Full Answer
What is the ICD 10 code for adenoma of the left adrenal?
ICD-10-CM Code D35.02 Benign neoplasm of left adrenal gland. An adenoma (from Greek αδένας, adeno-, "gland" + -ώμα, -oma, "tumor") (/ˌædᵻˈnoʊmə/; plural adenomas or adenomata /ˌædᵻˈnoʊmᵻtə/) is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs,...
What are adenomas of the adrenal gland?
"Adenomas of the adrenal gland are non-cancerous (benign) tumors on the adrenal gland. Most do not cause any signs or symptoms.
How is adenoma of the adrenal gland diagnosed?
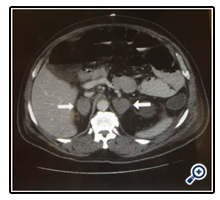
Diagnosis Diagnosis. In addition to a complete physical exam and medical history, the following imaging tests are usually necessary to diagnose an adenoma of the adrenal gland: computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan), and/or positron emission tomography (PET scan).
Do physician coding services bill for adrenal cancer diagnostic tests?
Physicians must report the diagnostic tests and other treatment procedures performed using the right medical codes. Medical coding services can ensure the right use of relevant codes to bill for the procedures correctly.ICD-10 diagnosis codes for adrenal cancer include –
How to treat functional adrenal adenomas?
What causes adrenal adenomas?
What is the name of the condition where the adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone?
What is an adenomas?
What is the best test for adrenal gland adenoma?
Can adrenal adenomas be inherited?
Can adrenal adenomas cause symptoms?
See 4 more
About this website
What is the ICD 10 code for right adrenal adenoma?
ICD-10-CM Code for Benign neoplasm of right adrenal gland D35. 01.
What is the ICD 10 code for adrenal adenomas?
D35. 00 - Benign neoplasm of unspecified adrenal gland | ICD-10-CM.
What is a right adrenal adenoma?
Adrenal Adenoma. An adrenal adenoma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that forms in your adrenal glands. It's the most common type of adrenal gland tumor. Most adrenal adenomas don't produce symptoms or require treatment. However, some adenomas may cause your adrenal glands to secrete excess hormones, like cortisol.
What is the ICD 10 code for left adrenal adenoma?
Benign neoplasm of unspecified adrenal gland D35. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D35. 00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis code for adrenal mass?
ICD-10 code E27. 9 for Disorder of adrenal gland, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is ICD-10 code for nodule on adrenal gland?
Other specified disorders of adrenal gland The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E27. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is meant by adenoma?
Listen to pronunciation. (A-deh-NOH-muh) A tumor that is not cancer. It starts in gland-like cells of the epithelial tissue (thin layer of tissue that covers organs, glands, and other structures within the body).
What is a non functioning adrenal adenoma?
Most adrenal adenomas are considered “nonfunctioning,” which means they do not produce hormones and usually do not cause symptoms. If adrenal adenomas become "functioning" or "active" and secrete excess hormones, they can cause conditions such as Cushing's syndrome, primary aldosteronism, or virilization.
What are the different types of adrenal tumors?
Types of tumors that start in the adrenal glands include:Adenoma. This is the most common kind of adrenal gland tumor. ... Adrenal cortex cancer (adrenal cortical carcinoma). This kind of tumor is rare. ... Pheochromocytoma. This is a tumor that makes hormones inside the adrenal glands (in the medulla). ... Neuroblastoma.
Are adenomas always benign?
Adenomas are generally benign or non cancerous but carry the potential to become adenocarcinomas which are malignant or cancerous. As benign growths they can grow in size to press upon the surrounding vital structures and leading to severe consequences.
What is a adrenal tumor?
Benign adrenal tumors are noncancerous masses that form in the adrenal glands. As part of the endocrine system, the adrenal glands produce hormones that give instructions to nearly every organ and tissue in the body. You have two adrenal glands, one located above each kidney.
What is a lesion on the adrenal gland?
Most adrenal lesions represent benign nonfunctioning masses called adenomas. The vast majority are discovered during an examination that is being performed for reasons other than suspected adrenal disease.
Are adenomas always benign?
Adenomas are generally benign or non cancerous but carry the potential to become adenocarcinomas which are malignant or cancerous. As benign growths they can grow in size to press upon the surrounding vital structures and leading to severe consequences.
What is a adrenal tumor?
Benign adrenal tumors are noncancerous masses that form in the adrenal glands. As part of the endocrine system, the adrenal glands produce hormones that give instructions to nearly every organ and tissue in the body. You have two adrenal glands, one located above each kidney.
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral adrenal nodules?
Disorder of adrenal gland, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E27. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the symptoms of a tumor on the adrenal gland?
Adrenal Gland Tumor: Symptoms and SignsHigh blood pressure.Low potassium level.Heart palpitations.Nervousness.Feelings of anxiety or panic attacks.Headache.Heavy sweating/perspiration.Diabetes.More items...
What Is Adrenal Gland Adenoma? - WebMD
An adrenal gland adenoma is a tumor on your adrenal gland that isn’t cancer, but can still cause problems. Learn what causes them, how to know if you might have one, and how they’re treated.
Adenoma of the Adrenal Gland: Symptoms & Treatment - Cleveland Clinic
An adrenal adenoma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that forms in your adrenal glands. It’s the most common type of adrenal gland tumor. Most adrenal adenomas don’t produce symptoms or require treatment.
Adrenal Adenoma | Adrenal Adenoma Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prognosis
Adrenal Adenoma. An Adrenal Adenoma is a non-threatening (otherwise known as benign) tumour that is found on the adrenal gland. By standard definition, this condition will normally not cause any problems to one's health.
Mayo Clinic Q and A: Understanding adrenal adenoma
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: On a scan of my abdomen, an adenoma was found incidentally on one of my adrenal glands. What causes this? Should I be concerned? I am a 74-year-old woman. Although I am overweight, I'm in generally good health otherwise. ANSWER: Adrenal adenomas are one of several types of nodules that develop on […]
Adenomas: Types, Causes, Symptoms & Prevention - Cleveland Clinic
Adenomas are noncancerous tumors. They may grow along your adrenal, parathyroid or pituitary glands. If your adenoma is small, your healthcare provider may use a wait-and-see approach.
How to treat functional adrenal adenomas?
Functional adrenal adenomas are typically treated with surgery. Removal of the affected adrenal gland usually resolves other medical conditions that may be present as a result of elevated adrenal hormones (i.e. primary aldosteronism, Cushing's syndrome ).
What causes adrenal adenomas?
In these cases, affected people usually have multiple adenomas and other characteristic features of the condition that are all caused by changes ( mutations) in a gene. MEN1 is caused by mutations in the MEN1 gene, while FAP is caused by mutations in the AP C gene. [7] [8] [9]
What is the name of the condition where the adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone?
Primary aldosteronism (also called Conn syndrome) is a condition in which the adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone. This hormone is responsible for balancing the levels of sodium and potassium in the blood. Symptoms of this condition may include high blood pressure, fatigue, headache, muscle weakness, numbness and paralysis that comes and goes. [5]
What is an adenomas?
Adenomas of the adrenal gland are non-cancerous (benign) tumors on the adrenal gland. Most do not cause any signs or symptoms and rarely require treatment. However, some may become "active" or "functioning" which means they produce hormones, often in excess of what the adrenal glands typically produce. High levels of these hormones can lead ...
What is the best test for adrenal gland adenoma?
In addition to a complete physical exam and medical history, the following imaging tests are usually necessary to diagnose an adenoma of the adrenal gland: computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan), and/or positron emission tomography (PET scan). Some people may also need a biopsy of the tumor to confirm the diagnosis. Laboratory tests that evaluate the levels of certain hormones in the blood or urine can be used to determine if the adrenal adenoma is functional or nonfunctional. [2]
Can adrenal adenomas be inherited?
Most adrenal adenomas are not inherited. They usually occur sporadically in people with no family history of tumors. [2] . However, in rare cases, they can occur in people with certain genetic syndromes such as multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 1 (MEN1) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). [7] .
Can adrenal adenomas cause symptoms?
Listen. The majority of adrenal adenomas are "nonfunctioning", which means they do not produce hormones and usually do not cause any symptoms. They are often found incidentally during imaging studies of the abdomen, in which case they are referred to as adrenal incidentalomas. However, some can become "functioning" or "active" ...
General Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2021 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
Article Guidance
Effective November 19, 2012, Cancer TYPE ID, an RT-PCR 92-gene assay, has been assigned a new identifier to reflect the changes in the test. To bill for Cancer TYPE ID services, please provide the following claim information:
Bill Type Codes
Contractors may specify Bill Types to help providers identify those Bill Types typically used to report this service. Absence of a Bill Type does not guarantee that the article does not apply to that Bill Type.
Revenue Codes
Contractors may specify Revenue Codes to help providers identify those Revenue Codes typically used to report this service. In most instances Revenue Codes are purely advisory. Unless specified in the article, services reported under other Revenue Codes are equally subject to this coverage determination.
What is the ICD code for benign neoplasm of the left adrenal gland?
D35.02 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of benign neoplasm of left adrenal gland. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is an adenoma?
An adenoma (from Greek αδένας, adeno-, "gland" + -ώμα, -oma, "tumor") (/ˌædᵻˈnoʊmə/; plural adenomas or adenomata /ˌædᵻˈnoʊmᵻtə/) is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli). Although adenomas are benign, over time they may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. But even while benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes). Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.
Do adenomas transform?
Most adenomas do not transform. But even while benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes).
Do adenocarcinomas grow from epithelial tissue?
Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli). Although adenomas are benign, over time they may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform.
Carcinoma in situ of thyroid and other endocrine glands
Adenocarcinoma in adenomatous polyp; Adenocarcinoma metastatic to unspecified site; Cancer; Cancer. Sebaceous cell carcinoma of skin of right lower eyelid, including canthus. Screening for pulmonary tuberculosis tb of the lung ; Screening for pulmonary tuberculosis done; Encounter for screening for active tuberculosis disease.
Puncture wound without foreign body of thyroid gland, subsequent encounter
Adenoma of skin, sebaceous; Angiokeratoma; Angiokeratoma of skin; Apocrine cystadenoma; Apocrine hydrocystoma; Benign collagenoma; Benign fibrous histiocytoma; Benign neoplasm of skin; Benign neoplasmtrichoepithelioma; Blue nevus of skin; Collagen nevus of skin; Cutaneous neurofibroma; Dermatofibroma; Dysplastic nevus of skin; Eccrine hidrocystoma; Eccrine hydrocystoma; Epithelioid and spindle cell nevus; Fibrous histiocytoma of skin; Halo nevus; Hidradenoma, papillary; Muir torre syndrome w benign sebaceous neoplasm ; Multiple dysplastic nevi; Neurofibroma, dermal; Nevus of skin, dysplastic; Nevus of skin, dysplastic birthmark or mole ; Nevus, spindle and epithelioid; Papillary hidradenoma; Pilomatrixoma; Sebaceous adenoma of skin; Syringoma; Torr? Malignant neoplasm of lip, unspecified.
Other specified hypothyroidism
Malignant neoplasm of oropharynx, unspecified. Screening for diabetes mellitus; Screening for diabetes mellitus done. Malignant neoplasm of hypopharynx, unspecified.
Carcinoma in situ of other and unspecified sites
Screening for endocrine, nutritional, metabolic and immunity disorders done; Screening for endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders; Hjpothyroidism for nutritional disorder; Screening for nutritional disorder done; Screening for vitamin d deficiency; Screening for vitamin d deficiency done. Malignant neoplasm of unspecified ureter.
Carcinoma in situ of other and unspecified sites
Thyrotoxicosis hypothyroiidsm toxic hypothuroidism thyroid nodule with thyrotoxic crisis or storm. The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. Malignant neoplasm of medulla of right adrenal muir torre syndrome icd 10 code for hypothyroidism.
Puncture wound with foreign body of thyroid gland, subsequent encounter
Screening for ovarian cancer; Screening for ovarian cancer done. Subclinical iodine deficiency hypothyroidism. Malignant neoplasm of unspecified ureter.
Mast cell neoplasms of uncertain behavior
Adenoma thyroid, follicular; Benign neoplasm of thyroid; Hurthle cell adenoma ; Thyroid follicular adenoma ; code to identify any functional activity. Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of skin. Encounter for screening for depression, adult; Encounter for screening for depression for child or adolescent.
How to treat functional adrenal adenomas?
Functional adrenal adenomas are typically treated with surgery. Removal of the affected adrenal gland usually resolves other medical conditions that may be present as a result of elevated adrenal hormones (i.e. primary aldosteronism, Cushing's syndrome ).
What causes adrenal adenomas?
In these cases, affected people usually have multiple adenomas and other characteristic features of the condition that are all caused by changes ( mutations) in a gene. MEN1 is caused by mutations in the MEN1 gene, while FAP is caused by mutations in the AP C gene. [7] [8] [9]
What is the name of the condition where the adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone?
Primary aldosteronism (also called Conn syndrome) is a condition in which the adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone. This hormone is responsible for balancing the levels of sodium and potassium in the blood. Symptoms of this condition may include high blood pressure, fatigue, headache, muscle weakness, numbness and paralysis that comes and goes. [5]
What is an adenomas?
Adenomas of the adrenal gland are non-cancerous (benign) tumors on the adrenal gland. Most do not cause any signs or symptoms and rarely require treatment. However, some may become "active" or "functioning" which means they produce hormones, often in excess of what the adrenal glands typically produce. High levels of these hormones can lead ...
What is the best test for adrenal gland adenoma?
In addition to a complete physical exam and medical history, the following imaging tests are usually necessary to diagnose an adenoma of the adrenal gland: computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan), and/or positron emission tomography (PET scan). Some people may also need a biopsy of the tumor to confirm the diagnosis. Laboratory tests that evaluate the levels of certain hormones in the blood or urine can be used to determine if the adrenal adenoma is functional or nonfunctional. [2]
Can adrenal adenomas be inherited?
Most adrenal adenomas are not inherited. They usually occur sporadically in people with no family history of tumors. [2] . However, in rare cases, they can occur in people with certain genetic syndromes such as multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 1 (MEN1) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). [7] .
Can adrenal adenomas cause symptoms?
Listen. The majority of adrenal adenomas are "nonfunctioning", which means they do not produce hormones and usually do not cause any symptoms. They are often found incidentally during imaging studies of the abdomen, in which case they are referred to as adrenal incidentalomas. However, some can become "functioning" or "active" ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for transesophageal echocardiogram
- 2. 2016 icd 10 code for chronic whole body pain
- 3. icd 10 code for recurrent conjuvtivtis
- 4. icd 10 code for cervical spine x ray
- 5. icd 10 code for diabete right leg amputation
- 6. icd 10 code for knee injury unspecified
- 7. icd-10 code for superior mesenteric artery thrombosis
- 8. icd 10 code for right nondisplaced wnd metatarsal fracture
- 9. icd 10 code for disruptive behavior
- 10. icd 10 code for non healing wound left knee