What is the ICD 10 code for diffuse axonal brain injury?
Diffuse axonal brain injury without loss of consciousness Diffuse brain injury with no loss of consciousness ICD-10-CM S06.2X0A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 082 Traumatic stupor and coma >1 hour with mcc
What is the ICD 10 code for unspecified intracranial injury?
Unspecified intracranial injury 1 S06.9 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S06.9 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S06.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 S06.9 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for external cause of injury?
The External Cause of Injuries index contains codes found in Chapter 19, Injury, poisoning & certain other consequences of external causes , and Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, of the ICD-10-CM. The codes begin with the letters S and T for Chapter 10, and V, W, X, and Y in Chapter 20.
How is diffuse axonal injury (DAI) treated following a motorcycle accident?
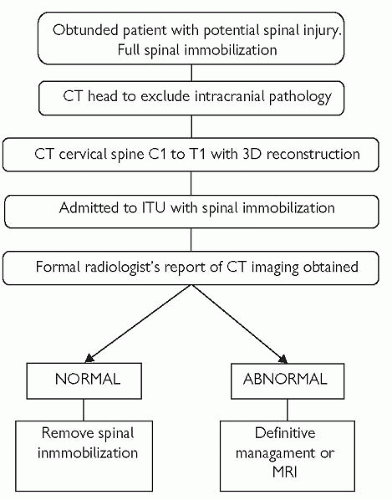
Figure 2 – MRI imaging demonstrating diffuse axonal injury following motorcycle accident (day 3) Following any trauma, patients should be appropriately resuscitated and stabilised, prior to transfer to a neuro-trauma centre. Therapeutic interventions for DAI are limited.

What is a grade 3 diffuse axonal injury?
grade 3: focal lesions in both the corpus callosum and dorsolateral quadrant of the rostral brainstem, in addition to diffuse axonal damage.
What is a axonal injury?
Diffuse axonal injury is the shearing (tearing) of the brain's long connecting nerve fibers (axons) that happens when the brain is injured as it shifts and rotates inside the bony skull. DAI usually causes coma and injury to many different parts of the brain.
Is diffuse axonal injury a primary injury?
Primary Injury lacerations (tears in brain tissue or blood vessels of the brain), diffuse axonal injury (traumatic shearing forces leading to tearing of nerve fibers in the white matter tracts).
What is the ICD-10 for traumatic brain injury?
*7th character of A, B, or missing (reflects initial encounter, active treatment); S09. 90— unspecified injury of head–is NOT included in the TBI definition....WISH: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) ICD-10-CM Codes.S02.0, S02.1Fracture of skullS06Intracranial injuryS07.1Crushing injury of skullT74.4Shaken infant syndrome2 more rows•Aug 23, 2021
Is diffuse axonal injury the same as a concussion?
DAI can occur across the spectrum of traumatic brain injury (TBI) severity, wherein the burden of injury increases from mild to severe. Concussion may be a milder type of diffuse axonal injury....Diffuse axonal injurySpecialtyNeurology2 more rows
What are the 4 types of traumatic brain injuries?
Types of traumatic brain injuries include:Concussions. A concussion is a minor brain injury that is caused by an impact to the head, shaking, or a sudden change in movement, like whiplash. ... Brain Contusions. ... Penetrating Brain Injuries. ... Anoxic Brain Injuries.
What are the levels of diffuse axonal injury?
Grading ClassificationGradePathologyGrade 1Diffuse axonal damage within the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres and grey-white matter interfacesGrade 2Tissue tear haemorrhages present; axonal damage of the white matter including grade 1 regions and the territory of the corpus callosum1 more row
How is diffuse axonal injury diagnosis?
Briefly, a diagnosis of DAI is made when a patient has experienced a LOC of more than 6 hours after head trauma, has shown related clinical manifestations, and has DAI lesions on a conventional brain MRI [4,8,10].
What are the three levels of severity of head injuries?
Grade 1: Mild, with symptoms that last less than 15 minutes and involve no loss of consciousness. Grade 2: Moderate, with symptoms that last longer than 15 minutes and involve no loss of consciousness. Grade 3: Severe, in which the person loses consciousness, sometimes for just a few seconds.
How do you code a traumatic brain injury?
Therefore, assign code S06. 9x0A for documentation of traumatic brain injury (initial encounter) without further specification. However, a more specific code from category S06 should be assigned to identify the documented injuries such as concussion, cerebral edema, contusion, laceration, and hemorrhage.
What is the ICD 10 code for anoxic brain injury?
ICD-10 code G93. 1 for Anoxic brain damage, not elsewhere classified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What causes axonal injury?
The most common etiology of diffuse axonal injury involves high-speed motor vehicle accidents. [2] The most common mechanism involves an accelerating and decelerating motion that leads to shearing forces to the white matter tracts of the brain.
Does axonal injury always lead to cell death?
Axonal injury consequent to head trauma was first described by Strich38 over 50 years ago. It results from exertion of powerful forces causing angular acceleration or impact injury; it is not necessarily lethal unless localized within brainstem structures controlling cardiorespiratory functions.
Can you fully recover from diffuse axonal injury?
4: Can I Recover Fully? For some, recovering from a diffuse axonal brain injury is possible—but there are no guarantees with such injuries. The severity of the brain lesions, which areas of the brain they are in, your treatment, and many other factors can affect whether or not you make a full recovery.
What causes axonal loss?
Inflammatory axonal transection and a lack of myelin trophic support seem to be responsible for axonal loss and subsequent disability in the initial stage of the illness. By comparison, in the progressive phase, the pathogenesis for neuronal and axonal loss is poorly understood.
What is the differential diagnosis of head injury?
The main differential in cases of head injury are cortical contusions, typically found superficially at the cortical level, not concentrated to the grey-white matter junction. Other differential diagnoses, from imaging, include diffuse vascular injury, amyloid angiopathy, and chronic hypertensive encephalopathy.
Is diffuse axonal injury fatal?
Diffuse Axonal Injury is often fatal and one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality following traumatic brain injury. Diffuse white matter tract lesions are histopathological and neuroimaging hallmarks of DAI.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for behavioral issue
- 2. icd 10 code for allergy to zithromax
- 3. icd 10 code for laryngoscopy
- 4. icd 10 code for mrsa empyema
- 5. icd 10 code for elevated appetite
- 6. icd 10 code for oral contraception
- 7. icd 10 code for mrsa cellulitis
- 8. icd-10 code for fracture to right distal fibula
- 9. icd 10 code for salmon colored mucosa
- 10. icd 10 code for history of heart cath