What is the ICD 10 code for alveolar maxillary hypoplasia?
Alveolar maxillary hypoplasia. M26.73 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM M26.73 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M26.73 - other international versions of ICD-10 M26.73 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for jaw disease?
Other specified diseases of jaws. M27.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM M27.8 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M27.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 M27.8 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for disturbance in tooth formation?
Disturbances in tooth formation 1 K00.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM K00.4 became effective on October 1, 2019. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K00.4 - other international versions of ICD-10 K00.4 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for congenital hypoplasia of the pulmonary artery?
Congenital anomaly of pulmonary artery. Hypoplasia of pulmonary artery. functional, unilateral J43.0. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J43.0. Unilateral pulmonary emphysema [MacLeod's syndrome] 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Swyer-James syndrome. Unilateral emphysema.

What is the ICD-10-CM code for zygomatic hypoplasia?
738.12 - Zygomatic hypoplasia | ICD-10-CM.
What is the code for denture hyperplasia?
K13.6Irritative hyperplasia of oral mucosa The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K13. 6 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K13.
What is the ICD-10 code for poor dentition?
Disorder of teeth and supporting structures, unspecified K08. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K08. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for cleft palate?
Q35.9Q35. 9 - Cleft palate, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
Is gingival hyperplasia common?
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) is a rare oral condition that causes slow, progressive gum enlargement. It often begins in childhood, but it may not be noticeable until adulthood. The gingival overgrowth from this condition is caused by an overproduction of collagen.
What is gingival enlargement?
Gingival (Gum) enlargement, also known as gingival hyperplasia or hypertrophy, is an abnormal overgrowth of gingival tissues.
How would you describe poor dentition?
Inadequate dentition (tooth loss) is defined as fewer than 21 teeth. Inadequate dentition means that a person is unlikely to have enough teeth that have a partner on the opposite jaw to be able to chew properly.
What does Anodontia mean?
Anodontia is a genetic disorder defined as the absence of all teeth. It usually occurs as part of a syndrome that includes other abnormalities. Also rare but more common than anodontia are hypodontia and oligodontia. Hypodontia is genetic in origin and usually involves the absence of from 1 to 5 teeth.
What does Edentulism mean?
Edentulism: Without teeth. Complete loss of all natural teeth can substantially reduce quality of life, self-image, and daily functioning.
What is a submucous cleft palate?
A submucous cleft palate (SMCP) results from a lack of normal fusion of the muscles within the soft palate as the baby is developing in utero. It occurs in about 1 in 1,200 children. There is no single cause of SMCP, but current research suggests a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Is cleft palate a disorder?
Cleft lip and cleft palate are birth defects that occur when a baby's lip or mouth do not form properly during pregnancy. Together, these birth defects commonly are called “orofacial clefts”.
What is the ICD-10 code for Micrognathia?
The ICD-10 code for “micrognathia” is Q75.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
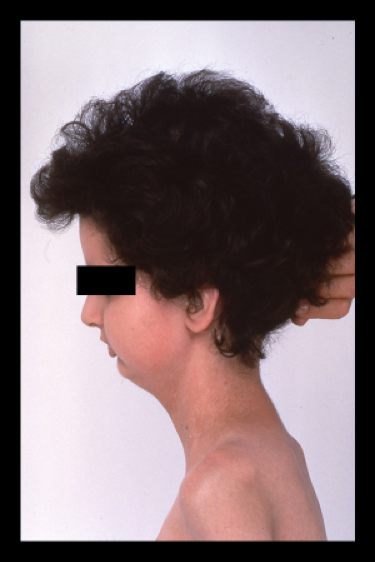
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'M26.02 - Maxillary hypoplasia'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code M26.02. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 524.03 was previously used, M26.02 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for prostate pain
- 2. icd 10 code for embolism and thrombosis
- 3. icd-10 code for traumatic brain injury sequelae
- 4. icd 10 code for sepsis with multilobar pneumonia
- 5. icd 10 code for cholecystectomy wound
- 6. icd 10 code for multidrug resistant organism pseudomonas sepsis
- 7. icd 10 code for pain sec to fiaching
- 8. icd 10 code for acute cystitis due to e. coli
- 9. icd 10 cm code for lab abnormalities
- 10. icd 10 cm code for cardiac stening