How to overcome dissociative identity disorder?
This can happen in various ways:
- Each of your identity states may have different patterns of thinking and relating to the world.
- Your identity states may come across as different ages and genders.
- You may feel you have one 'main' part of your identity that feels most like 'you' - some people call this a host identity.
What causes dissociative identity disorder?
What Are the Root Causes of Dissociative Identity Disorder?
- Emotional, Physical, or Sexual Abuse. According to the Cleveland Clinic, approximately 90 percent of cases of dissociative identity disorder involve some form of long-term abuse.
- Accidents. Sometimes, rather than a prolonged trauma, a short-term but intense trauma can bring on the symptoms of dissociative identity disorder.
- Natural Disasters. ...
- War. ...
What are the tests to diagnose dissociative identity disorder?
Dissociative identity disorder (DID) can be diagnosed using clinical observation, the Multidimensional Inventory of Dissociation, the Dissociative Disorders Interview Schedule, or the Structured Clinical Interview for Dissociative Disorders, the last of which is considered the "gold-star" for diagnosis. The Dissociative Experiences Scale is a screening tool for dissociative disorders but ...
Can You recover from dissociative identity disorder?
Can you recover from Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID)? Yes. Please seek a specialist who deals with personality integration and trauma. It is a long and often difficult process and requires a lot of trust - but personality can be integrated.
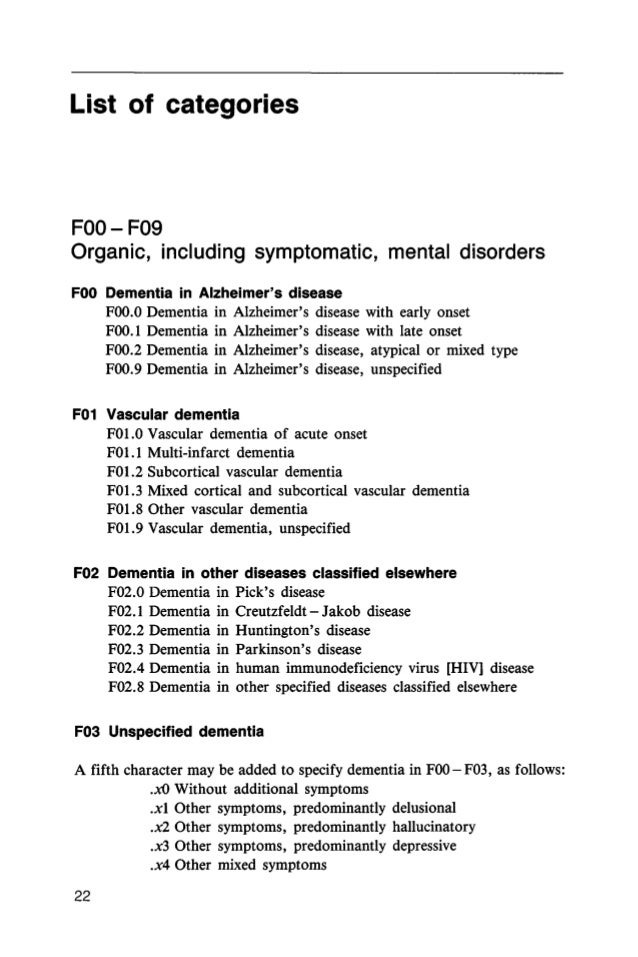
What are the 5 dissociative disorders?
The dissociative disorders that need professional treatment include dissociative amnesia, dissociative fugue, depersonalisation disorder and dissociative identity disorder. Most mental health professionals believe that the underlying cause of dissociative disorders is chronic trauma in childhood.
What is the DSM-5 code for dissociative identity disorder?
Dissociative identity disorder (DID) DSM5 code 300.14 (ICD-10 F44. 81)
Is dissociative identity disorder in the DSM?
In 1994, Multiple Personality Disorder was renamed to Dissociative Identity Disorder in the American DSM-IV psychiatric manual.
What is the dissociative disorder?
Dissociative disorders are mental disorders that involve experiencing a disconnection and lack of continuity between thoughts, memories, surroundings, actions and identity. People with dissociative disorders escape reality in ways that are involuntary and unhealthy and cause problems with functioning in everyday life.
Does DSM-5 have DDNOS?
Other Specified Dissociative Disorder is a diagnosis which was introduced in the DSM-5 psychiatric manual, released in 2013. [1] Along with Unspecified Dissociative Disorder it replaces the diagnosis of Dissociative Disorder Not Otherwise Specified (DDNOS).
What are the 3 main symptoms of dissociative disorder?
Symptoms and signs of dissociative disorders include:Significant memory loss of specific times, people and events.Out-of-body experiences, such as feeling as though you are watching a movie of yourself.Mental health problems such as depression, anxiety and thoughts of suicide.More items...
How is dissociative identity disorder diagnosed?
DiagnosisPhysical exam. Your doctor examines you, asks in-depth questions, and reviews your symptoms and personal history. ... Psychiatric exam. Your mental health professional asks questions about your thoughts, feelings, and behavior and discusses your symptoms. ... Diagnostic criteria in the DSM-5.
Are bpd and DID the same?
Scroppo et al. suggested that a fundamental difference between DID and BPD was the tendency among dissociative individuals to “elaborate upon and imaginatively alter their experience” (p. 281) in contrast to BPD patients, who simplify experience and respond in an affectively driven manner.
How are dissociative disorders classified?
There are three primary types of dissociative disorders: Dissociative identity disorder. Depersonalization/derealization disorder. Dissociative amnesia.
What are the three types of dissociative disorders?
There are three types of dissociative disorders:Dissociative identity disorder.Dissociative amnesia.Depersonalization/derealization disorder.
What is the most common dissociative disorder?
Dissociative amnesia (formerly psychogenic amnesia): the temporary loss of recall memory, specifically episodic memory, due to a traumatic or stressful event. It is considered the most common dissociative disorder amongst those documented.
What is the difference between depersonalization and dissociation?
Depersonalization is an aspect of dissociation. Dissociation is a general term that refers to a detachment from many things. Depersonalization is specifically a sense of detachment from oneself and one's identity.
What is a dissociative identity disorder?
Dissociative identity disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder (MPD), is a mental disorder on the dissociative spectrum characterized by the appearance of at least two distinct and relatively enduring identities or dissociated personality states that alternately control a person's behavior, accompanied by memory impairment for important information not explained by ordinary forgetfulness. These symptoms are not accounted for by substance abuse, seizures, other medical conditions, nor by imaginative play in children. Diagnosis is often difficult as there is considerable comorbidity with other mental disorders. Malingering should be considered if there is possible financial or forensic gain, as well as factitious disorder if help-seeking behavior is prominent.
What is the ICd 9 code for malingering?
Specialty: Psychiatry. MeSH Code: D009105. ICD 9 Code: 300.14. An artist's interpretation of one person with multiple "dissociated personality states.".
What is hysterical psychosis?
Clinical Information. A disorder whose predominant feature is a loss or alteration in physical functioning that suggests a physical disorder but that is actually a direct expression of a psychological conflict or need. Behavior exhibiting excessive or uncontrollable emotion, such as fear or panic;
What does a type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( F44) and the excluded code together.
What is the ICD code for dissociative and conversion disorders?
ICD Code F44 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the nine child codes of F44 that describes the diagnosis 'dissociative and conversion disorders' in more detail. F44 Dissociative and conversion disorders. NON-BILLABLE. BILLABLE.
What is conversion disorder?
Conversion disorder (CD) is a diagnostic category previously used in some psychiatric classification systems. It is sometimes applied to patients who present with neurological symptoms, such as numbness, blindness, paralysis, or fits, which are not consistent with a well-established organic cause, and which cause significant distress. It is thought that these symptoms arise in response to stressful situations affecting a patient's mental health or an ongoing mental health condition such as depression. Conversion Disorder was retained in DSM-5, but given the subtitle Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder. The new criteria cover the same range of symptoms, but remove the requirement for a psychological stressor to be present and for feigning to be disproved.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
F44. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code F44 is a non-billable code.
What does "type 2 excludes" mean?
Type-2 Excludes means the excluded conditions are different, although they may appear similar. A patient may have both conditions, but one does not include the other. Excludes 2 means "not coded here."

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right hand crush injury
- 2. icd 10 code for sigmoid adhesions
- 3. icd 10 code for femur replacement
- 4. icd 10 code for soleus muscle
- 5. icd 10 code for history of rectal polyp
- 6. icd-10 code for acute renal insufficiency
- 7. icd 10 code for history of tubal ligation
- 8. icd 10 code for fallrisk
- 9. icd 10 code for arrythmas
- 10. icd 10 code for gonorrheal infection of vulva