What is the ICD 10 for GERD?
Calculus of gallbladder w acute cholecyst w/o obstruction; Calculus of gallbladder with acute cholecystitis; Gallstone and acute cholecystitis. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K80.00. Calculus of gallbladder with acute cholecystitis without obstruction. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code.
What is the ICD 10 code for abnormal gallbladder?
· Disease of gallbladder, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. K82.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K82.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis code for bladder cancer?
· K82.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K82.8 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K82.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 K82.8 may differ. Applicable To.
What is the diagnosis code for gastric ulcer?
· Cholesterolosis of gallbladder. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. K82.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K82.4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
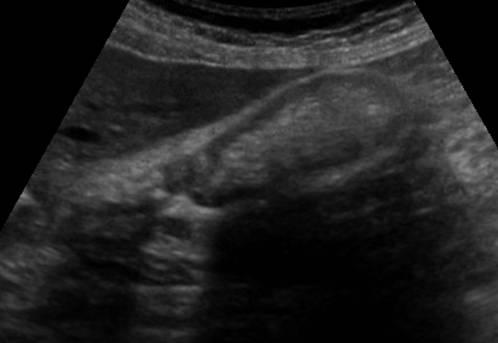
What is gallbladder sludge?
Gallbladder sludge. This is a thick material that can't be absorbed by bile in your gallbladder. The sludge builds up in your gallbladder. It happens mainly to pregnant women or to people who have had a very fast weight loss.
How do you code biliary sludge?
9.
What is Code K82 8?
8 Other specified diseases of gallbladder.
What are the symptoms of biliary sludge?
Symptoms of biliary sludge include pain in the abdomen, nausea and vomiting, particularly after a fatty meal. Biliary sludge can cause complications, including pain from obstruction of the bile ducts (biliary colic), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), and inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis).
What is the ICD-10 for abdominal pain?
ICD-10 | Unspecified abdominal pain (R10. 9)
What organs does a HIDA scan show?
A HIDA, or hepatobiliary, scan is a diagnostic test. It's used to capture images of the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and small intestine to help diagnose medical conditions related to those organs. Bile is a substance that helps digest fat.
What is DX code R10 11?
ICD-10 | Right upper quadrant pain (R10. 11)
What is the ICD 10 code for gallbladder mass?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K82 K82.
What is gallbladder wall thickening?
Thickening of the gallbladder wall is a relatively frequent finding at diagnostic imaging studies. Historically, a thick-walled gallbladder has been regarded as proof of primary gallbladder disease, and it is a well-known hallmark feature of acute cholecystitis.
Is gallbladder sludge the same as stones?
In other cases, sludge can thicken further, and can lead to the formation of the rock-like objects called gallstones. While the presence of sludge in the gallbladder is a step in the process of forming gallstones, having sludge in the gallbladder does not necessarily mean gallstones are inevitable.
What medication is used for gallbladder sludge?
Ursodiol is in a class of medications called gallstone dissolution agentss. It works by decreasing the production of cholesterol and by dissolving the cholesterol in bile to prevent stone formation and by decreasing toxic levels of bile acids that accumulate in primary biliary cirrhosis.
What is sludge medical term?
(emergency medicine, mnemonic) An acronym used to help remember the common symptoms of certain affections of a cholinergic toxidrome: "salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, gastrointestinal upset, emesis".
What is the gallbladder?
Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat.
What is a non-neoplastic gallbladder?
Gallbladder disease. Clinical Information. A non-neoplastic or neoplastic disorder that affects the gallbladder. Representative examples of non-neoplastic disorders include acute and chronic cholecystitis, often associated with the presence of gallstones.
What is the tube that connects the gallbladder to the small intestine?
As your stomach and intestines digest food, your gallbladder releases bile through a tube called the common bile duct. The duct connects your gallbladder and liver to your small intestine.your gallbladder is most likely to give you trouble if something blocks the flow of bile through the bile ducts.
What is a condition in which there is a deviation from or interruption of the normal structure or function of the gall
Condition in which there is a deviation from or interruption of the normal structure or function of the gallbladder; generally involves the impairment of bile flow, gallstones in the biliary tract, infections, neoplasms, or other diseases. Diseases of the gallbladder.
When will the ICD-10-CM K82.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K82.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can you get a gallstone after eating?
That is usually a gallstone. Gallstone attacks usually happen after you eat. Signs of a gallstone attack may include nausea, vomiting, or pain in the abdomen, back, or just under the right arm.many gallbladder problems get better with removal of the gallbladder.
What is the ICd code for acholia?
The ICD code K828 is used to code Acholia. the acholia is the lack or absence of bile secretion. acholia is an uncommon trouble of the biliary function in the liver, bile flow dissipates. Specialty: Gastroenterology. MeSH Codes:
What is DRG 444-446?
DRG Group #444-446 - Disorders of the biliary tract without CC or MCC.
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
What is the gallbladder?
Gallbladder Diseases. Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. As your stomach and intestines digest food, your gallbladder releases bile through a tube called the common bile duct.
What is the code for biliary tract?
K83.8 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other specified diseases of biliary tract. The code K83.8 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
When was the ICd 10 code implemented?
FY 2016 - New Code, effective from 10/1/2015 through 9/30/2016 (First year ICD-10-CM implemented into the HIPAA code set)
How long does gallstone pain last?
Gallstones, which can increase pressure in the gallbladder and cause a gallbladder attack. The pain usually lasts from one to several hours.
Why does bile cause a gallbladder attack?
The bile helps break down fat. It also helps the liver get rid of toxins and wastes. Different diseases can block the bile ducts and cause a problem with the flow of bile: Gallstones, which can increase pressure in the gallbladder and cause a gallbladder attack. The pain usually lasts from one to several hours.
Can you live without a gallbladder?
Many gallbladder problems get better with removal of the gallbladder. Fortunately, you can live without a gallbladder . Bile has other ways of reaching your small intestine.
Known As
Gallbladder sludge is also known as acquired cystic dilatation of common bile duct, acquired dilated bile duct, acquired dilation of bile duct, adhesion of bile duct, adhesions of biliary tree, aschoff-Rokitansky sinuses, atrophy of bile duct, atrophy of biliary tree, benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis, bile duct proliferation, biliary ascariasis, biliary cyst, biliary sludge, biliary tract dysplasia, cholangiectasis, choledochocele, cholestasis, cholestasis (gallbladder condition) in pregnancy, cholestasis (gallbladder disorder) in childbirth, cholestasis in childbirth, cholestasis in newborn, cholestasis in pregnancy, cholestasis of parenteral nutrition, cholestasis of pregnancy, cholestasis postpartum, cholestasis-edema syndrome Norwegian type, cirrhosis secondary to cholestasis, cyst of bile duct, cyst of biliary tract, cyst of intrahepatic bile ducts, cystic dilatation of common bile duct, disorders of biliary tract anastomosis, drug-induced intrahepatic cholestasis, dysfunction of sphincter of oddi, extrahepatic cholestasis, familial arthrogryposis-cholestatic hepatorenal syndrome, fibrosis of bile duct, hemobilia, hepatic duct dysplasia, hypertrophy of bile duct, hypertrophy of biliary tract, intrahepatic cholestasis, jaundice obstructive, north American Indian intrahepatic cholestasis, obstructive hyperbilirubinemia, obstructive jaundice, papillary mass of biliary tract, postpartum cholestasis, postpartum cholestasis (gallbladder disorder after childbirth), progressive intrahepatic cholestasis, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, stasis of bile duct, toxic liver disease w cholestasis, toxic liver disease with cholestasis, ulcer of bile duct, ulcer of cystic duct, ulceration of biliary tree, vanishing bile duct syndrome, and verbrycke’s syndrome.
Gallbladder Sludge Definition and Symptoms
Gallbladder sludge is a mixture of mucus and particulate matter that forms in bile. Sludge is detected by a transabdominal ultrasonography. Symptoms include chills, indigestion, sweating, nausea, severe pain in the abdomen, fever, and bloating.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for stent status
- 2. icd 10 code for stung bee
- 3. icd code for 300.01
- 4. icd code 10 for weakness
- 5. icd 10 code for chemical burn base
- 6. icd 10 code for poisoning by 4-aminophenol intentional
- 7. icd 10 code for cytopenia due to chemo
- 8. icd 10 code for wrist injury left
- 9. icd 10 code for attention to surgical wound
- 10. icd 10 code for winged scapula