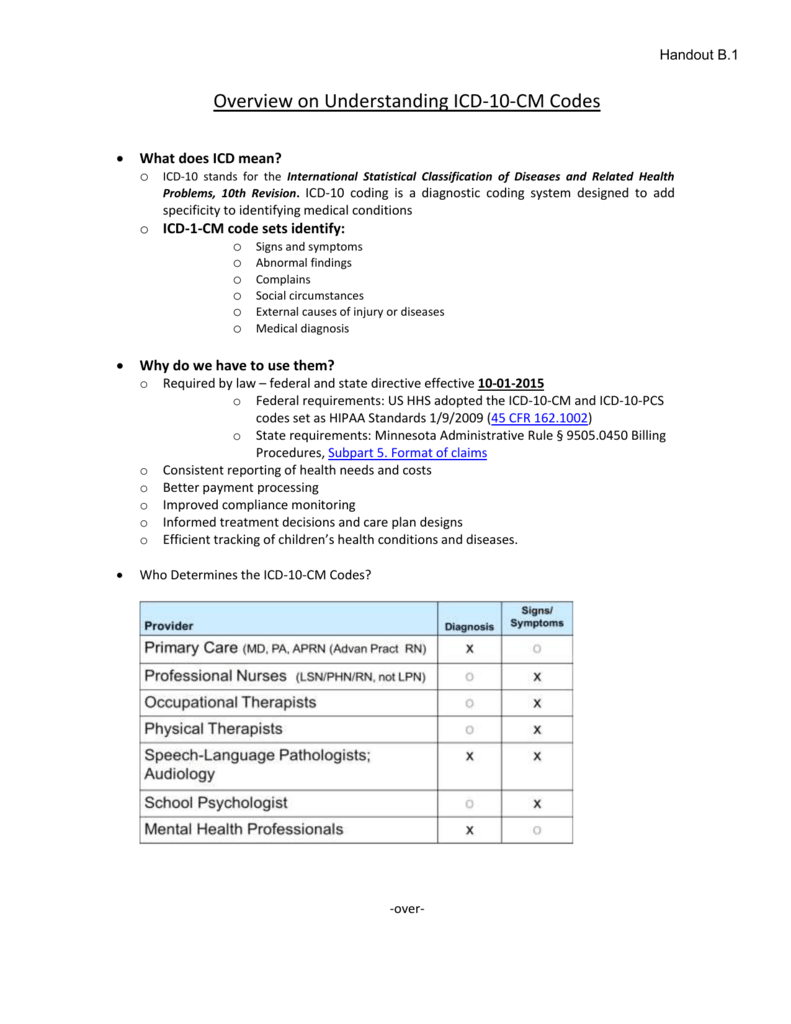
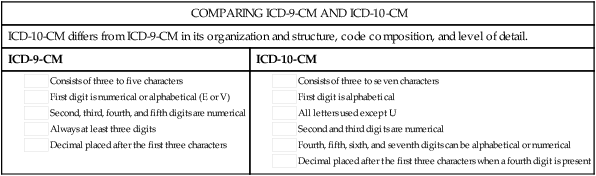
What is a valid ICD 10 code?
Z20.822 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z20.822 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z20.822 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z20.822 may differ. Z codes represent reasons for encounters.
What is the ICD 10 code for CLL?
- Abstractor Notes. Code 9823/3 is used for CLL, SLL, and CLL/SLL. ...
- Diagnostic Confirmation. This histology can be determined by positive histology (including peripheral blood) with or without genetics and/or immunophenotyping.
- Grade
- Module Rule
- Alternate Names
- Definition. ...
- Definitive Diagnostic Methods
- Genetics Data
- Immunophenotyping
- Treatments
What is the ICD 10 code for colon cancer?
The following services are considered colorectal cancer screening services:
- Fecal-occult blood test (FOBT), 1-3 simultaneous determinations (guaiac-based);
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy;
- Colonoscopy; and,
- Barium enema
What is the diagnosis code for chronic tonsillitis?
Chronic tonsillitis. J35.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J35.01 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J35.01 - other international versions of ICD-10 J35.01 may differ.
How do you code CLL?
Code 9823/3 is used for CLL, SLL, and CLL/SLL.
What is chronic lymphocytic Leukaemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (also called CLL) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow that usually gets worse slowly.
What is the difference between CLL and leukemia?
The cancer (leukemia) cells start in the bone marrow but then go into the blood. In CLL, the leukemia cells often build up slowly. Many people don't have any symptoms for at least a few years. But over time, the cells grow and spread to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
Is CLL a leukemia or lymphoma?
In SLL cancer cells are found mostly in the lymph nodes. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Also called CLL/SLL.
What is the life expectancy of a person with CLL?
The prognosis of patients with CLL varies widely at diagnosis. Some patients die rapidly, within 2-3 years of diagnosis, because of complications from CLL. Most patients live 5-10 years, with an initial course that is relatively benign but followed by a terminal, progressive, and resistant phase lasting 1-2 years.
Is CLL a death sentence?
CLL is not an imminent death sentence, especially now. A significant chunk of us will never need treatment and even more of die with the disease, not from it.
What are the 2 types of CLL?
There are two main types of lymphocytes: B cells and T cells. CLL may start in either of these cell types, but it usually affects B cells. B-cell CLL makes up more than 95 percent of all CLL cases, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). T-cell CLL is much rarer.
Is CLL a terminal illness?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) can rarely be cured. Still, most people live with the disease for many years. Some people with CLL can live for years without treatment, but over time, most will need to be treated. Most people with CLL are treated on and off for years.
Which is worse all or CLL?
Summary. ALL and CLL are both cancers that affect the bone marrow and blood. ALL is an acute form of leukemia that progresses rapidly, while CLL is slow-growing. Doctors treat ALL more aggressively than CLL because it spreads more rapidly.
What are the four stages of CLL?
What are the stages of CLL?Stage 0. The blood has too many white blood cells called lymphocytes. This is called lymphocytosis. ... Stage I. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage II. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage III. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage IV. The blood has too many lymphocytes.
How long does CLL stay in remission?
It's hard to say how long your remission will last. It depends on your treatment, age, and overall health. Remissions may last as much as 3-5 years after your first retreatment. Because future retreatments usually don't work as well as the first one, your next remissions may be shorter.
Can CLL turn into non Hodgkin's lymphoma?
In the most cases the normally slow growing, or indolent, CLL transforms into a common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) known as Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Rarer cases transform into Hodgkin lymphoma(HL)/Hodgkin Disease (HD), and some types of T-cell lymphomas also have been reported.
What is the main cause of chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
The exact cause of chronic lymphocytic leukemia is not known. Multiple genetic mutations occur in the DNA of blood-producing cells. These mutations cause the blood cells to produce abnormal lymphocytes, which are not effective at fighting infection. Usually, an abnormal chromosome is present in a patient with CLL.
Can chronic lymphocytic leukemia be cured?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) can rarely be cured. Still, most people live with the disease for many years. Some people with CLL can live for years without treatment, but over time, most will need to be treated. Most people with CLL are treated on and off for years.
Who is most likely to get CLL?
CLL is most common in older adults, is rare in young adults, and hardly ever develops in children. About 90% of people diagnosed with CLL are older than 50. The average age of people diagnosed with CLL is 71.
How does chronic lymphocytic leukemia affect the body?
CLL causes a slow increase in a certain type of white blood cells called B lymphocytes, or B cells. Cancer cells spread through the blood and bone marrow. CLL can also affect the lymph nodes or other organs such as the liver and spleen. CLL eventually can cause the bone marrow to lose its function.
What is a CLL?
In patients presenting predominately with blood and bone marrow involvement it is called chronic lymphocytic leukemia (cll); in those predominately with enlarged lymph nodes it is called small lymphocytic lymphoma. These terms represent spectrums of the same disease.
When will the ICd 10 C91.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C91.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the term for cancer of the white blood cells?
Chronic leukemia characterized by morphologically mature but immunologically less mature lymphocytes; manifested by an abnormal accumulation of these cells in blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic tissue. leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells help your body fight infection.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Is lymphocytic leukemia hard on the blood?
These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells, making it hard for blood to do its work. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia ( cll), there are too many lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.cll is the second most common type of leukemia in adults.
Is lymphoma a clonal disease?
Molecular genetic studies suggest that in approximately half of the cases, the lymphoma is clonally related to the underlying chronic lymphocytic leukemia, whereas in the remaining cases the lymphoma probably represents a secondary, unrelated neoplasm. Code History.
What is the ICd code for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
The ICD code C911 is used to code B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL), also known as chronic lymphoid leukemia (CLL), is the most common type of leukemia (a type of cancer of the white blood cells) in adults. CLL affects B cell lymphocytes, which originate in the bone marrow, develop in the lymph nodes, ...
What is the ICD code for B cell leukemia?
C91.10 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia of B-cell type not having achieved remission. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the ICd code for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
The ICD code C911 is used to code B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL), also known as chronic lymphoid leukemia (CLL), is the most common type of leukemia (a type of cancer of the white blood cells) in adults. CLL affects B cell lymphocytes, which originate in the bone marrow, develop in the lymph nodes, ...
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code C91.1 is a non-billable code.
When will the ICd 10 C83.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C83.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a primary nodal B cell lymphoma?
A primary nodal b-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma which morphologically resembles lymph nodes involved by marginal zone lymphomas of extranodal or splenic types, but without evidence of extranodal or splenic disease. This is a rare entity, and most patients present with localized or generalized lymphadenopathy.
What is a clonal neoplasm?
A clonal neoplasm of small b-lymphocytes, lymphoplasmacytoid cells, and plasma cells involving the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and the spleen. The majority of patients have a serum igm paraprotein. A malignant neoplasm composed of lymphocytes (b-cells), lymphoplasmacytoid cells, and plasma cells.
What is a B cell lymphoma?
A b-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma composed of small lymphocytes which surround and replace the splenic white pulp germinal centers. It involves the spleen and splenic hilar lymph nodes, bone marrow, and often the peripheral blood. When lymphoma cells are present in the peripheral blood, they are usually, but not always, characterized by the presence of short polar villi. Patients present with splenomegaly and the clinical course is indolent. (who)
What is an indolent lymphoma?
An indolent (slow-growing) type of non-hodgkin lymphoma marked by abnormal levels of igm antibodies in the blood and an enlarged liver, spleen, or lymph nodes.
Abstractor Notes
Code 9823/3 is used for CLL, SLL, and CLL/SLL. CLL and SLL are no longer coded separately because it is almost impossible to differentiate between the two diseases. See the hematopoietic PH rules for information on coding primary site for CLL/SLL.
Diagnostic Confirmation
This histology can be determined by positive histology (including peripheral blood) with or without genetics and/or immunophenotyping. Review the Definitive Diagnostic Methods, Immunophenotyping and Genetics Data sections below, and the instructions in the Hematopoietic Manual for further guidance on assigning Diagnostic confirmation.
Definition
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia /small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) is a neoplasm composed of monomorphic small mature B cell s that coexpress CD5 and CD23. There must be a monoclonal B-cell count greater than or equal to 5 x 10 (to the ninth (9th))/L, with the characteristic morphology and phenotype of CLL, in the peripheral blood.
Sources
International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, Third Edition, Second Revision. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2020.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for tonsillomegaly
- 2. icd 10 code for personal assistance
- 3. what is the icd-10 cm code for dimorphous leprosy
- 4. icd 10 code for renal hypertension
- 5. icd 10 code for knee trauma
- 6. icd 10 cm code for unprotected sx
- 7. icd-10 code for pityriasis rosea
- 8. icd 10 code for lgif
- 9. icd 10 code for morphine addiction
- 10. icd 10 code for empyema with pneumonia