How to reduce anxiety and depression in 10 ways?
- Take time to make yourself feel good. Maybe you feel overwhelmed.
- Take a mental health day, or even better go on vacation.
- Go out to a spa and make yourself feel refreshed. Anything that helps clear your mind is great for you right now.
What are some home remedies for anxiety and depression?
Tips to Get Rid of Anxiety and Depression
- Set some goals or objectives to accomplish. ...
- Exercise regularly to come out of anxiety and depression.
- Volunteer yourself to help somebody who is not privileged.
- You can also try going for regular strolls in gardens. ...
- Engage yourself in social activities. ...
What is the code for depression with anxiety?
The ICD 10 code for depression with anxiety coded based on the following codes. F41.1 IT is generalized with the anxiety disorder problems. F43.23 here the adjustment disorder is mixed up with anxiety and the depressed mood. F43.22 is coded for the adjustment of disorder with the anxieties problems.
How to get diagnosed with depression and anxiety?
This disorder is diagnosed by the presence of symptoms that persist for over four weeks including intense and repeated flashbacks (either while awake or while asleep) of the event, a perceived inability to discuss the event and an avoidance of any reminders of it, emotional numbness, and the belief that life has been irrevocably tainted by the experience, resulting in social and work-related problems that did not exist before.
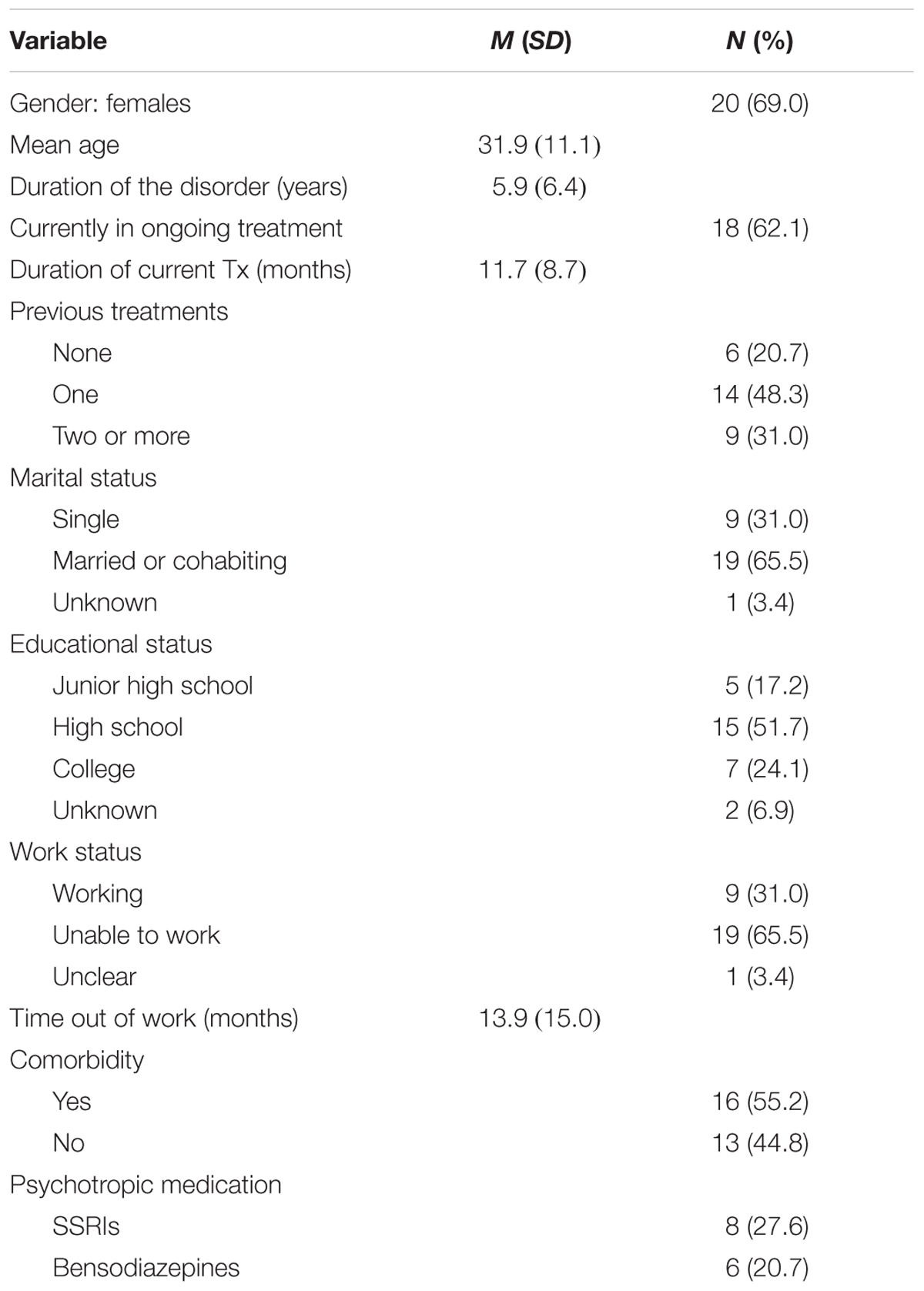
Can you code anxiety and depression together?
Anxiety may be associated with depression. If both are documented by a physician, assign codes 311 and 300.00. However, if the physician links the two conditions, such as “depression with anxiety,” then code 300.4, Dysthymic disorder, may be assigned (AHA Coding Clinic for ICD-9-CM, 2001, third quarter, page 6).
How do you code MDD with anxious distress?
1 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Major depressive Disorder, Recurrent, Moderate. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 296.3. Code F33.
What is the ICD-10 code for major depressive disorder severe?
Major depressive disorder, single episode, severe without psychotic features. F32. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the difference between F41 8 and F41 9?
ICD-9 code 300.00 for unspecified anxiety disorder is now F41. 9 for unspecified anxiety disorder, F41. 1 for generalized anxiety disorder, and F41. 8 for other specified anxiety disorders.
What is the ICD-10 code for major depression with anxiety?
2 Mixed anxiety and depressive disorder.
Can you have MDD with anxious distress and GAD?
Background. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and major depressive disorder (MDD) are highly comorbid. A possible explanation is that they share four symptoms according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition – Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR).
What is the ICD-10 code for generalized anxiety disorder?
ICD-Code F41. 1 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 300.02.
What is F33 diagnosis?
1 Recurrent depressive disorder, current episode moderate. A disorder characterized by repeated episodes of depression, the current episode being of moderate severity, as in F32. 1, and without any history of mania.
Is F32 9 still a valid code?
The default code F32. 9 as previously used for “depression NOS” was determined by subject matter experts to be clinically incorrect. A new code effective October 1, 2021 for “depression NOS” or “unspecified depression” is F32. A Depression unspecified.
What is F32 89?
ICD-10 code F32. 89 for Other specified depressive episodes is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
What is the DSM code for GAD?
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) DSM-5 300.02 (F41. 1) - Therapedia.
What is the difference between generalized anxiety disorder and unspecified anxiety?
According to the Mayo Clinic, an unspecified anxiety disorder is one that does not fit all the diagnostic criteria of a specific anxiety disorder. Generalized anxiety and generalized social phobias are disorders that typically fit diagnostic criteria.
What is the ICd 10 code for bipolar disorder?
ICD-10 code F31.1 in this case will be used to specify a bipolar disorder that is mild without any psychotic features.
What is the difference between bipolar 1 and bipolar 2?
Bipolar 2 is similar to bipolar 1 characterized with mood swings cycling between high and low over time, the only difference in this case is that the mood swings never reach full on mania. F31.8 ICD-10 code will thus be used to specify the Bipolar II disorder. Depression associated with psychotic symptoms will be specified by F32.3 while F06.32 will be used to specify any mood disorder caused by known psychological conditions with major depressive like episodes.
Is dysthymia a chronic disorder?
The condition is common in relatives with bipolar parents. Dysthymia on its part is a chronic depression of moods that lasts for years. This condition is not severe with its episodes not being prolonged to justify diagnosis of either mild moderate or severe.
What is the meaning of fear and anxiety?
Apprehension or fear of impending actual or imagined danger, vulnerability, or uncertainty. Fear and anxiety are part of life.
What are the symptoms of GAD?
Other symptoms of gad include being restless, being tired or irritable, muscle tension, not being able to concentrate or sleep well, shortness of breath, fast heartbeat, sweating, and dizziness. An anxiety disorder characterized by excessive and difficult-to-control worry about a number of life situations.
What is the F41.8 mental illness?
Hysteria (F41.8)- Excessive, uncontrollable or exaggerated emotion or excitement. Neurosis (F41.1) – Mild form of mental illness irrational in nature, not caused by organic disease. Separation anxiety (F93.0) – Excessive anxiety experienced by an individual regarding separation from home or from loved ones.
What is the diagnosis of a 30-year-old woman?
She was recently diagnosed with adjustment disorder with anxiety due to death of her parents in an accident last year and being fired recently from her job. She has since noticed long periods of restlessness, feeling overwhelmed, and difficulty concentrating, with occasional chest pain and excessive sweating, which interferes with her daily life. A physical and psychological assessment was performed. Anti-anxiety medication was adjusted, and the patient was encouraged to continue psychotherapy sessions.
What is F51.5?
Answer: F51.5. 4. Anxiety disorder induced by drugs – Individuals develop anxiety disorders also as a result of long-term use of certain medications like corticosteroids, ADHD drugs, drugs containing caffeine, Asthma medications, Seizure drugs etc..
Can alcohol cause anxiety?
Anxiety associated with other mental disorders. 1. Alcohol abuse with alcohol-induced anxiety disorder – Change in neurotransmitter levels in the brain due to influence of alcohol can cause anxiety that can last for several hours.
Is anxiety a psychiatric disorder?
While anxiety is a normal human emotion, an anxiety disorder is a psychiatric disorder characterized by regular or frequent feelings of restlessness, worry, tension, rapid heartbeat or phobias which can cause disruption in the everyday life of the individual. This is a very common emotional disorder affecting all age groups.
What is the difference between a major depressive episode and a generalized anxiety disorder?
The primary difference between the diagnoses of a Major Depressive Episode and Generalized Anxiety Disorder is that a person who experiences depression usually describe their mood as sad, hopeless, feeling “down in the dumps” or “blah” while a person who struggles with Generalized Anxiety Disorder reports feeling constantly worried and having a hard time controlling the worry. The physical symptoms of depression and anxiety can also help us differentiate between the diagnoses.
What are the symptoms of anxiety and depression?
There are many symptoms which overlap between Depression and Anxiety, such as irritability, restlessness, problems sleeping, and difficulties with concentrating. However, each diagnosis has its own cause and emotional and physical symptoms.
What is the difference between depression and anxiety?
In anxiety, there is an expectation that something bad is going to happen. Anxiety is mostly worrying about something that has not happened yet. Depression is a sadness about the current state of affair s or rumination about past events .
What is the common feature of depression?
Another feature that is common in depression is a feeling of worthlessness or preoccupation self-blame or guilt. In anxiety, there is an expectation that something bad is going to happen.
Why is anxiety a part of the body?
With anxiety, your body is preparing for an emergency because your mind is anticipating something bad will happen. Your body diverts blood supply and energy to muscles that will help you fight off an attack or run from a threat.
What happens to the body during depression?
Other bodily functions like digestion are left without the energy they need to continue until after the threat is mitigated. Depression brings about a general slowing of all physical functioning. Little energy is made available for movement, even the movement of small facial muscles that display expression.
Is anxiety a mental illness?
Understanding your diagnosis is an important part of getting the right treatment. Anxiety and depression are two common mental illnesses that often co-occur, meaning that many people may suffer from both disorders. There are many symptoms which overlap between Depression and Anxiety, such as irritability, restlessness, problems sleeping, and difficulties with concentrating. However, each diagnosis has its own cause and emotional and physical symptoms. The best way to confirm your condition is with a diagnosis from a mental health professional.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lichen planus like keratosis
- 2. icd 10 code for preseptal cellulietis left lower lid
- 3. icd 10 code for abnormal glucose screening
- 4. icd 10 code for clotted dialysis catheter
- 5. icd 10 code for enterogastric reflux
- 6. icd 10 code for lumbar osteophytes
- 7. icd-10 code for hospital discharge follow-up
- 8. icd code for mild depression
- 9. icd 10 code for left leg weaker post spinal surgery
- 10. icd 10 code for myopia right eye