What is the diagnosis code for ovarian cancer?
Oct 01, 2021 · Malignant neoplasm of unspecified ovary 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code C56.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C56.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Screening for ovarian cancer; Screening for ovarian cancer done. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z12.73. Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of ovary. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt. ICD …
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
C56- Malignant neoplasm of ovary › 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C56 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C56 Malignant neoplasm of ovary 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code C56 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is the CPT code for ovarian cancer?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z15.02 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z15.02 Genetic susceptibility to malignant neoplasm of ovary 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Z15.02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
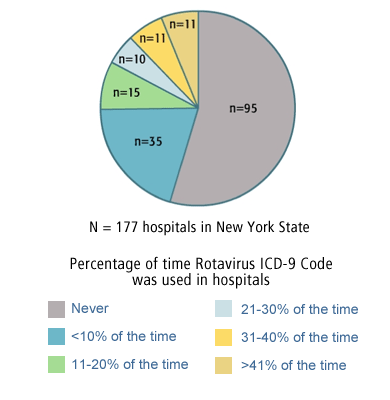
What is the code for ovarian cancer?
The codes for ovarian cancer procedures are in the 58943-58958 for open procedures.Mar 15, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for metastatic ovarian cancer?
Secondary malignant neoplasm of ovary The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C79. 6 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C79. 6 - other international versions of ICD-10 C79.
What is C56?
C56: Malignant neoplasm of ovary.
What are the cancer ICD-10 codes?
Chapter II Neoplasms (C00-D48)C00-C97 Malignant neoplasms. C00-C75 Malignant neoplasms, stated or presumed to be primary, of specified sites, except of lymphoid, haematopoietic and related tissue. ... D00-D09 In situ neoplasms.D10-D36 Benign neoplasms.D37-D48 Neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behaviour.
What is the ICD-10 code for ovarian cyst?
N83.2ICD-10 | Other and unspecified ovarian cysts (N83. 2)
What are inclusion notes located in ICD-10-CM?
“Inclusions and exclusions,” are terms used in ICD-10-CM code assignment and can be found in the Alphabetical Index and/or Tabular Lists within the code set.Sep 3, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code for ovarian mass?
Noninflammatory disorder of ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament, unspecified. N83. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N83.
What is the ICD-10 code for chemotherapy?
11.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
I25. 10 - Atherosclerotic Heart Disease of Native Coronary Artery Without Angina Pectoris [Internet]. In: ICD-10-CM. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the National Center for Health Statistics; 2018.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for primary malignant thymoma?
C372022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C37: Malignant neoplasm of thymus.
What is the ICD 9 code for cancer?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 199.1 : Other malignant neoplasm without specification of site.
How do you know cancer has metastasized?
Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:pain and fractures, when cancer has spread to the bone.headache, seizures, or dizziness, when cancer has spread to the brain.shortness of breath, when cancer has spread to the lung.jaundice or swelling in the belly, when cancer has spread to the liver.Nov 10, 2020
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
What is the name of the cancer that forms in the ovary?
Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial carcinomas (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface of the ovary) or malignant germ cell tumors (cancer that begins in egg cells).
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified ( C25.9 ). A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm involving the ovary.
Is ovarian cancer common?
They produce a woman's eggs and female hormones. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond.cancer of the ova ry is not common, but it causes more deaths than other female reproductive cancers. The sooner ovarian cancer is found and treated, the better your chance for recovery.
What is ovarian cancer?
by OSI. Ovarian cancer, considered as the tenth most common cancer among women in the United States, refers to any cancerous growth that appears in the ovary (reproductive glands). It occurs when abnormal cells in the ovary begin to multiply out of control and form a tumor. Most ovarian cancers develop initially in the epithelium, ...
What is the median age for ovarian cancer?
As per estimates from the Ovarian Cancer Research Fund Alliance, the median age of a diagnosis is 63 years. The risk of developing this condition could be higher if you have a strong family history of ovarian cancer or if you carry certain genetic mutations.
How early can you detect ovarian cancer?
Diagnosis and Treatment. Ovarian cancer can be hard to detect in the early stages as most signs and symptoms do not appear until the disease has progressed fully. Early and timely diagnosis helps in better treatment. It is estimated that early diagnosis of ovarian cancer (in the primary stages) leads to 94 percent chance ...
Where does ovarian cancer develop?
Most ovarian cancers develop initially in the epithelium, or outer lining of the ovary and often come with symptoms such as – abdominal bloating and pain, weight loss, abnormal fullness after eating, frequent urination, difficulty eating, discomfort in the pelvis area and changes in bowel habits, such as constipation.
What is the treatment for cancer?
The type of treatment for this cancer may depend on how far the cancer has spread. Treatment methods for this condition may include – chemotherapy, radi ation, hormone therapy, target ed therapy and surgery to stage ...
How long does ovarian cancer last?
It is estimated that early diagnosis of ovarian cancer (in the primary stages) leads to 94 percent chance of survival for at least 5 years. A woman’s lifetime risk for developing ovarian cancer is 1 in 75. There is no specific routine diagnostic screening test available for detecting ovarian cancer. However, physicians may recommend ...
Can ovarian cancer be reversed?
With appropriate and timely treatment, the serious complications caused by ovarian cancer can be reversed. It is important for physicians to instruct their medical coding outsourcing service providers or clinical staff to be specific and document their diagnosis and medical procedures with accurate medical codes.
What is ovarian cancer?
Vol. 25 No. 2 P. 26. Ovarian cancer is a type of gynecological cancer that origina tes in the ovaries. Unfortunately, it may not be diagnosed until it has progressed to a more advanced stage because it rarely causes symptoms in the early stages.
Where does ovarian cancer begin?
The cell where the cancer begins determines the type of ovarian cancer and may include the following: • Epithelial tumor: begins in the thin layer of tissue that covers the outside of the ovaries; • Germ cell tumor: begins in the egg-producing cells and occurs more commonly in younger women; and.
What is the code for a malignant neoplasm?
Assign first the appropriate code from category T86.-, Complications of transplanted organs and tissue, followed by code C80.2, Malignant neoplasm associated with transplanted organ. Use an additional code for the specific malignancy.
What is the Z85 code for a primary malignancy?
When a primary malignancy has been previously excised or eradicated from its site and there is no further treatment directed to that site and there is no evidence of any existing primary malignancy at that site, a code from category Z85, Personal history of malignant neoplasm, should be used to indicate the former site of the malignancy. Any mention of extension, invasion, or metastasis to another site is coded as a secondary malignant neoplasm to that site. The secondary site may be the principal or first-listed with the Z85 code used as a secondary code.
What is the ICd-10 guidelines?
These guidelines, developed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services ( CMS) and the National Center for Health Statistics ( NCHS) are a set of rules developed to assist medical coders in assigning the appropriate codes. The guidelines are based on the coding and sequencing instructions from the Tabular List and the Alphabetic Index in ICD-10-CM.
When a patient is admitted because of a primary neoplasm with metastasis and treatment is
When a patient is admitted because of a primary neoplasm with metastasis and treatment is directed toward the secondary site only , the secondary neoplasm is designated as the principal diagnosis even though the primary malignancy is still present .
What is Chapter 2 of the ICD-10-CM?
Chapter 2 of the ICD-10-CM contains the codes for most benign and all malignant neoplasms. Certain benign neoplasms , such as prostatic adenomas, may be found in the specific body system chapters. To properly code a neoplasm, it is necessary to determine from the record if the neoplasm is benign, in-situ, malignant, or of uncertain histologic behavior. If malignant, any secondary ( metastatic) sites should also be determined.
When a pregnant woman has a malignant neoplasm, should a code from subcatego
When a pregnant woman has a malignant neoplasm, a code from subcategory O9A.1 -, malignant neoplasm complicating pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium, should be sequenced first, followed by the appropriate code from Chapter 2 to indicate the type of neoplasm. Encounter for complication associated with a neoplasm.
Can a patient have more than one malignant tumor?
These tumors may represent different primaries or metastatic disease, depending on the site. Should the documentation be unclear, the provider should be queried as to the status of each tumor so that the correct codes can be assigned.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for chronic migraine with status migrainosus
- 2. icd 10 code for low back injury
- 3. icd 10 code for pseudomembranous colitis
- 4. icd 10 code for pressure ulcer right buttock unstageable
- 5. icd 10 code for right groin cellulitis
- 6. icd 10 code for coronary artery fistula
- 7. icd 10 cm code for stingray sting
- 8. icd-10 code for learning disability
- 9. icd 10 cm code for s/p hernia repair
- 10. icd-10 code for essential (primary) hypertension