What triggers reactive airway disease?
Reactive airway disease, like asthma, occurs most often after you've had an infection.It's caused by some irritant that triggers the airways to overreact and swell or narrow. Some causes or irritants may include: pet hair or dander.
What are the symptoms of reactive airway disease?
They indicate that the airways have been irritated and include:
- coughing
- wheezing
- shortness of breath
- breathing difficulties
- mucus in the airways
- swelling of the airway lining
- hypersensitive airways
What is the difference between reactive airway disease and asthma?
Reactive airway illness is a one-time event. As a result, it is typically seen as a sort of acute condition that is not taken as seriously as Asthma. The difference between Asthma and Reactive Airway Disease is that Corticosteroids, inhalers, and bronchodilators can be used to treat the condition of Asthma regularly.
Is reactive airway disease the same as asthma?
The symptoms of reactive airway disease are similar to those of asthma. These symptoms may include: Reactive airway disease, like asthma, occurs most often after you’ve had an infection. It’s caused by some irritant that triggers the airways to overreact and swell or narrow. Some causes or irritants may include:

What is reactive airway disease?
Reactive airway disease in children is a general term that doesn't indicate a specific diagnosis. It might be used to describe a history of coughing, wheezing or shortness of breath triggered by infection. These signs and symptoms might or might not be caused by asthma.
Is Reactive airway the same as asthma?
No, reactive airways disease is not the same as asthma. 2. Asthma is a form of reactive airways disease in that it exhibits hyperreactivity to substances like those mentioned above, but reactive airways disease as a phrase refers to other, less well-defined conditions.
Is reactive airway disease COPD?
Reactive airway disease is sometimes used to describe symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, reactive airway disease and COPD are not the same. COPD requires more involved treatment. It is a group of lung diseases that make it hard to breathe.
Is reactive airway disease a respiratory disease?
Reactive airway disease (RAD) is a term used to refer to respiratory conditions in which the bronchial tubes in the lungs overreact to an irritant, triggering wheezing and shortness of breath. These include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and certain bronchial infections.
Is bronchiolitis a reactive airway disease?
Kinds of Reactive Airway Diseases Some conditions that may fall under the RAD diagnosis include: Asthma. Bronchiolitis (virus that causes wheezing or coughing) Airway hyper responsiveness (quick narrowing of airways)
Can Covid cause reactive airway disease?
Overall, the findings show that disease of the small airways in the lungs is a potential long-lasting effect of COVID-19. Using a form of artificial intelligence known as supervised machine learning, the team was also able to quantify the amount of small airway disease.
Is obstructive airway disease the same as COPD?
Obstructive airway diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are among the most common noncommunicable diseases. Asthma often presents early in life; for many, it persists into adulthood and may precede COPD.
Is restrictive airway disease the same as COPD?
While both types can cause shortness of breath, obstructive lung diseases (such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder) cause more difficulty with exhaling air, while restrictive lung diseases (such as pulmonary fibrosis) can cause problems by restricting a person's ability to inhale air.
Is chronic obstructive airways disease the same as COPD?
Contents. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung conditions that cause breathing difficulties.
Is reactive airway disease a chronic condition?
Reactive airway disease is not the same as reactive airways dysfunction syndrome (RADS). Even though the symptoms are similar, the causes are different. RADS is caused by excessive exposure to some sort of corrosive gas, its fumes, or its vapors. RADS also usually occurs just one time and is not chronic.
Is reactive airway disease pneumonia?
Thus, the term “reactive airways disease” may be used as a nonspecific term in clinical contexts ranging from asthma, to wheezy bronchitis, to viral bronchiolitis, or even to pneumonia.
Is small airway disease the same as asthma?
The small airways of the lungs are commonly affected in pediatric and adult asthma. Small airways disease has been related to asthma control, severity, and risk of exacerbation. Diagnosis of small airways disease can be best made through evaluation of surgical lung specimens.
Why is asthma considered a reactive airway disease?
What is reactive airway disease? Reactive airway disease (RAD) is similar to asthma. RAD occurs when your bronchial tubes, which bring air into your lungs, overreact to an irritant, swell, and cause breathing problems.
Can you outgrow reactive airway disease?
Most often, what you are describing is called “Reactive Airway Disease” (RAD) and, yes, many babies and children will outgrow it.
Is reactive airway disease a chronic condition?
Reactive airway disease is not the same as reactive airways dysfunction syndrome (RADS). Even though the symptoms are similar, the causes are different. RADS is caused by excessive exposure to some sort of corrosive gas, its fumes, or its vapors. RADS also usually occurs just one time and is not chronic.
What is another name for asthma?
Asthma, also called bronchial asthma, is a disease that affects your lungs. It's a chronic (ongoing) condition, meaning it doesn't go away and needs ongoing medical management. Asthma affects more than 25 million people in the U.S. currently.
What is reactive airway disease?
Reactive airway disease is a general term for respiratory illnesses that are usually described by a family of diseases that shares an airway sensitivity to chemical, physical, or pharmacologic stimuli.
What are the complications of asthma?
Possible complications include: side effects from long-term use of some drugs which are used to stabilize severe asthma; signs and symptoms which interfere with work, restful sleep, or recreational activities; hospitalizations and emergency room visits for severe asthma attacks;
Does vapor help with asthma?
It has been used for thousands of years as a natural remedy for many different conditions , and inhaling its vapor can help people with breathing problems such as bronchitis (an infection which results from the inflammation of the lining of the lungs), RAD, or asthma.
Can asthma cause wheezing?
Both can cause wheezing, but asthma is ongoing, while RAD may occur only now and then. Children under the age of 5 are usually diagnosed with reactive airway disease as it can be difficult to come up with a precise diagnosis of an airway condition at such a young age. Even though it is generally experienced by kids, RAD can occur in adults too.
What is asthma characterized by?
It is characterized by spasmodic contraction of airway smooth muscle, wheezing, and dyspnea (dyspnea, paroxysmal). Asthma is a chronic disease that affects your airways. Your airways are tubes that carry air in and out of your lungs. If you have asthma, the inside walls of your airways become sore and swollen.
What is bronchial disease?
A chronic respiratory disease manifested as difficulty breathing due to the narrowing of bronchial passageways. A form of bronchial disorder with three distinct components: airway hyper-responsiveness (respiratory hypersensitivity), airway inflammation, and intermittent airway obstruction.
What are the symptoms of a bronchial infection?
Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, and rapid breathing. An attack may be brought on by pet hair, dust, smoke, pollen, mold, exercise, cold air, or stress. A chronic respiratory disease manifested as difficulty breathing due to the narrowing of bronchial passageways.
What happens when your airways are sore?
If you have asthma, the inside walls of your airways become sore and swollen. That makes them very sensitive, and they may react strongly to things that you are allergic to or find irritating. When your airways react, they get narrower and your lungs get less air.symptoms of asthma include. wheezing.
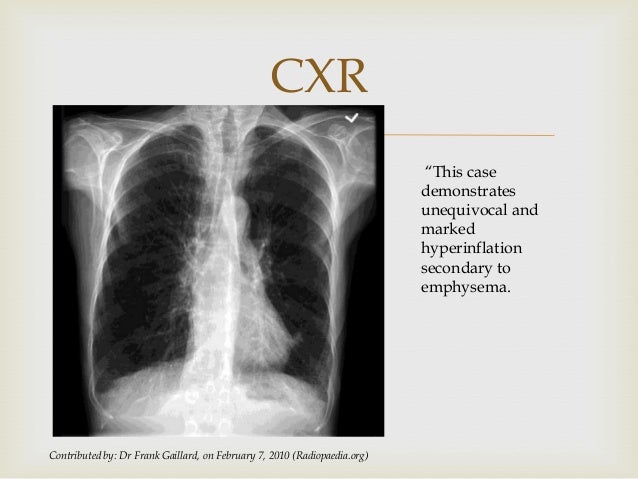
Statistics
Causes
- It develops within 24 hours after the inhalation of excessive amounts of non-allergen smoke, dust, and gas, leading to bronchial hyperreactivity. The chemical agents which are most commonly associated with reactive airway disease are: 1. nitrogen oxide; 2. toluene diisocyanate (a toxic and highly reactive organic compound); 3. inhaled chlorine. Som...
Risk Factors
- Possible risk factorsinclude: 1. lack of exclusive breastfeeding for less than 3 months; 2. having a family history of asthma or allergy; 3. exposure to irritants which can trigger an allergic response like pollen, dust, pets; 4. lung infection in the recent past; 5. excessive physical exercise; 6. weather changes; 7. smoking habit in the mother while she was pregnant; 8. a regular presence …
Symptoms
- The symptoms of reactive airway disease may include any of the following: 1. a runny nose; 2. fast heartbeat; 3. a cough; 4. trouble breathing; 5. wheezing.
Complications
- Possible complications include: 1. side effects from long-term use of some drugs which are used to stabilize severe asthma; 2. signs and symptoms which interfere with work, restful sleep, or recreational activities; 3. hospitalizations and emergency room visits for severe asthma attacks; 4. permanent narrowing of the bronchial tubes which affects how well you can breathe; 5. sick day…
When to Call The Doctor
- Contact your healthcare professional if: 1. your child’s wheezing gets worse; 2. your child has a fever; 3. your child coughs up dark brown, yellow, or bloody mucus.
Treatment
- Since RAD is mainly caused by stimuli or irritants, it would be helpful if the sufferer is situated in another location away from such materials or these irritants can be removed. Your doctor may recommend the following treatments:
Natural Treatments
- Eucalyptus Essential Oil<img loading="lazy" class="aligncenter size-full wp-image-5667" src="htt…
It has been used for thousands of years as a natural remedy for many different conditions, and inhaling its vapor can help people with breathing problems such as bronchitis (an infection which results from the inflammation of the lining of the lungs), RAD, or asthma. Note– place one to tw… - Evening Primrose Oil
Evening primrose oil is produced from the seeds of the flowers of a plant that is native to North America. This essential oil is rich in an essential fatty acid called gamma-linolenic acid, which is converted by the human body into anti-inflammatory substances.
Nutrition
- Kale
It has more vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid) per cup than a whole orange. According to research, ascorbic acid reduces muscle contraction in your airway passages. - Ginger<img loading="lazy" class="aligncenter size-full wp-image-5683" src="https://healthguiden…
According to research, ginger is strongly associated with an improvement in the RAD symptoms most likely since it decreases inflammation. In addition, ginger contains isoproterenol, acompound that is similar to a type of asthma medication.
Prognosis
- The outlook for individuals with RAD is good, particularly once a healthcare professional determines the irritants and makes a firm diagnosis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd-10-cm code for family hx heart disease
- 2. icd-10 code for benign lesion of bacl
- 3. icd 10 code for pregnancy complicated by depression
- 4. icd-10 code r 35.1 is for what
- 5. icd 10 code for scoliosis
- 6. 2021 icd 10 code for chf
- 7. icd 10 code for major depressive disorder recurrent unspecified
- 8. icd 10 code for bmi 27
- 9. icd 10 code for eed
- 10. icd-10 code for sinus bradycardia, borderline 1st degree a-v