What is the ICD 10 code for Olecranon bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis, left elbow. M70.22 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M70.22 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M70.22 - other international versions of ICD-10 M70.22 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for lumbar puncture?
M70.22 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M70.22 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 for fracture of olecran pro w/o intraarticular extension?
Short description: Fracture of olecran pro w/o intraarticular extension of ulna The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM S52.02 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S52.02 - other international versions of ICD-10 S52.02 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for urinalysis?
M70.22 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M70.22 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M70.22 - other international versions of ICD-10 M70.22 may differ.

What is diagnosis code M77 8?
ICD-10 code: M77. 8 Other enthesopathies, not elsewhere classified.
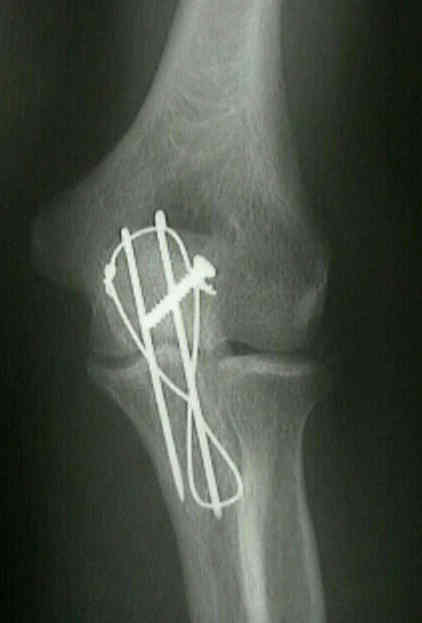
What is the ICD-10 code for right olecranon fracture?
ICD-10 Code for Displaced fracture of olecranon process without intraarticular extension of right ulna, initial encounter for closed fracture- S52. 021A- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for olecranon bursitis?
ICD-10 Code for Olecranon bursitis, right elbow- M70. 21- Codify by AAPC.
What is the meaning of Osteophytosis?
Bone spurs, or osteophytes, are smooth, bony growths, usually near joints. They develop over time in patients with arthritis or joint damage. The feet, hands, knees and spine often develop bone spurs.
What is olecranon fracture?
An olecranon fracture is a break in the “pointy bone” of your elbow that sticks out when you bend your arm, which is actually the end of the ulna. This type of fracture is common and usually occurs in isolation (there are no other injuries) but can also be a part of a more complex elbow injury.
What is the left olecranon?
An olecranon (oh-LEK-rah-nun) fracture is a break in the bony "tip" of the elbow. This pointy segment of bone is part of the ulna, one of the three bones that come together to form the elbow joint. The olecranon is located under the skin of the elbow, without much protection from muscles or other soft tissues.
What is olecranon bursa?
Elbow bursitis occurs in the olecranon bursa, a thin, fluid-filled sac that is located at the boney tip of the elbow (the olecranon). There are many bursae located throughout the body that act as cushions between bones and soft tissues, such as skin.
What is the CPT code for olecranon bursa excision?
24105Files related to Excision, olecranon bursa (24105) Synovectomy CPT Codes.
How does olecranon bursitis occur?
A common cause of olecranon bursitis is trauma, such as falling on the elbow or hitting the elbow on a hard surface. This can occur during any sporting event when someone has a fall on their elbow and has been described often in football, hockey, basketball, and volleyball players.
Is osteophytes the same as osteoarthritis?
Bone spurs (osteophytes) often form where bones meet each other — in your joints. They can also form on the bones of your spine. The main cause of bone spurs is the joint damage associated with osteoarthritis. Most bone spurs cause no symptoms and can go undetected for years.
Is an osteophyte and exostosis the same thing?
An exostosis is an extra growth of bone that extends outward from an existing bone. Common types of exostoses include bone spurs, which are bony growths also known as osteophytes. An exostosis can occur on any bone, but is often found in the feet, hip region, or ear canal.
What is a Syndesmophyte?
Definition. Syndesmophytes: osseous excrescences or bony outgrowths from the spinal ligaments as they attach to adjacent vertebral bodies.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
Can S52.02 be used for reimbursement?
S52.02 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for abnormal urinary ph
- 2. is there a v code in the icd 10 for melancholia
- 3. icd 10 code for meibomian gland dysfunction bilateral
- 4. icd 10 code for muscle dystonia
- 5. icd 10 code for 2nd degree heart block
- 6. icd 10 diagnosis code for bladder cancer
- 7. icd 10 cm code for swollen tonsils.
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for bird headed dwarf
- 9. icd 10 dx code for magnessium, serum.
- 10. icd 10 cm code for cerebral atrophy