How deadly is chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
The slow-growing form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the least serious type of leukemia. It is a disease of older people; the average age at diagnosis is around 71. CLL is a malignancy of mature lymphocytes, which usually grow and divide slowly, resulting in a slowly progressive disease. Most individuals have no symptoms early in the disease and the diagnosis is often made only after finding an increased white blood cell count on a routine blood test.
How to pronounce acute lymphocytic leukemia?
Pronunciation of lymphocytic with 1 audio pronunciation, 5 synonyms, 1 meaning, 13 translations, 7 sentences and more for lymphocytic. ... Global Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Therapeutics Market 2021 by Key Countries, Companies, Type and Application revealed by MarketQuest.biz describes the market structure, scope, ability, and g..
What are the early symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
- Night sweats
- Discomfort in bones or joints
- Enlarged spleen, liver or lymph nodes
- Pain or feeling of fullness below the ribs
- Unexplained weight loss or loss of appetite
- Wheezing, coughing or painful breathing
Who gets acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (acute lymphocytic leukemia or ALL) is a cancer of the bone marrow that can spread quickly to blood cells. It can develop at any age, but it’s most common in children between ages three and five. With treatment, the condition can be cured in most children and many adults.
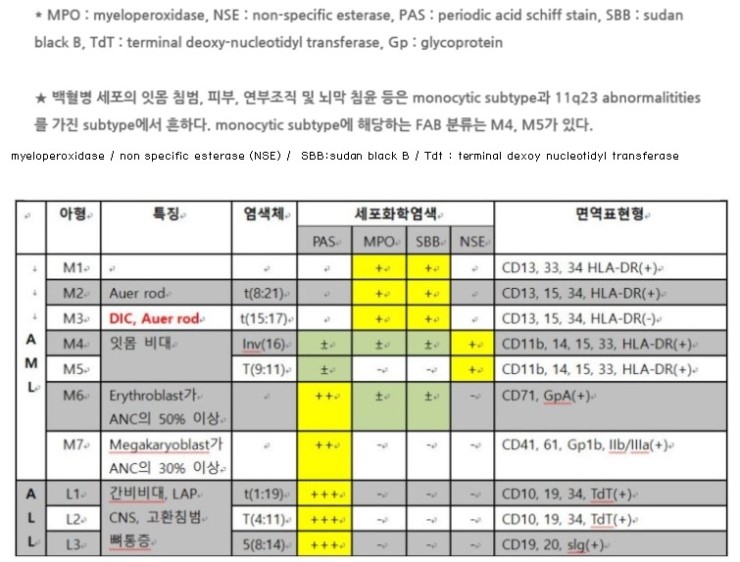
What are the two types of acute lymphocytic leukemia?
Types of leukaemiaacute myeloid leukaemia (AML) affects myeloid cells.acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) affects lymphoid cells.
What is the ICD-10 code for small lymphocytic lymphoma?
Code 9823/3 is used for CLL, SLL, and CLL/SLL.
What code is acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission?
C91.01ICD-10-CM Code for Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, in remission C91. 01.
What is acute lymphocytic lymphoma?
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is a type of cancer of the blood and bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are made. The word "acute" in acute lymphocytic leukemia comes from the fact that the disease progresses rapidly and creates immature blood cells, rather than mature ones.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia of B-cell type not having achieved remission. C91. 10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C91.
What is the difference between CLL and SLL?
CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) and SLL (small lymphocytic lymphoma) are the same disease, but in CLL cancer cells are found mostly in the blood and bone marrow. In SLL cancer cells are found mostly in the lymph nodes. CLL/SLL is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
What is the ICD-10 code for leukemia?
C95. 9 - Leukemia, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for ALL in remission?
01 - Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, in remission. C91. 01 - Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, in remission is a topic covered in the ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for Hodgkin's lymphoma?
ICD-10 code C81. 9 for Hodgkin lymphoma, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Malignant neoplasms .
What is lymphoid leukemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (also called CLL) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow that usually gets worse slowly. CLL is one of the most common types of leukemia in adults.
Is it true that acute lymphoid leukemia is?
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the immature lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell involved in the body's immune system. ALL is also called acute lymphoid leukemia or acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Acute means that the disease begins and gets worse quickly.
How is acute lymphocytic leukemia classified?
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies ALL based on the immunophenotype of the leukemia cells. The immunophenotype is determined by lab tests including flow cytometry and cytogenetic tests. Rarely, acute leukemia may have characteristics of both ALL and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
ICD-10-CM Code C91.0 - Acute lymphoblastic leukemia [ALL]
ICD Code C91.0 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the three child codes of C91.0 that describes the diagnosis 'acute lymphoblastic leukemia [all]' in more detail.
ICD-10 code for T-lymphoblastic leukemia - AAPC
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C91.1: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia of B ...
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C91.10: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia of B ...
C91.02 - ICD-10 Code for Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, in relapse ...
What is the term for cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes?
A type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (white blood cells). Leukemia associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue; there are increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts.
What is a B cell neoplasm?
A malignant lymphocytic neoplasm of b-cell or t-cell lineage involving primarily the bone marrow and the peripheral blood. This category includes precursor or acute lymphoblastic leukemias and chronic leukemias. A progressive, proliferative disease of blood cells, originating from lymphoid cells.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
tests that examine the blood and bone marrow diagnose all. Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplants, and targeted immune therapy. Once the leukemia is in remission, you need additional treatment to make sure that it does not come back. nih: national cancer institute.
What is the function of white blood cells in leukemia?
Your blood cells form in your bone marrow. In leukemia, however, the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells. These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells , making it hard for blood to do its work.
What is the name of the cancer that is caused by too many lymphoblasts?
An aggressive (fast-growing) type of leukemia (blood cancer) in which too many lymphoblasts (immature white blood cells) are found in the blood and bone marrow. leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells help your body fight infection. Your blood cells form in your bone marrow.
What is a malignant lymphocytic neoplasm?
Clinical Information. A malignant lymphocytic neoplasm of b-cell or t-cell lineage involving primarily the bone marrow and the peripheral blood. This category includes precursor or acute lymphoblastic leukemias and chronic leukemias.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the disease associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue?
Leukemia associated with hyperplasia and overactivity of the lymphoid tissue; there are increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Leukemia associated with hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissues and increased numbers of circulating malignant lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Code History.
What is the ICd code for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
The ICD code C910 is used to code Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, also known as acute lymphocytic leukemia or acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL), is an acute form of leukemia, or cancer of the white blood cells, characterized by the overproduction and accumulation of cancerous, immature white blood cells, ...
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code C91.0 is a non-billable code.
How do lymphoblasts cause death?
In persons with ALL, lymphoblasts are overproduced in the bone marrow and continuously multiply, causing damage and death by inhibiting the production of normal cells (such as red and white blood cells and platelets) in the bone marrow and by spreading (infiltrating) to other organs.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
secondary and unspecified neoplasm of lymph nodes ( C77.-) A clonal (malignant) hematopoietic disorder affecting the bone marrow and the peripheral blood.
Is morphology included in the category and codes?
In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is a malignant neoplasm?
secondary and unspecified neoplasm of lymph nodes ( C77.-) A clonal (malignant) hematopoietic disorder affecting the bone marrow and the peripheral blood.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as C95.0. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for immunity status
- 2. icd 10 code for quantiferon tb gold test screening
- 3. icd 10 code for hypertension affecting pregnancy
- 4. icd 10 code for right cartoid stenosis
- 5. icd 10 code for aftercare following er
- 6. icd 10 code for family history of shemachromatosis
- 7. icd 10 code for cut by table saw
- 8. icd 10 code for hep c virus
- 9. icd-10 code for tracheocutaneous fistula
- 10. icd 10 code for oblique subcapital right femoral neck fracture