What are the new features of ICD 10?
May 05, 2020 · Z86. 73 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Click to see full answer. Similarly, it is asked, how do I code history of CVA? When a patient has a history of cerebrovascular disease without any sequelae or late effects, ICD-10 code Z86. 73 should be assigned.
How many codes in ICD 10?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z86.73 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Personal history of transient ischemic attack (TIA), and cerebral infarction without residual deficits. Prsnl hx of TIA (TIA), and cereb infrc w/o resid deficits; H/o: cva; H/o: tia; Has had parietal... of atherosclerotic stroke wo residual deficits; History of cardioembolic stroke; History of cerebellar stroke; History of cerebral …
What are the common ICD 10 codes?
When a patient has a history of cerebrovascular disease without any sequelae or late effects, ICD-10 code Z86.73 should be assigned. If a physician clearly documents that a patient is being seen who has a history of cerebrovascular disease or accident with residual effects, a code from category I69* should be assigned.
What is ICD 10 used for?
History codes are used to explain a patient’s past medical ... (ICD -10 CM) that CMS and NCHS provide. Organizations that make up ICD-10-CM include AHA, PC-450HE-1527 . Title: Best Practices for ICD-10 Coding and Documenting MI and CVA Author: Rock, Christina Created Date: 11/7/2019 12:02:16 PM ...
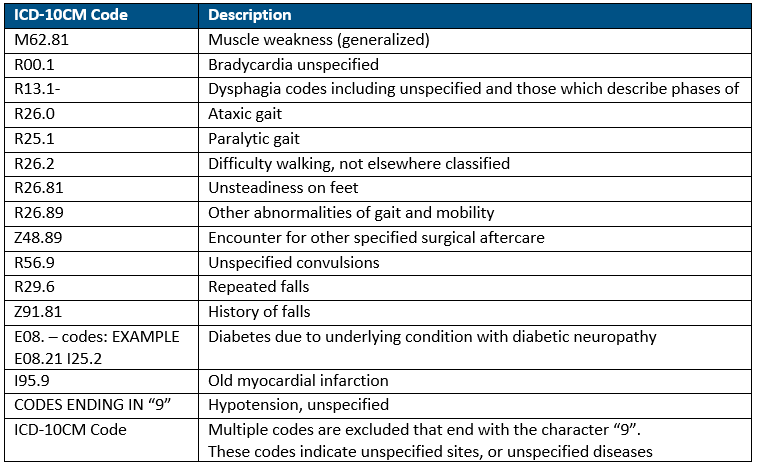
What is the ICD-10 for history of CVA?
When a patient has a history of cerebrovascular disease without any sequelae or late effects, ICD-10 code Z86. 73 should be assigned.
How do you code a CVA in ICD-10?
I63. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you code history of stroke?
5. History of Stroke (ICD-10 code Z86. 73) should be used when the patient is being seen in an out patient setting subsequent to an inpatient stay. In addition, this code should be used when the patient does not exhibit neurologic deficits due to cerebrovascular disease (i.e., no late effects due to stroke).
Is CVA and cerebral infarction the same?
Obstruction in blood flow (ischemia) to the brain can lead to permanent damage. This is called a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). It is also known as cerebral infarction or stroke. Rupture of an artery with bleeding into the brain (hemorrhage) is called a CVA, too.
What is the CPT code for CVA?
Residual neurological effects of a stroke or cerebrovascular accident (CVA) should be documented using CPT category I69 codes indicating sequelae of cerebrovascular disease. Codes I60-67 specify hemiplegia, hemiparesis, and monoplegia and identify whether the dominant or nondominant side is affected.Aug 25, 2021
What is the ICD 10 code for HTN?
That code is I10, Essential (primary) hypertension. As in ICD-9, this code includes “high blood pressure” but does not include elevated blood pressure without a diagnosis of hypertension (that would be ICD-10 code R03. 0).
What is the ICD code for stroke?
TABLE 1. ICD Stroke Codes*ICD-9ICD-10CodeCode433.x1I63.x434.x1I64.x4366 more rows•Jul 14, 2005
What is CVA infarct?
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is the medical term for a stroke. A stroke is when blood flow to a part of your brain is stopped either by a blockage or the rupture of a blood vessel.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of MI?
ICD-10 code I25. 2 for Old myocardial infarction is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What does history of CVA mean?
Cerebrovascular accident: The sudden death of some brain cells due to lack of oxygen when the blood flow to the brain is impaired by blockage or rupture of an artery to the brain. A CVA is also referred to as a stroke. Symptoms of a stroke depend on the area of the brain affected.Jan 13, 2022
What are the three most common causes of a CVA?
Overall, the most common risk factors for stroke are:high blood pressure,high cholesterol,smoking,diabetes, and.increasing age.
How can you tell the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke?
A stroke is a bleeding or clotting event that interferes with blood flow to the brain. An ischemic stroke is when blood vessels to the brain become clogged. A hemorrhagic stroke is when bleeding interferes with the brain's ability to function.Mar 1, 2021
How is a stroke classified?
Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810) A stroke is a medical emergency.
How long does it take for a patient to have a hemorrhage?
Infarction or hemorrhage may be demonstrated either directly by imaging, laboratory, or pathologic examination in patients with symptom duration less than 24 hours, or inferred by symptoms lasting greater than or equal to 24 hours (or fatal within 24 hours) that cannot be attributed to another cause.
What is the term for a loss of blood flow to the brain?
An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries. In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
What is Category I69?
Category I69 is to be used to indicate conditions in I60 - I67 as the cause of sequelae. The 'sequelae' include conditions specified as such or as residuals which may occur at any time after the onset of the causal condition. Type 1 Excludes.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for post traumatic arthritis shoulder
- 2. icd 9 cm code for bruising on buttocks
- 3. icd 10 code for left lower back pain
- 4. icd 10 code for hypercoagulable state
- 5. icd-10 code for cellulitis left arm
- 6. icd 10 code for pressure ulcer r great toe unstageable
- 7. icd 10 code for cellulitis left 4th finger
- 8. icd 10 code for diabetes hypertension
- 9. icd 10 code for peripheral vascular disease of lower extremity with ulceration
- 10. icd 10 code for right ring finger non-displaced distal phalanx fracture