0 - Calculus of kidney | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary obstruction?
N13. 9 - Obstructive and reflux uropathy, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is ICD-10 code for history of kidney stones?
ICD-10 code Z87. 442 for Personal history of urinary calculi is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10-CM code for right renal calculi and bladder calculus?
N21. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N21.
What is left renal calculus?
Kidney stones, or renal calculi, are solid masses made of crystals. Kidney stones usually originate in your kidneys. However, they can develop anywhere along your urinary tract, which consists of these parts: kidneys. ureters.
What is ureteral obstruction?
A ureteral obstruction is a blockage in one or both of the tubes (ureters) that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Ureteral obstruction can be cured. However, if it's not treated, symptoms can quickly move from mild — pain, fever and infection — to severe — loss of kidney function, sepsis and death.
What is urinary obstruction?
Urinary tract obstruction is a blockage that inhibits the flow of urine through its normal path (the urinary tract), including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
What is an obstruction of the urethra called?
What is obstructive uropathy? Obstructive uropathy is when your urine can't flow (either partially or completely) through your ureter, bladder, or urethra due to some type of obstruction. Instead of flowing from your kidneys to your bladder, urine flows backward, or refluxes, into your kidneys.
How do you code for calculi in both the kidney and ureter?
ICD-10 code N20. 2 for Calculus of kidney with calculus of ureter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What K57 92?
ICD-10 code: K57. 92 Diverticulitis of intestine, part unspecified, without perforation, abscess or bleeding.
What does Pyonephrosis mean?
Pyonephrosis—pus in the renal pelvis—results from urinary tract obstruction in the presence of pyelonephritis. Purulent exudate (inflammatory cells, infectious organisms, and necrotic, sloughed urothelium) collects in the hydronephrotic collecting system ("pus under pressure") and forms an abscess.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for undescended testicle unilateral
- 2. icd 10 code for history of facial fracture
- 3. icd 10 code for elevated hep c virus antibody
- 4. icd 10 code for routine pap and pelvic
- 5. icd 10 code for cephalic vein occlusion
- 6. icd 10 code for vascular line removal
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for subclavian steal syndrome
- 8. icd 10 code for r63.5
- 9. icd-10 code for avian flu
- 10. icd 10 code for basal ganglia infarction