Is bronchospasm and bronchitis the same thing?
Definition. Bronchospasm is an abnormal contraction of the smooth muscle of the bronchi, resulting in an acute narrowing and obstruction of the respiratory airway. A cough with generalized wheezing usually indicates this condition. Bronchospasm is a chief characteristic of asthma and bronchitis.
What bronchospasm means?
Bronchospasms happen when the muscles that line your bronchi (airways in your lungs) tighten. This results in wheezing, coughing, and other symptoms. Many things can cause bronchospasm, including asthma, and it's usually managed with bronchodilators.
What causes bronchospasm?
Any swelling or irritation in your airways can cause bronchospasm. This condition commonly affects people with asthma. Other factors that can contribute to bronchospasm include: allergens, such as dust and pet dander.
What is the ICD 10 code for Acute viral bronchitis?
9: Acute bronchitis, unspecified.
What is the difference between bronchospasm and bronchoconstriction?
Bronchospasm is a common diagnosis during anesthesia but it is rarely the correct one. Bronchoconstriction or narrowing of airways from loss of lung volume is a far more common cause of wheezing and difficulty with ventilation during anesthesia.
What is the treatment for bronchospasm?
Exercise bronchospasm treatment Use a regular inhaler before you exercise. Take a mast cell stabilizer. Use a long-acting inhaler. Take specialized, anti-inflammatory medication.
What medication causes bronchospasm?
The major categories of medications known to induce bronchospasm or cough, including beta-blockers, cholinesterase inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, and inhalational agents are reviewed.
What happens during a bronchospasm?
Bronchospasm occurs when the airways (bronchial tubes) go into spasm and contract. This makes it hard to breathe and causes wheezing (a high-pitched whistling sound). Bronchospasm can also cause frequent coughing without wheezing.
Can albuterol cause bronchospasm?
This medicine may cause paradoxical bronchospasm, which means your breathing or wheezing will get worse. Paradoxical bronchospasm may be life-threatening. Check with your doctor right away if you or your child have coughing, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, or wheezing after using this medicine.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute bronchiolitis?
J21. 9 - Acute bronchiolitis, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
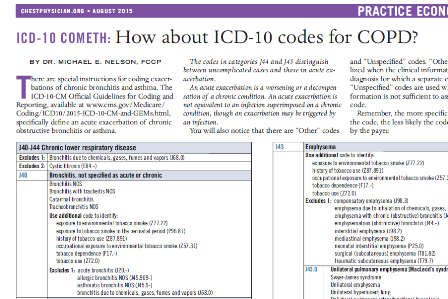
How do you code acute bronchitis with asthma?
ICD-10-CM J45. 901 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 202 Bronchitis and asthma with cc/mcc.
Are bronchospasms serious?
Bronchospasm is a narrowing of your airway that usually comes and goes. It may make it hard for you to breathe. Severe bronchospasm may be life-threatening.
Can bronchospasm be cured?
When that happens, it's called a bronchial spasm, or a bronchospasm. During a bronchial spasm, breathing becomes more difficult. You may find yourself wheezing as you try to catch your breath. In many cases, bronchial spasms are treatable or preventable.
What does a bronchospasm sound like?
Bronchospasm occurs when the airways (bronchial tubes) go into spasm and contract. This makes it hard to breathe and causes wheezing (a high-pitched whistling sound). Bronchospasm can also cause frequent coughing without wheezing.
How do you treat bronchospasm at home?
In addition to any prescription treatments and medication your doctor recommends, there are several home remedies that may help you wheeze less.Drink warm liquids. ... Inhale moist air. ... Eat more fruits and vegetables. ... Quit smoking. ... Try pursed lip breathing. ... Don't exercise in cold, dry weather.
What is a fibrinous bronchitis?
acute and subacute purulent bronchitis. acute and subacute septic bronchitis. Clinical Information. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to your lungs.
What is tobacco dependence?
tobacco dependence ( F17.-) "Includes" further defines, or give examples of, the content of the code or category. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to your lungs. It causes a cough that often brings up mucus, as well as shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness.
Do you need antibiotics for bronchitis?
You may need inhaled medicine to open your airways if you are wheezing. You probably do not need antibiotics. They don't work against viruses - the most common cause of acute bronchitis. If your healthcare provider thinks you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe antibiotics.
Can a virus cause bronchitis?
The same viruses that cause colds and the flu often cause acute bronchitis. These viruses spread through the air when people cough, or through physical contact (for example, on unwashed hands). Being exposed to tobacco smoke, air pollution, dusts, vapors, and fumes can also cause acute bronchitis.
What is chronic bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis with acute exacerbation. Clinical Information. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to your lungs. It causes a cough that often brings up mucus, as well as shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness.
When will the ICD-10 J20.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J20.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Do you need antibiotics for bronchitis?
You may need inhaled medicine to open your airways if you are wheezing. You probably do not need antibiotics. They don't work against viruses - the most common cause of acute bronchitis. If your healthcare provider thinks you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe antibiotics.
Can a virus cause bronchitis?
The same viruses that cause colds and the flu often cause acute bronchitis. These viruses spread through the air when people cough, or through physical contact (for example, on unwashed hands). Being exposed to tobacco smoke, air pollution, dusts, vapors, and fumes can also cause acute bronchitis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for middle turbinate concha bullosa
- 2. icd 10 code for combative
- 3. icd 9 code for chronic pulmonary disease unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for acutej pseudomonas tracheobronchitis
- 5. icd 10 code for urinary bladder diverticula
- 6. icd-10 code for multinodular goiter
- 7. icd 10 code for post covid vaccination reaction
- 8. icd 9 code for puncture wound shoulder
- 9. icd 10 code for distal fibula
- 10. icd-10-pcs code for transfusion nonautologous plasma peripheal