How to tell if you have eustachian tube dysfunction?
What are the signs and symptoms of ETD?
- Fullness or pressure in your ears
- Muffled hearing, or a feeling you are hearing under water or have clogged ears
- Pain in one or both ears
- Ringing in your ears
- Popping, crackling, or clicking feeling in your ears
- Trouble keeping your balance
How can I clear my Eustachian tube naturally?
There are several techniques you can try to unclog or pop your ears:
- Swallowing. When you swallow, your muscles automatically work to open the Eustachian tube. ...
- Yawning. ...
- Valsalva maneuver. ...
- Toynbee maneuver. ...
- Applying a warm washcloth. ...
- Nasal decongestants. ...
- Nasal corticosteroids. ...
- Ventilation tubes.
How do I treat a blocked eustachian tube?
- Identifying the particular allergen you are sensitive to and eliminating it from the environment
- Giving allergy shots, though it may take a long time to notice beneficial effects
- Giving intranasal steroids to reduce inflammation of the mucosal lining of the nose. ...
What is the function of Eustachian tube?
- Nasal saline spray
- Decongestants
- Antihistamines
- Corticosteroids

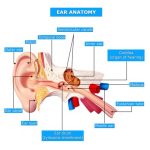
What is the Eustachian tube in the ear?
The Eustachian tube is an opening that connects the middle ear with the nasal-sinus cavity. This tube helps to: Balance pressure in the middle ear (commonly felt as your ears popping) Drain fluid from the middle ear.
Do I have eustachian tube dysfunction?
Eustachian tube dysfunction may occur when the mucosal lining of the tube is swollen, or does not open or close properly. If the tube is dysfunctional, symptoms such as muffled hearing, pain, tinnitus, reduced hearing, a feeling of fullness in the ear or problems with balance may occur.
What code is R06 09?
Other forms of dyspneaICD-10 code R06. 09 for Other forms of dyspnea is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Is Eustachian tube dysfunction serious?
Eustachian tube dysfunction usually isn't serious. But if symptoms linger for several weeks and are left untreated, it could lead to serious health problems, such as hearing loss, tinnitus or damage to your eardrum and middle ear.
What are the symptoms of a blocked Eustachian tube?
Blocked eustachian tubes can cause several symptoms, including:Ears that hurt and feel full.Ringing or popping noises in your ears.Hearing problems.Feeling a little dizzy.
How do you treat chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction usually go away without treatment. You can do exercises to open up the tubes. This includes swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum. You can help relieve the “full ear” feeling by taking a deep breath, pinching your nostrils closed, and “blowing” with your mouth shut.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
10 for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is I10 diagnosis?
ICD-Code I10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Essential (Primary) Hypertension.
What is DX R05?
1 (Acute cough) R05.
What is the best medication for eustachian tube dysfunction?
Oral decongestants are used in the treatment of eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) and can help decrease peritubal edema provoked by allergies or URI. Oxymetazoline is an ingredient found in topical decongestants.
Does eustachian tube dysfunction cause vertigo?
In most or perhaps all cases, symptoms of vertigo are caused by unilateral ETD or by a Eustachian tube obstruction due to ETD that is more severe on one side than on the other. The direction of gait can indicate which side is affected, as most patients stagger towards the direction of the obstructed side [2].
Does eustachian tube dysfunction cause neck pain?
The nerve supply to the eustachian tube is complex, and thus any discomfort may contribute to referred pain to other areas of the head and neck.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #154-156 - Other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with MCC.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H69.93 and a single ICD9 code, 381.9 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for z7982
- 2. icd 10 code for wound care
- 3. icd 10 code for right bka status
- 4. icd 10 code for parkinsons debilitation
- 5. icd 9 code for primary biliary cirrhosis
- 6. icd 10 code for vitiligo skin
- 7. icd code for sleep problems
- 8. icd 9 code for pigment dispersion syndrome
- 9. icd 10 code for foot ulcer unspecified
- 10. what is the icd-10-cm code for ascending aortic aneurysm