What is the ICD 10 code for rapid AFIB?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48. I48. Click to see full answer. Likewise, what is atrial fibrillation with RVR? A-fib with RVR is the common term for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. A common disorder that involves a rapid heart rate, it requires medical attention and, in many cases, hospitalization.
What is the best medicine for atrial fibrillation?
- Rhythmol and Tambocor are relatively well tolerated as long as they do not cause proarrhythmia. ...
- Betapace and Tikosyn are also relatively well tolerated as long as they do not cause proarrhythmia. ...
- Cordarone is a truly unique antiarrhythmic drug. ...
Which specialists can diagnose atrial fibrillation?
Your physician will diagnose atrial fibrillation with a physical exam and an electrocardiogram (EKG). Electrophysiologists are specialists trained in diagnosing and treating problems with the heart’s electrical system.
What is the right treatment for atrial fibrillation?
What Are the Treatments for AFib?
- Treating the Causes of AFib. If problems such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, or an overactive thyroid caused your AFib, you'll need to treat the root cause.
- Complementary Treatments. We need more research into alternative and complementary treatments for AFib. ...
- Lifestyle Changes. Change your diet -- eat heart-healthy, low-salt food. ...

Is Z76 89 a billable code?
Z76. 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the CPT code for atrial fibrillation?
The CPT® section notes state, “Code 93656 is a primary code for reporting treatment of atrial fibrillation by ablation to achieve complete pulmonary vein electrical isolation.” (emphasis added).
What is the 2021 ICD-10 code for AFIB with RVR?
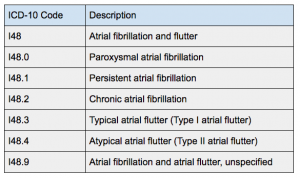
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48 I48.
What is the ICD-10 code for atrial arrhythmia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cardiac arrhythmia, unspecified I49. 9.
What is unspecified atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) is an irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots in the heart. A-fib increases the risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications.
What is the CPT code 93653?
CPT® Code 93653 - Intracardiac Electrophysiological Procedures/Studies - Codify by AAPC.
What is atrial fib with RVR?
What is Afib with RVR? Some cases of Afib involve atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response (RVR). This is when the rapid contractions of the atria make the ventricles beat too quickly. If the ventricles beat too fast, they can't receive enough blood. So they can't meet the body's need for oxygenated blood.
What is the CPT code for I48 91?
ICD-10-CM Code for Unspecified atrial fibrillation I48. 91.
What does RVR mean in medical terms?
Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response (RVR) is common during critical illness.
What is the ICD 10 code for new onset AFib?
ICD-10-CM Code for Atrial fibrillation and flutter I48.
What is the CPT code for arrhythmia?
Although 93462 may continue to be reported in addition to SVT (93653) or VT (93654) ablation codes for tracking, it is bundled into the atrial fibrillation code (93656) by CPT definition. 93603, 93615, 93616, and 92618 are assigned to APC 5211.
How do you document the atrial fibrillation?
Documenting AFib as a confirmed condition if it is suspected; rather, document signs and symptoms in the absence of a confirmed diagnosis. Describing AFib as “history of” if the condition is still active (in diagnosis, “history of” implies the condition has resolved or no longer exists).
What is atypical atrial flutter?
Atypical atrial flutter, while similar in heartbeat abnormality to Type 1 Atrial Flutter, refers to the clockwise pattern of electrical impulses of the heart beat pattern.
What are the two chambers of the heart called?
It is divided into four chambers. The two chambers on the top are called the left and right atria and the two on the bottom are called the left and right ventricles.
How to regulate heartbeat?
Heartbeat patterns can be regulated with medications and/or electrocardioversion ( an electrical shock of the heart). There are also procedures and surgeries that can be done to regulate abnormal heartbeat patterns. The following may be options of surgical procedures to treat atrial fibrillation: Catheter Ablation.
How many beats does a heart beat?
What we normally refer to as one heart beat, can actually be divided into two beats. (Think “lub-dub, lub-dub, lub-dub”). The first is usually a little softer and the second is has more emphasis. During this first beat, or the ‘lub’ beat, the atria and ventricles are relaxed and are filling with blood.
What is a type 1 flutter?
Typical Atrial Flutter (Type I Atrial Flutter) An atrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm where the heart beats regularly but at a much faster beat than normal. In this condition they actually beat faster and the ventricles beat at their normal rate, so the atria can beat at a rate of 4:1 with the ventricles.
What tests are used to detect AFIB?
Tests to be used to detect Afib are electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, holter monitor, stress test and chest X-ray. Afib can be managed with anti-arrhythmic or anticoagulant drugs. Even after doing ablation procedure to correct Afib there may be need of medication.
How long does AFIB last?
There are different types of afib based on how long it lasts. Persistent – Lasts more than 7 days and it needs an intervention to restore the rhythm. Chronic (Permanent) – Chronic stays more than 12 months and it is called permanent when the abnormal heart rhythm cannot be restored.
Is AFIB fatal?
Atrial Fibrillation is an irregular (often rapid) heartbeat which may lead to blood clot in the heart and travel to other parts of the body and make blocks. Afib itself is not fatal but it is critical when it leads to stroke or heart failure. Hence Afib needs to be managed.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for abrasion scalp
- 2. icd 10 code for struck by object
- 3. icd 10 code for undisplace rt proximal fibula fracture
- 4. icd 10 cm code for drug eruption
- 5. icd 10 code for collaterol blood vessels
- 6. icd 10 code for lumbar
- 7. icd 10 code for left breast capsular contracture
- 8. icd 10 code for cholecystitis unspecified
- 9. icd 10 code for pv bleeding
- 10. icd 10 code for contusion right ribs