Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland. D35.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM D35.2 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for pituitary macroadenoma?
Oct 01, 2021 · Pituitary microadenoma Prolactinoma Clinical Information A neoplasm without metastatic potential arising from the anterior or the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The vast majority are adenomas. ICD-10-CM D35.2 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 643 Endocrine disorders with mcc 644 Endocrine disorders with cc
How to pronounce pituitary adenoma?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T38.812 Poisoning by anterior pituitary [adenohypophyseal] hormones, intentional self-harm 2016 2017 2018 2019 …
What is the diagnosis code for pituitary tumor?
Oct 01, 2019 · What is the ICD 10 code for pituitary adenoma? Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland D35. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM D35. 2 became effective on October 1, 2019. Click to see full answer.
What is the prognosis for a pituitary tumor?
Oct 01, 2019 · Furthermore, what is the ICD 10 code for History of pituitary tumor? Z86. 011 is a billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of personal history of benign neoplasm of the brain. The code is valid for the year 2020 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code Z86.
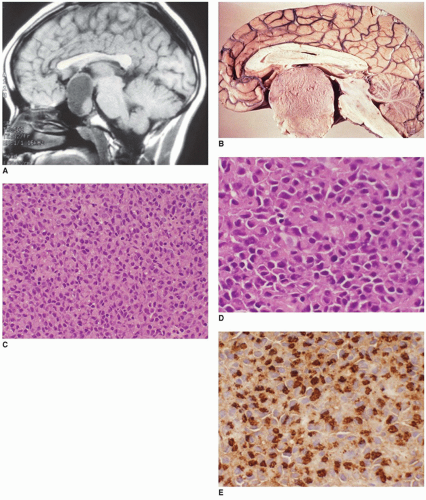
What is the ICD 10 code for pituitary adenoma?
D35.2D35. 2 - Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland | ICD-10-CM.
What are the types of pituitary adenomas?
Types of Pituitary TumorsNonfunctional Adenomas. At least half of pituitary adenomas are nonfunctional, meaning they do not cause levels of pituitary hormones in your body to rise. ... Functional Adenomas. ... Pituitary Carcinoma or Cancer. ... Hyperprolactinemia. ... Cushing's Disease. ... Acromegaly. ... Hypopituitarism. ... Secondary Hyperthyroidism.
What is diagnosis code D35 2?
2: Benign neoplasm: Pituitary gland.
What is the most common pituitary adenoma?
Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas are the most common type of pituitary tumor, accounting for approximately 30 percent of all pituitary tumors.
How is pituitary adenoma diagnosed?
An imaging test, such as an MRI or CT scan*, can show a growth on the pituitary. These tests can confirm the diagnosis of a pituitary adenoma. If you are having problems with your sight, the doctor might also have you take a visual field test to check your eye function.Mar 22, 2017
What causes adenoma of the pituitary?
Pituitary microadenomas develop when DNA mutations cause cells in the pituitary gland grow and divide uncontrollably. Experts are not entirely sure what causes these genetic mutations to happen. A small percentage of pituitary tumors run in families, but most cases do not have any obvious hereditary factor.
What is Gonadotroph adenoma?
Gonadotroph adenomas are adenomas that secrete the gonadotropins FSH and LH. Clinically active gonadotroph adenomas are regarded as uncommon tumors; unlike other secreting tumors, gonadotroph adenomas do not usually cause a clinical syndrome related to hormone overproduction.
What is the pituitary glands?
Your pituitary gland is a small, pea-sized endocrine gland located at the base of your brain below your hypothalamus. It releases several important hormones and controls the function of many other endocrine system glands.Apr 4, 2022
What is R79 89?
Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistryICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Who manages a pituitary adenoma?
Pituitary tumors often require care from a team of doctors. Doctors on your team may include: Neurosurgeon: a doctor who uses surgery to treat brain and pituitary tumors. Endocrinologist: a doctor who treats diseases in glands that make hormones.
What is meant by adenoma?
Listen to pronunciation. (A-deh-NOH-muh) A tumor that is not cancer. It starts in gland-like cells of the epithelial tissue (thin layer of tissue that covers organs, glands, and other structures within the body).
Which of the following may occur with a pituitary adenoma?
Pituitary adenomas may cause problems because of hormonal hypersecretion, pituitary hormonal failure, vision loss, headaches and/or bleeding into the tumor (apoplexy).Feb 24, 2022
What are the symptoms of pituitary adenoma?
What is the ICD 10 code for pituitary adenoma? 1 Headaches. 2 Vision problems. 3 Unexplained tiredness. 4 Mood changes. 5 Irritability. 6 Changes in menstrual cycles in women. 7 Erectile dysfunction, which is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection in men and is caused by hormone changes. 8 Infertility, which is the inability to have children.
What are the causes of erection problems?
Mood changes. Irritability. Changes in menstrual cycles in women. Erectile dysfunction, which is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection in men and is caused by hormone changes. Infertility, which is the inability to have children.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for kidney cyst
- 2. icd 9 code for tracheostomy with complications
- 3. icd 9 code for tinniyud``
- 4. icd 10 code for gilbert's syndrome
- 5. icd 10 code for high risk of breast cancer
- 6. icd 9 code for history of oral surgery
- 7. icd 10 code for left distal radius comminuted fracture
- 8. icd 10 code for hx tbi
- 9. icd 1 cm code for fracture left patella
- 10. icd 10 code for progressive multiple sclerosis