What is the ICD 10 code for ureter?
Calculus of ureter. N20.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM N20.1 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N20.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 N20.1 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for hydronephrosis with renal and ureteral obstruction?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N13.2. Hydronephrosis with renal and ureteral calculous obstruction. N13.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the new ICD-10 version for kidney stones?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N20.1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N20.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 N20.1 may differ. Stones in the ureter that are formed in the kidney. They are rarely more than 5 mm in diameter for larger renal stones cannot enter ureters.
What is a ureteric stone?
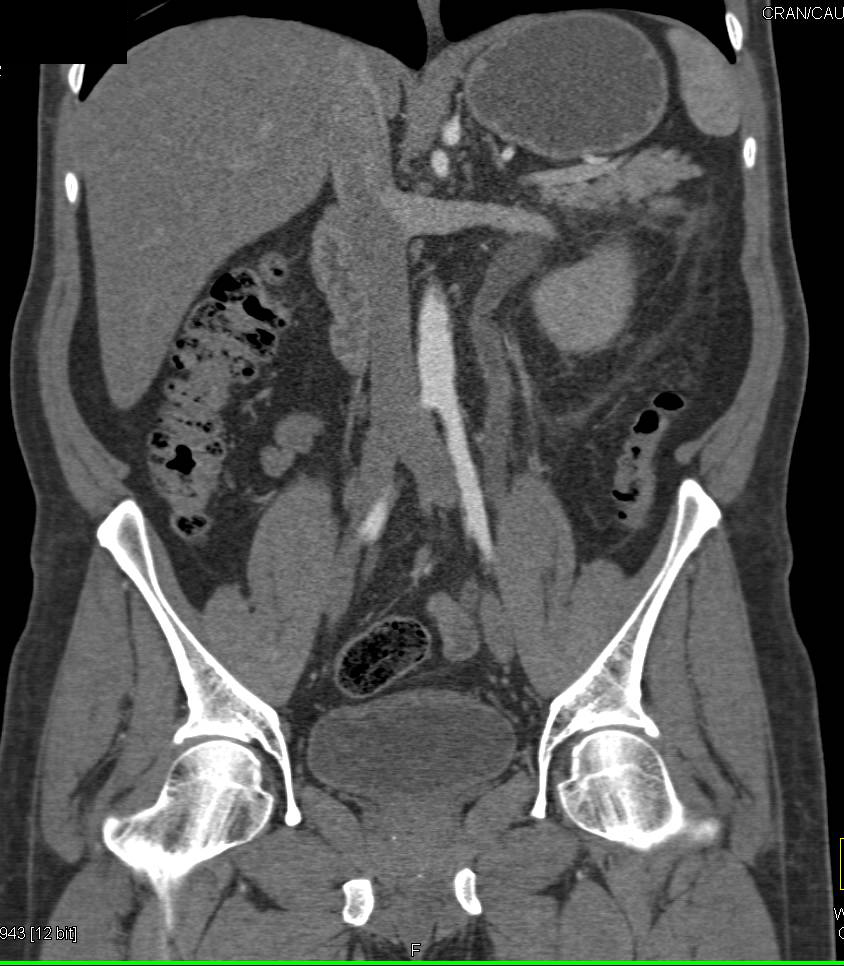
Ureteric stone; Clinical Information. Stones in the ureter that are formed in the kidney. They are rarely more than 5 mm in diameter for larger renal stones cannot enter ureters. They are often lodged at the ureteral narrowing and can cause excruciating renal colic. ICD-10-CM N20.1 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 38.0):

What is the ICD-10 code for left ureteral stone?
N20. 1 - Calculus of ureter | ICD-10-CM.
What is ICD-10 code N20?
"N20. 0 - Calculus of Kidney." ICD-10-CM, 10th ed., Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the National Center for Health Statistics, 2018.
What code is n28 89?
89 Other specified disorders of kidney and ureter.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for ureteric stone?
N20. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N20.
What is the ICD-10 code for kidney stone?
ICD-10-CM Code for Calculus of kidney N20. 0.
What is the ICD 10 code for ureteral mass?
N28. 89 - Other specified disorders of kidney and ureter | ICD-10-CM.
What is Caliectasia?
Caliectasis is a condition that affects the calyces in your kidneys. Your calyces are where urine collection begins. Each kidney has 6 to 10 calyces. They're on the outer edges of your kidneys. With caliectasis, the calyces become dilated and swollen with extra fluid.
Is the ureter part of the kidney?
The ureter is a tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. There are two ureters, one attached to each kidney. The upper half of the ureter is located in the abdomen and the lower half is located in the pelvic area.
What is the diagnosis code for renal mass?
Other specified disorders of kidney and ureter The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N28. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N28.
What is the hydronephrosis in kidney?
Hydronephrosis is a condition where one or both kidneys become stretched and swollen as the result of a build-up of urine inside them. It can affect people of any age and is sometimes spotted in unborn babies during routine pregnancy ultrasound scans.
What is cortical thinning of the kidney?
Bilateral renal cortical thinning (or thinning of the kidney cortex) means that the kidney has been scarred and the amount of functioning tissue (functioning nephrons) in the kidney cortex has decreased.
What is the CPT code for gross hematuria?
ICD-10 code R31. 0 for Gross hematuria is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
How do you know if you have kidney stones?
The following may be signs of kidney stones that need a doctor's help: extreme pain in your back or side that will not go away. blood in your urine. fever and chills. vomiting. urine that smells bad or looks cloudy.
Can kidney stones go away?
Most kidney stones pass out of the body without help from a doctor. But sometimes a stone will not go away.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for trunkal asymmetry
- 2. what are the icd-10 code use for tpn tree
- 3. icd 10 code for mononucleosis without complications
- 4. icd 10 code for removal of port a cath
- 5. icd 10 code for history of heart disease
- 6. icd 10 code for contact with grinder
- 7. icd 10 code for multiple renal cyst
- 8. icd 10 code for v01.89
- 9. icd 10 code for depressiom
- 10. icd 10 code for chronic venous insufficiency of left lower extremity with superficial ulcerations