Bariatric surgery status. Z98.84 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98.84 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for history of hypothyroidism?
H/o: git bypass/anastomosis; H/o: intestinal by-pass; History of gastrointestinal tract bypass or anastomosis; History of intestinal bypass; bariatric surgery status (Z98.84); gastric bypass status (Z98.84); obesity surgery status (Z98.84) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z98.0. Intestinal bypass and anastomosis status.
What is the ICD 10 code for history of hypertension?
Oct 01, 2021 · Z98.84 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98.84 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z98.84 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z98.84 may differ. Applicable To Gastric banding status
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z85.040 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Personal history of malignant carcinoid tumor of rectum. History of malignant carcinoid tumor of rectum; History of malignant carcinoid tumor of the rectum; Conditions classifiable to C7A.026. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z85.040.
What is the history of ICD - 10?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I70.798 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Other atherosclerosis of other type of bypass graft (s) of the extremities, other extremity Oth athscl type of bypass of the extremities, oth extremity ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I70.799 [convert to ICD-9-CM]
What is the ICD-10 code for history of gastric bypass?
Valid for SubmissionICD-10:Z98.84Short Description:Bariatric surgery statusLong Description:Bariatric surgery status
What is the ICD-10 code for personal history of gastric sleeve?
Z98. 84 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you code gastric bypass surgery?
Open Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Open gastric bypass (CPT code 43846) involves both a restrictive and a malabsorptive component, with the horizontal or vertical partition of the stomach performed in association with a Roux-en-Y procedure (ie, a gastrojejunal anastomosis).Mar 15, 2020
What is bariatric surgery status?
Bariatric surgery: Surgery on the stomach and/or intestines to help a person with extreme obesity lose weight. Bariatric surgery is an option for people who have a body mass index (BMI) above 40.Mar 29, 2021
What is DX code E66 01?
E66. 01 is morbid (severe) obesity from excess calories.Jun 25, 2017
What is Roux-en-Y reconstruction?
In general surgery, a Roux-en-Y anastomosis, or Roux-en-Y, is an end-to-side surgical anastomosis of bowel used to reconstruct the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, it is between stomach and small bowel that is distal (or further down the gastrointestinal tract) from the cut end.
What is the CPT code for bariatric surgery?
Noridian Local Coverage for Laparoscopic Sleeve GastrectomyCodeDescription43775LAPAROSCOPY, SURGICAL, GASTRIC RESTRICTIVE PROCEDURE; LONGITUDINAL GASTRECTOMY (IE, SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY)
What is procedure code 43774?
CPT 43774 Description This code is defined by the CPT manual as: “Laparoscopy, surgical, gastric restrictive procedure. Removal of subcutaneous port components and adjustable gastric restrictive device.”
What is procedure code 43644?
43644- Laparoscopy, surgical, gastric restrictive procedure; with gastric bypass and Roux-en-Y gastroenterostomy (roux limb 150 cm or less).Apr 28, 2006
What are the 4 types of bariatric surgery?
The most common types of bariatric surgery are sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, and adjustable gastric banding. Lap banding is also known as laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding.
What are the 3 bariatric surgery?
There are currently three primary weight loss (or bariatric) surgeries being performed across the United States. They are Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding and sleeve gastrectomy. All of these surgeries have pros and cons to them, and none of them are a quick, simple fix for losing weight.Aug 26, 2013
What is the DRG code for bariatric surgery?
1 Must be accompanied by DRG 288. 2 Must be accompanied by DRG 288 or another bariatric surgery procedure. DRG = Diagnosis-Related Groups; CPT = Current Procedural Terminology. HCPCS = Health Care Common Procedure Coding System, Level II.
What is the dumping syndrome?
Dumping syndrome is a condition that can develop after surgery to remove all or part of your stomach or after surgery to bypass your stomach to help you lose weight. Also called rapid gastric emptying, dumping syndrome occurs when food, especially sugar, moves from your stomach into your small bowel too quickly.
What is meant by bariatric?
Baros means "weight" in Greek; so, for example, a barometer is an instrument that measures air pressure or weight. Bariatric describes the medical treatment of serious overweight—that is, obesity. Bariatric surgery is only employed when other methods of weight loss have been tried and failed.
What is the purpose of bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery is done to help you lose excess weight and reduce your risk of potentially life-threatening weight-related health problems, including: Heart disease and stroke. High blood pressure.
Who does gastric bypass surgery?
Newer studies have found gastric bypass surgery can be safe and effective for adults ages 60 and older. The procedure is also now considered an option for some teenagers with a BMI of 35 or more and serious obesity-related health problems.
How does gastric sleeve work?
A gastric sleeve works by permanently removing a large portion of your stomach. As the capacity of your stomach is vastly reduced, it can only hold a small portion of food. A sleeve gastrectomy also removes the part of your stomach that produces the hunger stimulating hormone ghrelin.
What is gastric sleeve surgery for weight loss?
Sleeve gastrectomy is a surgical procedure that induces weight loss by restricting food intake. With this procedure, which is usually performed laparoscopically, the surgeon removes approximately 75 percent of the stomach. This results in the stomach taking on the shape of a tube or "sleeve" which holds much less food.
What is CPT code s2083?
S2083 is a valid 2020 HCPCS code for Adjustment of gastric band diameter via subcutaneous port by injection or aspiration of saline or just “Adjustment gastric band” for short, used in Other medical items or services.
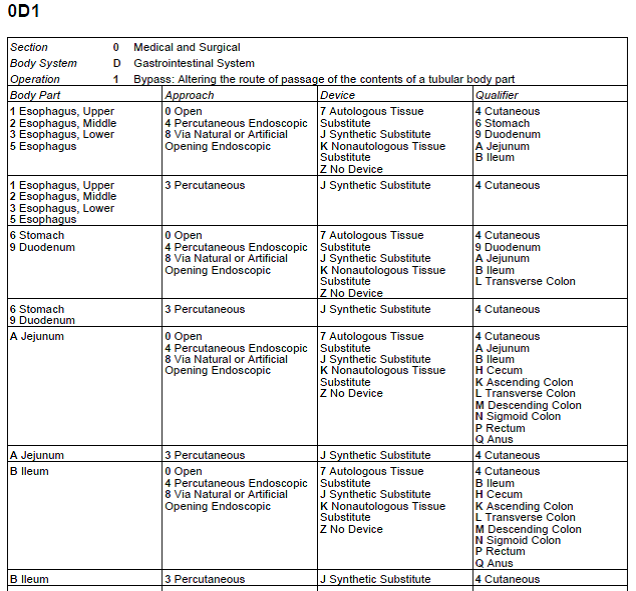
Open Approach
Cutting through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to expose the site of the procedure
Percutaneous Approach
Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach the site of the procedure
Percutaneous Endoscopic Approach
Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach and visualize the site of the procedure
Via Natural or Artificial Opening Endoscopic Approach
Entry of instrumentation through a natural or artificial external opening to reach and visualize the site of the procedure

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2015 icd 10 code for cardiomegaly
- 2. icd 10 code for pancytopenia with neutropenic sepsis s
- 3. icd 10 code for swollen lips,
- 4. icd 10 code for post right hip arthroplasty
- 5. icd 10 code for low transverse cesarean delivery following attempted vaginal delivery
- 6. icd 10 code for left tibial shaft fracture
- 7. icd 10 code for k62.89
- 8. icd-10 code for d dimer
- 9. icd-10 code for fall from monkey bars
- 10. icd 10 code for costochondral pain