What is the life expectancy for decompensated cirrhosis?
The score for cirrhosis determines the types, such as:
- Class A is relatively mild liver cirrhosis. Those with class A and a 5-6 score usually have a life expectancy predicted at 15-20 years.
- Class B is still considered mild liver cirrhosis. Those in this class with a point score of 7-9 tend to have a life expectancy between 6-10 years.
- Class C is the most severe class of liver cirrhosis. ...
Can primary biliary cirrhosis be cured?
The only "cure" for primary biliary cirrhosis is liver transplant, but it is only considered as a treatment option if other less aggressive treatments have failed and the patient develops liver failure. Ursodiol (Actigal) or ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is the first line treatment for PBC.
What is the ICD 10 code for history of cirrhosis?
Unspecified cirrhosis of liver
- K74.60 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K74.60 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K74.60 - other international versions of ICD-10 K74.60 may differ.
How much alcohol can you drink with cirrhosis?
The threshold 2 of high risk for alcoholic hepatitis is generally considered 3-4 drinks a day over an extended period of time. People who develop cirrhosis often drink more than 6 servings of alcohol per day. Can someone with liver disease drink alcohol?
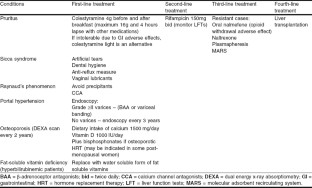
What is primary biliary cirrhosis called now?
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease resulting from progressive destruction of the bile ducts in the liver – called the intrahepatic bile ducts.
What is the ICD 10 code for liver cirrhosis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Unspecified cirrhosis of liver K74. 60.
What is biliary cirrhosis unspecified?
Cirrhosis of the liver caused either by destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts (primary biliary cirrhosis) or blockage of the extrahepatic bile ducts (secondary biliary cirrhosis).
Is primary biliary cirrhosis the same as autoimmune hepatitis?
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) are main autoimmune liver diseases. The term overlap syndrome describes the coexistence of two autoimmune liver diseases in the same patient, and AIH/PBC overlap is the most common form 1–3.
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic liver disease?
ICD-10-CM Code for Liver disease, unspecified K76. 9.
What is the ICD 10 code for liver mass?
There are four different ICD-10 diagnosis codes for the four conditions listed above. For example, a liver lesion is coded as K76. 9; a liver mass is coded as R16. 0, a liver tumor is coded as D49.
Is primary biliary cirrhosis the same as primary sclerosing cholangitis?
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) are two major types of chronic cholestatic liver disease. Each disorder has distinguishing features and variable progression, but both may ultimately result in cirrhosis and hepatic failure.
Is primary biliary cirrhosis and primary biliary cholangitis the same thing?
Primary biliary cholangitis, previously called primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic disease in which the bile ducts in your liver are slowly destroyed.
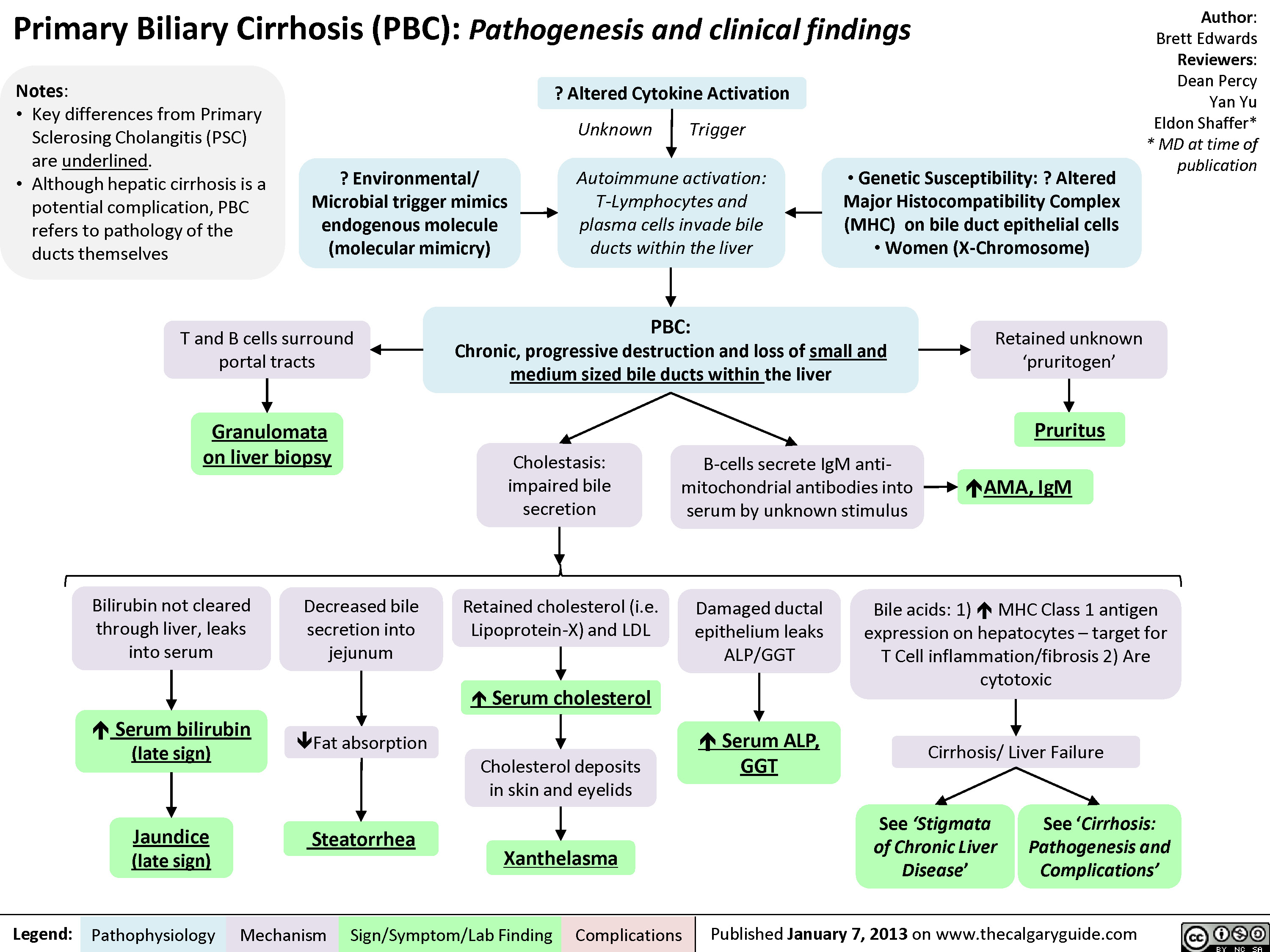
What causes primary biliary cirrhosis?
Primary biliary cirrhosis is considered an autoimmune disease, which means it is caused by the body's own immune system mistakenly attacking itself. Most patients do not experience any symptoms when diagnosed. But as damage to the liver becomes more severe, serious health complications can emerge.
How is primary biliary cirrhosis diagnosed?
PBC can usually be diagnosed just using blood tests. Once PBC is diagnosed, you'll also need an ultrasound scan to help rule out other problems with your bile ducts and assess your liver. A liver biopsy is occasionally recommended to assess your liver and help doctors decide on the best treatment.
Can you reverse primary biliary cirrhosis?
There's no cure for primary biliary cholangitis, but medications are available to help slow the progression of the disease and prevent complications.
What is the life expectancy of someone with primary biliary cirrhosis?
People with PBC may not develop any symptoms for up to 10 years. And if a person has an earlier stage of PBC (stage 1 or 2), their life expectancy is normal. If a person with PBC has advanced symptoms as seen in an advanced stage, the average life expectancy is about 10-15 years . However, everyone is different.
What is biliary cirrhosis?
Biliary cirrhosis. Clinical Information. Cirrhosis of the liver caused either by destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts ( primary biliary cirrhosis) or blockage of the extrahepatic bile ducts (secondary biliary cirrhosis). Fibrosis of the hepatic parenchyma due to obstruction of bile flow ...
What is a fibrosis of the hepatic parenchyma?
Fibrosis of the hepatic parenchyma due to obstruction of bile flow (cholestasis) in the intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile ducts (bile ducts, intrahepatic; bile ducts, extrahepatic). Primary biliary cirrhosis involves the destruction of small intra-hepatic bile ducts and bile secretion.
What is the ICd code for biliary cirrhosis?
The ICD code K743 is used to code Primary biliary cirrhosis. Primary biliary cirrhosis, also known as primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It is marked by slow progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, with the intralobular ducts and the Canals of Hering (intrahepatic ductules) ...
What happens when bile ducts are damaged?
This can lead to scarring, fibrosis and cirrhosis. Micrograph of PBC showing bile duct inflammation and injury. H&E stain.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for diabetic foot wound
- 2. icd 10 code for left sided diverticulitis
- 3. icd 10 code for pelvic mass unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for elevated androgens
- 5. icd 10 code for history iron deficiency anemia
- 6. icd 10 code for kidney cyst pain
- 7. icd 10 code for right anterior cerebral artery embolism
- 8. icd 10 e code for fall from bicycle
- 9. icd 10 code for ss recurrent bacteremia
- 10. icd 10 code for migrainosus