How to lower your risk of future pancreatitis attacks?
- Blood tests to measure the levels of enzymes produced in the pancreas
- A CT scan, which can determine if there is swelling of the pancreas or a buildup of fluid in your abdomen
- An ultrasound, which your doctor may use if they suspect you have gallstones
- A stool sample, which can help determine if your body isn’t digesting food properly
What are the signs of chronic pancreatitis?
Signs of Pancreatitis
- Abdominal Pain. One of the main signs of pancreatitis is pain in the upper abdomen that may also spread to the back.
- Nausea And Vomiting. Abdominal pain may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Swelling Or Tenderness In The Abdomen. ...
- Bowel Movement Issues. ...
- Weight Loss. ...
- Fever. ...
- Rapid Heartbeat. ...
- Jaundice. ...
What are symptoms of autoimmune pancreatitis?
Symptoms of AIP include:
- Mass or growth in the pancreas
- Stomach pain
- Weight loss
- Back pain
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness)
What were your symptoms of chronic pancreatitis?
When symptoms occur, they may include:
- pain in your upper abdomen
- diarrhea
- fatty stools, which are loose, pale, and don’t flush away easily
- nausea and vomiting
- shortness of breath
- unexplained weight loss
- excessive thirst and fatigue
What is the ICD-10 DX code for pancreatitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute pancreatitis, unspecified K85. 9.
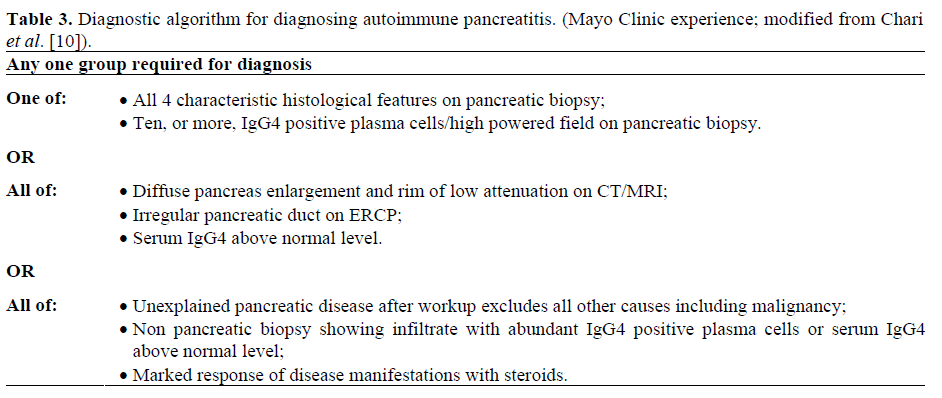
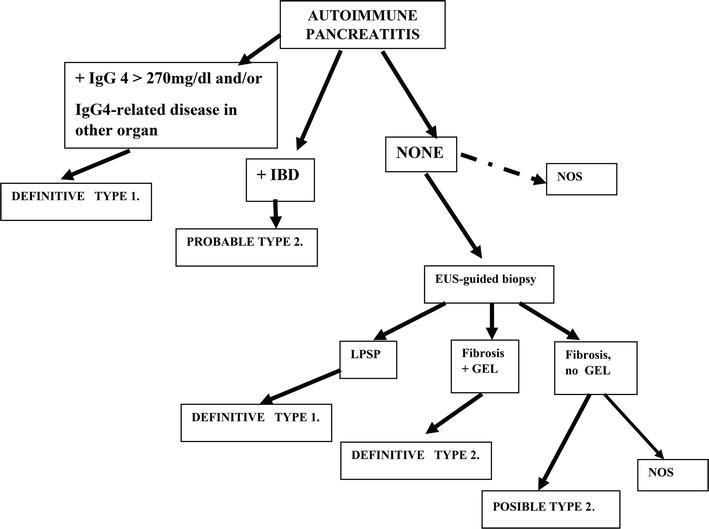
Can pancreatitis be autoimmune?
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a chronic inflammation that is thought to be caused by the body's immune system attacking the pancreas and that responds to steroid therapy. Two subtypes of AIP are now recognized, type 1 and type 2.
How do you code autoimmune pancreatitis?
Other chronic pancreatitisK86. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K86. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K86. 1 - other international versions of ICD-10 K86.
What is the difference between pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis?
There are two forms of pancreatitis: Acute pancreatitis is a sudden and short bout of inflammation. Chronic pancreatitis is ongoing inflammation.
What is Type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis?
Type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a rare inflammatory disease of the pancreas. Very few data have been published on this particular subtype, which differs from the 'classical' IgG4-related type 1 AIP in terms of pathological features, epidemiology and risk of relapse.
Is chronic pancreatitis considered an autoimmune disease?
Autoimmune pancreatitis is a disease in itself. Pancreatitis may also be a symptom of another autoimmune disease, such as lupus.
What is IgG4 autoimmune pancreatitis?
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a rare form of chronic pancreatitis that is characterized by lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and increased IgG4+ plasma cells. Serum IgG4 levels usually are elevated.
What is chronic pancreatitis?
Chronic pancreatitis is a painful disease of the pancreas in which inflammation has resolved, but with resultant damage to the gland characterized by fibrosis, calcification and ductal inflammation. It is possible for patients with chronic pancreatitis to have episodes of acute pancreatitis.
What is idiopathic pancreatitis?
The label of “idiopathic pancreatitis” (IP) was originally designated to cases of pancreatitis wherein a diagnosis could not be made through a thorough history, physical examination, laboratory studies, and noninvasive imaging modalities such as abdominal ultrasonography/computerized tomography.
How do you diagnose chronic pancreatitis?
X-ray images are often the first step in diagnosing chronic pancreatitis. Your doctor can examine the images for signs of disease on the pancreas. Ultrasound uses sound wave technology to create images. This is helpful in detecting changes to the pancreatic ducts or the presence of calcium deposits.
How common is chronic pancreatitis?
The prevalence of chronic pancreatitis is 50/100,000 people. Chronic pancreatitis often develops in patients between the ages of 30 and 40, and is more common in men than women.
How do you know if it is acute or chronic pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis is generally temporary, and the person will often fully recover within a few days. On the other hand, pain from chronic pancreatitis may come and go or be consistent for months at a time.
What is the cause of inflammation of the pancreas?
Acute or chronic inflammation of the pancreas due to autodigestion of pancreatic tissue by its own enzymes. An acute inflammatory process that leads to necrosis of the pancreatic parenchyma. Signs and symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and shock.
How long does it take for pancreatitis to go away?
Pancreatitis can be acute or chronic. Either form is serious and can lead to complications.acute pancreatitis occurs suddenly and usually goes away in a few days with treatment.
What is subcutaneous nodular fat necrosis?
Pancreatitis, hereditary. Subcutaneous nodular fat necrosis in pancreatitis. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. Acute or chronic inflammation of the pancreas due to autodigestion of pancreatic tissue by its own enzymes.
Is pancreatitis an acute condition?
Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis (international symposium on acute pancreatitis, atlanta, 1992).
What are the problems with the pancreas?
Problems with the pancreas can lead to many health problems. These include. pancreatitis, or inflammation of the pancreas: this happens when digestive enzymes start digesting the pancreas itself. pancreatic cancer. cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder in which thick, sticky mucus can also block tubes in your pancreas.
Why does the pancreas no longer make insulin?
In type 1 diabetes, the beta cells of the pancreas no longer make insulin because the body's immune system has attacked them. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas loses the ability to secrete enough insulin in response to meals.
What is the function of the pancreas?
It produces juices that help break down food and hormones that help control blood sugar levels. Problems with the pancreas can lead to many health problems.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for laceration with 2 staples
- 2. icd 9 code for shoulder trapezius strain
- 3. icd 10 code for personal history of cataract surgery
- 4. icd 10 code for b12\ def
- 5. icd 10 code for nasal obstruction secondary to adenoid hypertrophy
- 6. icd-9 code for
- 7. icd 10 code for sharp pain shoulder
- 8. icd 10 code for secondary peritoneal carcinomatosis
- 9. icd 10 code for high testosterone
- 10. icd 10 code for pressure ulcer stage 2 coccyx