What is the ICD 10 code for ischemic heart disease?
Demand ischemia Demand ischemia, reported with ICD-10-CM code I24.8 (other forms of acute ischemic heart disease), refers to the mismatch between myocardial oxygen supply and demand, which is evidenced by the release of cardiac troponin.
What is the ICD 10 code for myocardial infarction type 2?
Myocardial infarction type 2 1 I21.A1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I21.A1 became effective on October 1, 2018. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I21.A1 - other international versions of ICD-10 I21.A1 may differ.
What is the code for mi due to demand ischemia?
When you look up the code I24.A1 for a Type 2 MI, the inclusions under the main term include MI due to demand ischemia, and also MI secondary to ischemic imbalance. There’s also a “code first” note for the underlying cause if known, and a direction to read the Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, section I.C.9.e5.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute myocardial injury?
Chronic myocardial injury, acute myocardial injury without accompanying evidence of acute myocardial ischemia, or myocardial injury not otherwise specified would be reported with ICD-10-CM code I51.89 (other ill-defined heart diseases) for a nontraumatic myocardial injury, according to Coding Clinic, Second Quarter 2019, p.
What is the ICD 10 code for demand ischemia?
Demand ischemia, reported with ICD-10-CM code I24. 8 (other forms of acute ischemic heart disease), refers to the mismatch between myocardial oxygen supply and demand, which is evidenced by the release of cardiac troponin.
What is the ICD 10 code for type 2 demand ischemia?
When you look up the code I24. A1 for a Type 2 MI, the inclusions under the main term include MI due to demand ischemia, and also MI secondary to ischemic imbalance.
Is demand ischemia the same as type 2 MI?
Supply/demand ischemia can be either “demand ischemia” (no infarction) or “Type 2 MI” (infarction due to supply/demand mismatch). Because the troponins were within the normal range, this would not be classified as a Type 2 myocardial infarction.
How do you code demand ischemia?
Q: How would you code elevated troponin due to demand ischemia? A: I would code I24. 8 (other forms of acute ischemic heart disease). Per the Alphabetic Index, reference Ischemia, demand, I24.
What is a type 2 myocardial infarction?
Type 2 myocardial infarction (MI) is defined by a rise and fall of cardiac biomarkers and evidence of ischemia without unstable coronary artery disease (CAD), due to a mismatch in myocardial oxygen supply and demand. Myocardial injury is similar but does not meet clinical criteria for MI.
What is the ICD-10 code for ischemic heart disease?
Code I25* is the diagnosis code used for Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease, also known as Coronary artery disease (CAD). It is a is a group of diseases that includes: stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden coronary death.
What are the 4 types of myocardial infarction?
A heart attack is also known as a myocardial infarction....The three types of heart attacks are:ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)coronary spasm, or unstable angina.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 MI?
Type 1 MI is a primary coronary arterial event attributable to atherothrombotic plaque rupture or erosion. Type 2 MI occurs secondary to an acute imbalance in myocardial oxygen supply and demand without atherothrombosis.
What is the difference between myocardial injury and myocardial infarction?
Specifically, myocardial injury is defined by at least 1 cardiac troponin concentration above the 99th percentile upper reference limit. Myocardial infarction is a form of myocardial injury but requires clinical evidence of acute myocardial ischemia.
What is myocardial ischemia?
Myocardial ischemia occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium) is obstructed by a partial or complete blockage of a coronary artery by a buildup of plaques (atherosclerosis). If the plaques rupture, you can have a heart attack (myocardial infarction).
What is supply/demand mismatch?
The term supply-demand mismatch usually refers to type 2 myocardial infarctions (T2MI) in which cell death results from an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand.
What ischemia means?
Ischemia is a condition in which the blood flow (and thus oxygen) is restricted or reduced in a part of the body. Cardiac ischemia is the name for decreased blood flow and oxygen to the heart muscle.
What is the ICD-10 code for a nontraumatic myocardial injury?
Chronic myocardial injury, acute myocardial injury without accompanying evidence of acute myocardial ischemia, or myocardial injury not otherwise specified would be reported with ICD-10-CM code I51.89 (other ill-defined heart diseases) for a nontraumatic myocardial injury, according to Coding Clinic, Second Quarter 2019, p. 5.
What is myocardial injury?
At the most basic level, myocardial injury refers to injury of the muscle cells of the heart. Injured heart muscle cells leak enzymes, namely cardiac troponin. A myocardial injury is defined as cardiac troponins measured at above the 99th percentile of the upper reference limit.
What is the ICD-10 code for ischemia?
Demand ischemia, reported with ICD-10-CM code I24.8 (other forms of acute ischemic heart disease), refers to the mismatch between myocardial oxygen supply and demand, which is evidenced by the release of cardiac troponin.
Is myocardial ischemia the same as myocardial injury?
While “myocardial ischemia” is a familiar term to CDI professionals and inpatient coders, the term “myocardial injury” does not share the same widespread recognition. Taking the time to review the clinical criteria and reporting for myocardial injuries will help inpatient coders accurately report these diagnoses.
Can myocardial injury be attributed to oxygen supply/demand mismatch?
Furthermore, one must look at the clinical situation to determine if the myocard ial injury could be attributed to an oxygen supply/demand mismatch. If so, then it would be appropriate to query whether the myocardial injury could be further specified as demand ischemia. If neither an acute myocardial infarction nor demand ischemia are appropriate, then one is simply left with a broken heart.
Is myocardial injury chronic or acute?
Myocardial injury can be acute or chronic in nature. In an acute injury, one will see a pattern of rising and falling elevated cardiac troponin levels, as opposed to a chronic injury where the cardiac troponin levels would be elevated but would not demonstrate the rising/falling pattern of an acute injury.
Can myocardial injury be seen with other conditions?
Chronic myocardial injury can be seen with other diagnoses such as chronic ki dney disease and congestive heart failure. Acute myocardial injury can be seen in many situations, including atrial fibrillation, sepsis, and hypovolemia.
What is the code for myocardial infarction?
Codes. I21 Acute myocardial infarction.
What is a myocardial disorder?
A disorder characterized by gross necrosis of the myocardium; this is due to an interruption of blood supply to the area.
What causes a heart muscle to die?
A blockage that is not treated within a few hours causes the affected heart muscle to die. Gross necrosis of the myocardium, as a result of interruption of the blood supply to the area, as in coronary thrombosis. Gross necrosis of the myocardium, as a result of interruption of the blood supply to the area.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What does a type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here". A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I21) and the excluded code together.
What is the default for acute myocardial infarction?
Acute myocardial infarction, unspecified, is the default for unspecified acute myocardial infarction or unspecified type.
What is the code for sepsis?
If the type of infection or causal organism is not further specified, assign code A41.9, Sepsis, unspecified organism.
What does type 2 excludes mean?
A type 2 Excludes note represents "Not included here." An excludes2
What does "excluded" mean in a code?
It means "NOT CODED HERE!" An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. If two conditions are not related to one another, it is possible to report both codes despite the presence of an Exclude note 1. Ex: Mental disorder (F01-F99) cannot be assigned with the R40-R46 codes but if dizziness (R42) is not component if mental health condition then we can code it separately.
How long does it take for an AMI to change?
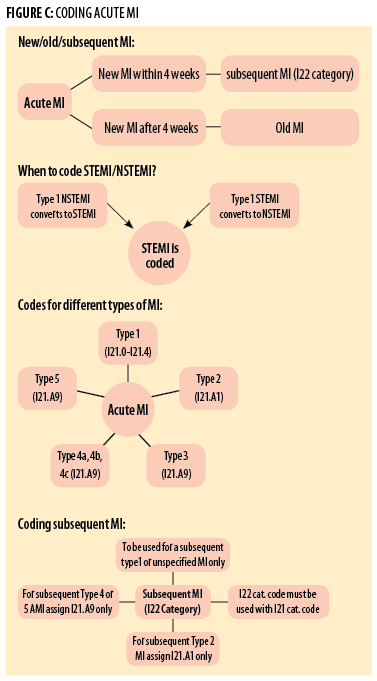
When a patient who has suffered a type 1 or unspecified AMI has a new AMI within the 4 week time frame of the initial AMI.
What is asymptomatic HIV?
Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is applied when the patient is HIV positive and does not have any documented symptoms of an HIV related illness. What is the code?
Which is sequenced first or second?
the condition or nature of the sequela is sequenced first. The sequela code is sequenced second.
What is type 1 MI?
Type 1 MI is myocardial necrosis, or cell death, caused by an anatomic blockage of blood flow for a prolonged period of time. This is usually due to atherosclerotic plaque and rupture or thrombosis, causing mechanical coronary artery obstruction. Type 2 MI is also cell death, but in a non-anatomic distribution due to generalized hypoperfusion, ...
What causes Type 2 MI?
There is always an underlying condition or disease process that causes the Type 2 MI. Ischemia means insufficient blood perfusion, and prolonged ischemia leads to infarction, i.e., cell death. When cells die and break down, they release their contents, including troponin, a heart-muscle protein.
Can a second MI be a type 1?
A second Type 1 MI can either be reinfarction in the same anatomic distribution, as an extension of the first MI, or a patient can have another Type 1 MI in a different vessel , with a different area of the heart being affected. Treatment of myocardial infarction has always been informed by the desire to prevent death, reinfarction, ...
Why should we document and code conditions?
The reasons we should be documenting and coding conditions is for communicating with other clinicians, recognizing clinical significance and prognostication, and receiving appropriate compensation for utilization of resources. The implication that a Type 2 MI is different than a Type 1 MI and the new guidelines reflect this.
Who is Erica Remer?
She was a physician advisor of a large multi-hospital system for four years before transitioning to independent consulting in July 2016. Her passion is educating CDI specialists, coders, and healthcare providers with engaging, case-based presentations on documentation, CDI, and denials management topics. She has written numerous articles and serves as the co-host of Talk Ten Tuesdays, a weekly national podcast. Dr. Remer is a member of the ICD10monitor editorial board, a former member of the ACDIS Advisory Board, and the board of directors of the American College of Physician Advisors.
Is a type 2 MI a sequitur?
It is a non sequitur to have a subsequent Type 2 MI. Type 2 MI is related to flogging a heart on the basis of some other condition, not a direct reflection of the heart’s intrinsic health (although Type 2 MIs are more likely to occur in older patients with underlying generalized heart disease), and it is limited to the index admission. If one survives septic shock with a Type 2 MI, one might follow up with a cardiologist to rule out coronary artery and heart disease – which might respond to chronic treatment, but not for long-term treatment of the Type 2 MI, per se.
Is type 2 MI the same as type 1 MI?
However, Type 2 MI does not have the same course, prognosis, or treatment as Type 1 MI. Once the underlying condition is brought under control, the Type 2 MI resolves. Healthcare providers were gun-shy about calling out Type 2 MIs initially because the inability to code and separate out the condition caused them to fall out of the AMI Core Measures. Most facilities bypassed this problem by using “not indicated due to Type 2 MI” as an exclusion in their order set.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for klebsiella
- 2. icd 10 code for right middle finger extensor tendon laceration
- 3. icd 10 code for displaced subtrochanteric left femur fracture
- 4. icd 10 code for post covid 19 pneumonia
- 5. icd 10 code for depressio
- 6. icd 10 code for wenckebach
- 7. what is correct icd 10 code for right upper lobe neuroendocrine carcinoid tumor
- 8. icd 10 code for menstruation pain
- 9. icd 10 cm code for drowning afer fall in bath tub
- 10. icd 10 code for tick bites