Is there a cure for benign positional vertigo?
There’s also no cure for BPV. And it can occur again without warning, even after successful treatment. However, while BPV may sometimes be uncomfortable, it is manageable and usually improves with time.
How to prevent and treat positional vertigo?
Vertigo Treatment: Getting Rid of the Spins
- Physical therapy to improve balance and inner ear issues. ...
- Canalith Repositioning —also known as the Epley Maneuver. ...
- Medication that targets the cause of our symptoms. ...
- Surgery — an uncommon treatment for special cases. ...
- Injections — when other treatments haven't worked. ...
- Psychotherapy can help alleviate the stress of symptoms. ...
How to treat benign positional vertigo (BPV)?
What advice should I provide for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo?
- Advise the person: Most people recover over several weeks, even without treatment, but symptoms can last much longer and may recur. ...
- Advise on safety issues. ...
- Offer the person written information about BPPV, for example the NHS A-Z information on Vertigo which includes details on BPPV.
Can you say benign positional vertigo?
Benign positional vertigo (BPV) is the most common cause of vertigo, the sensation of spinning or swaying. It causes a sudden sensation of spinning, or like your head is spinning from the inside. You can have brief periods of mild or intense dizziness if you have BPV. Changing the position of your head can trigger an episode.
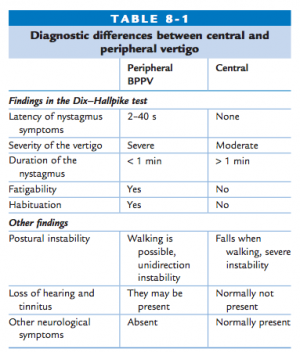
What is the ICD 10 code for benign positional vertigo?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (ICD-10 : H81) - Indigomedconnect.
Is positional vertigo the same as BPPV?
Overview. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is one of the most common causes of vertigo — the sudden sensation that you're spinning or that the inside of your head is spinning. BPPV causes brief episodes of mild to intense dizziness. It is usually triggered by specific changes in your head's position.
What is positional vertigo caused by?
BPPV occurs when tiny calcium crystals called otoconia come loose from their normal location on the utricle, a sensory organ in the inner ear. If the crystals become detached, they can flow freely in the fluid-filled spaces of the inner ear, including the semicircular canals (SCC) that sense the rotation of the head.
What is another name for positional vertigo?
Causes. Benign positional vertigo is also called benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). It is caused by a problem in the inner ear. The inner ear has fluid-filled tubes called semicircular canals.
What are the 3 types of vertigo?
Types of Vertigo: Peripheral, Central, BPPV, and More.
What is the difference between vertigo and dizziness?
Dizziness can be a range of sensations including feeling light-headed, faint, woozy, unsteady or off-balance. Vertigo is a type of dizziness that feels as though you or your surroundings are spinning.
What is the most common cause of BPPV?
Having a past head injury is a major cause. Other times, BPPV may result from other problems with the vestibular system. These can include Ménière disease or vestibular neuritis. Ear surgery is a less common cause.
Is BPPV caused by stress?
Conclusions: Within the poorly understood mechanisms implicated in the aetiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), the results of this trial provide clinical evidence of a potential role of emotional stress connected to adverse life events as a trigger of otoconial dysfunction.
Can earwax cause vertigo?
Vertigo is also possible if the earwax pushes against the eardrum, or tympanic membrane. This symptom can cause nausea and a sensation of moving even when a person is staying still.
What causes BPPV in both ears?
BPPV is caused by otoliths, or calcium carbonate crystals, being out of alignment in one or both of your inner ear balance canals. These otoliths, which we frequently call “crystals” or “stones,” are a normal part of your inner ear anatomy.
Why do I get dizzy when I close my eyes to go to sleep?
However, when you close your eyes, your brain no longer gets accurate information from your visual system, and it relies on information from the vestibular system. If your vestibulocochlear nerve is inflamed, it is constantly sending out incorrect information, leading your brain to think you are moving when you're not.
What is a BPPV?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV occurs when canalith particles (otoconia) break loose and fall into the wrong part of the semicircular canals of your inner ear, causing vertigo.
How do you fix benign positional vertigo?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo may go away on its own within a few weeks or months. But, to help relieve BPPV sooner, your doctor, audiologist or physical therapist may treat you with a series of movements known as the canalith repositioning procedure.
What is the fastest way to cure BPPV?
0:512:17Vertigo Cure (BPPV) Self Treatment Video - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPosition. Hold this position until the spinning stops. Now quickly return to the upright kneelingMorePosition. Hold this position until the spinning stops. Now quickly return to the upright kneeling position keeping your head turned. And hold for 30 seconds.
What is the most common cause of BPPV?
Having a past head injury is a major cause. Other times, BPPV may result from other problems with the vestibular system. These can include Ménière disease or vestibular neuritis. Ear surgery is a less common cause.
Why does BPPV keep coming back?
A: Unfortunately, BPPV is a condition that can sometimes return. Your risk for BPPV returning can shift from low risk (few experiences in your lifetime) to a higher risk which is often caused by some other factor such as trauma (physical injury), other inner ear or medical conditions, or aging.
What is the name of the disorder that causes spin in the inner ear?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder arising in the inner ear. Its symptoms are repeated episodes of positional vertigo, that is, of a spinning sensation caused by changes in the position of the head. BPPV is the most common cause of the symptoms of vertigo.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code H81.1 is a non-billable code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history atrial fibrillation
- 2. icd 10 code for catatonia unspecified
- 3. icd 10 dx code for epigastric pain
- 4. icd 10 code for depress
- 5. icd 10 external cause code for chemical burn
- 6. icd 10 code for history of substance abuse
- 7. icd 10 code for receptive expressive language delay
- 8. 2017 icd 10 code for disc bulge lumbar
- 9. icd 10 code for painful spinal hardware
- 10. icd 10 code for legswelling