How do we diagnose acute myeloid leukemia?
Types of samples used to test for AML
- Blood samples. Blood tests are generally the first tests done to look for leukemia. Blood is taken from a vein in the arm.
- Bone marrow samples. Leukemia starts in the bone marrow, so checking the bone marrow for leukemia cells is a key part of testing for it.
- Spinal fluid. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain and spinal cord. ...
How do we treat acute myeloid leukemia?
- Treatment overview. ...
- Intensive chemotherapy. ...
- Chemotherapy by phase. ...
- Side effects of chemotherapy. ...
- Targeted therapy. ...
- Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) treatment. ...
- Radiation therapy. ...
- Getting care for symptoms and side effects. ...
- Refractory AML. ...
- Remission and the chance of recurrence. ...
How to find a specialist to treat chronic myeloid leukemia?
What you can do
- Be aware of any pre-appointment restrictions. ...
- Write down any symptoms you're experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment.
- Write down key personal information, including any major stresses or recent life changes.
- Make a list of all medications, vitamins or supplements that you're taking.
Is acute leukemia more painful than chronic leukemia?
The symptoms of acute leukemia, which tend to appear earlier and be more severe than the symptoms of chronic leukemia, can include: Chronic leukemia inhibits the development of blood stem cells, ultimately causing them to function less effectively than healthy mature blood cells.
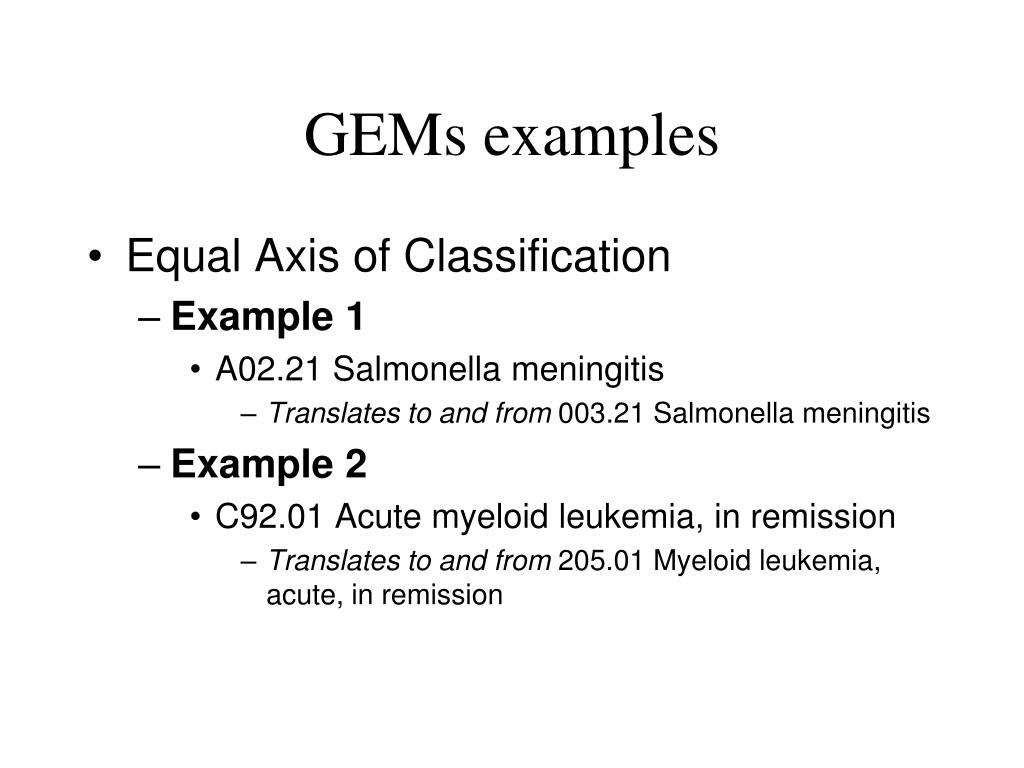
What is remission in acute myeloid leukemia?
A person living with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) achieves remission when treatment successfully removes most of the leukemia blast cells from the bone marrow and blood. This is the goal of treatment. Doctors measure AML remission by the number of months or years that leukemia does not return.
What is acute myeloid leukemia not having achieved remission?
Most often, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) will go into remission after the initial treatment. But sometimes it doesn't go away completely, or it comes back (relapses) after a period of remission. If this happens, other treatments can be tried, as long as a person is healthy enough for them.
What is the DX code for AML?
C92. 0 - Acute myeloblastic leukemia. ICD-10-CM.
What is diagnosis code C92 00?
00 for Acute myeloblastic leukemia, not having achieved remission is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Malignant neoplasms .
What is considered remission in leukemia?
A remission (complete remission) is usually defined as having no evidence of leukemia after treatment. This means the bone marrow contains fewer than 5% blast cells, the blood cell counts are within normal limits, and there are no signs or symptoms of the disease.
What is complete remission?
Remission means that the signs and symptoms of your cancer are reduced. Remission can be partial or complete. In a complete remission, all signs and symptoms of cancer have disappeared. If you remain in complete remission for 5 years or more, some doctors may say that you are cured.
What is the ICD-10 code for leukemia?
C95. 9 - Leukemia, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
Are myeloid cells white blood cells?
The 2 main types of white blood cells are: lymphocytes – which fight viral infections. myeloid cells – which do different things, such as fighting bacterial infections, defending the body against parasites and preventing the spread of tissue damage.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute promyelocytic leukemia?
C92.40ICD-10 code C92. 40 for Acute promyelocytic leukemia, not having achieved remission is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Malignant neoplasms .
What does anemia D64 9 mean?
Code D64. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Anemia, Unspecified, it falls under the category of diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. Anemia specifically, is a condition in which the number of red blood cells is below normal.
What is the ICD-10 code for chemotherapy?
1 for Encounter for antineoplastic chemotherapy and immunotherapy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for MDS?
9.
What is the life expectancy of someone with acute myeloid leukemia?
The 5-year overall survival rate for AML is 29.5 percent , according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI). This means that an estimated 29.5 percent of people in America living with AML are still living 5 years after their diagnosis.
What are the final stages of acute myeloid leukemia?
profound weakness and exhaustion. resting or sleeping most of the time. loss of interest in events and things previously held as important.
Does anyone survive acute myeloid leukemia?
The 5-year survival rate for people 20 and older with AML is 27%. For people younger than 20, the survival rate is 69%. However, survival depends on several factors, including biologic features of the disease and, in particular, a patient's age (see Subtypes for more information).
Is acute myeloid leukemia terminal?
Overall survival for AML People with AML must be treated. Without treatment, survival is usually measured in days to weeks. With current treatment regimens, 65%–70% of people with AML reach a complete remission (which means that leukemia cells cannot be seen in the bone marrow) after induction therapy.
What is granulocytic leukemia?
myelogenous leukemia. Clinical Information. A clonal proliferation of myeloid cells and their precursors in the bone marrow, peripheral blood, and spleen. When the proliferating cells are immature myeloid cells and myeloblasts, it is called acute myeloid leukemia. When the proliferating myeloid cells are neutrophils, ...
What does "type 1 excludes" mean?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. personal history of leukemia (.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for htn retinopathy unspecified
- 2. icd 10 code for intraventricular conduction block
- 3. icd-10-cm code for neurotic excoriation
- 4. icd 10 code for left lung cancer
- 5. what is icd 10 code for angiodysplasia of duodenum
- 6. icd-10 code for squamous cell carcinoma of multiple sites
- 7. icd 10 code for status prostatectomy
- 8. icd 10 code for start birth control
- 9. icd 10 code for elevated pra
- 10. icd 10 code for right toenail wound