Hypertrophy of salivary gland
- K11.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K11.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K11.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 K11.1 may differ.
How to reduce salivary gland swelling?
Method 2 of 3: Clearing the Blocked Salivary Duct at Home
- Drink a lot of water to keep the mouth hydrated. ...
- Take over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and swelling. If you’re experiencing intense pain from a blocked salivary gland, relieve your symptoms with an over-the-counter pain reliever.
- Suck on citrus fruits or hard candies to dislodge a stone. ...
- Massage the salivary gland with your fingers. ...
What is the prognosis for salivary gland cancer?
What are the symptoms of salivary gland cancer?
- For parotid cancers: Pain, sensory loss or difficulty open the jaw can occur.
- Probable cancer: rapid recent tumor enlargement, facial nerve weakness, deep tumor fixation and enlargement of the neck lymph node.
- Submandibular cancers usually present as a painless neck mass. ...
- Sublingual gland cancers usually present as a mass in the floor of the mouth.
Why is my parotid gland swollen?
- Tender, painful lump in your cheek
- Foul-tasting discharge from the duct into your mouth
- Fever, chills, and fatigue
- Difficulty fully opening your mouth, speaking, chewing, or swallowing
What is the survival rate for salivary cancer?
This means that, on average, about 69% of people diagnosed with cancer of the major salivary glands will survive for at least 5 years. Survival varies with each stage of salivary gland cancer. The grade of the salivary gland cancer has an effect on survival. High-grade tumours have a lower survival rate than low-grade tumours.
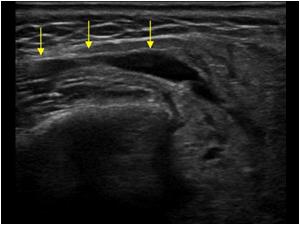
Is parotid a salivary gland?
The parotid glands are two salivary glands that sit just in front of the ears on each side of the face. Salivary glands produce saliva to aid in chewing and digesting food. There are many salivary glands in the lips, cheeks, mouth and throat.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute Parotitis?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K11. 21 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K11.
What is the medical term for salivary gland inflammation?
What You Need to Know. A salivary gland infection is also called sialadenitis and is caused by bacteria or viruses. A salivary stone or other blockage of the salivary gland duct can contribute to an acute infection. Chronic inflammation of a salivary gland can cause it to stop functioning.
What is parotid swelling?
Overview. Parotitis is a painful swelling of your parotid glands, which are salivary glands located between the ear and jaw. The most common cause is a virus, such as mumps, herpes, or Epstein-Barr. Bacterial infections, diabetes, tumours or stones in the saliva glands, and tooth problems also may cause parotitis.
Is parotitis the same as sialadenitis?
Classically, HIV parotitis is either asymptomatic or a non-painful swelling, which is not characteristic of sialadenitis. Some common bacterial causes are S. aureus, S. pyogenes, viridans streptococci and H. influenzae.
What Are salivary glands?
Salivary glands make saliva, which aids in digestion, keeps your mouth moist and supports healthy teeth. You have three pairs of major salivary glands under and behind your jaw — parotid, sublingual and submandibular.
What causes a swollen salivary gland?
A salivary gland infection occurs when a bacterial or viral infection affects your salivary gland or duct. The infection can result from reduced saliva flow, which can be due to a blockage or inflammation of your salivary duct. The condition is called sialadenitis.
What is a blocked salivary gland?
Parotid duct obstruction is when part of your parotid duct becomes blocked. Saliva then can't flow normally from the parotid gland into your mouth. Salivary gland stones are the most common cause of this condition. Symptoms can include pain and swelling in the area around the back of your jaw.
What is acute parotitis?
Acute parotitis is recent swelling of one or both of the salivary glands. There are a number of causes, including viruses and bacteria. Acute viral parotitis is not a common symptom of influenza virus infection and is much more commonly seen following infection with the mumps virus.
What are the glands under your jaw?
Submandibular glands -- These two glands are located just under both sides of the lower jaw and carry saliva up to the floor of the mouth under the tongue. Sublingual glands -- These two glands are located just under the front most area of the floor of the mouth.
What is acute parotitis?
Acute parotitis is recent swelling of one or both of the salivary glands. There are a number of causes, including viruses and bacteria. Acute viral parotitis is not a common symptom of influenza virus infection and is much more commonly seen following infection with the mumps virus.
What are the symptoms of parotitis?
SymptomsFace pain.Fever.Headache.Sore throat.Loss of appetite.Swelling of the parotid glands (the largest salivary glands, located between the ear and the jaw)Swelling of the temples or jaw (temporomandibular area)
What is suppurative parotitis?
Acute bacterial suppurative parotitis, also called acute parotitis, sialadenitis, or sialoadenitis, is an inflammatory and infectious process of the parotid gland. The parotid gland is the major salivary gland in humans and is the most common salivary gland affected by the inflammatory process.
What is acute sialadenitis?
Acute sialadenitis is an acute inflammation of a salivary gland.
The ICD code K118 is used to code Necrotizing sialometaplasia
Necrotizing sialometaplasia (NS) is a benign, ulcerative lesion, usually located towards the back of the hard palate. It is thought to be caused by ischemic necrosis (death of tissue due to lack of blood supply) of minor salivary glands in response to trauma. Often painless, the condition is self-limiting and should heal in 6–10 weeks.
Coding Notes for K11.8 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K11.8 - Other diseases of salivary glands'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K11.8. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code K11.8 and a single ICD9 code, 527.8 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for adverse effect of caffeine
- 2. icd 10 code for skin wound left groin followup
- 3. icd-10 code for ureteral stent removal
- 4. icd 10 code for clotting disorder
- 5. icd 10 code for osteomyelitis toe
- 6. icd 10 code for aftercare following surgery on circulatory system
- 7. icd 9 code for nasal deformity
- 8. icd 10 code for cardiac ablation diagnosis
- 9. icd 10 code for acute and chronic cholecystitis with cholelithiasis
- 10. icd 9 code for premature atrial complexes