What is the ICD 10 code for sunburn?
| ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 L55.1 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of sunburn of second degree. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. A sunburnt back that was partially protected by a bathing suit top.
What is the ICD 10 code for second degree burn?
Burn of second degree of head, face, and neck, unspecified site, initial encounter. T20.20XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM T20.20XA became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the latest version of the ICD 10 for Burns?
Short description: Burn second degree of head, face, and neck, unsp site, init The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T20.20XA became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T20.20XA - other international versions of ICD-10 T20.20XA may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for uremia?
T30.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM T30.0 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T30.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 T30.0 may differ. This code is not for inpatient use.
What is the ICD-10 code for 2nd degree Sunburn?
L55.1ICD-10-CM Code for Sunburn of second degree L55. 1.
What is the ICD-10 code for second degree burn on face?
T20.29XABurn of second degree of head, face, and neck ICD-10-CM T20. 29XA is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0):
What is the ICD-10 code for first degree Sunburn?
L55.0ICD-10-CM Code for Sunburn of first degree L55. 0.
How do you code a burn in ICD-10?
ICD-10 burn codes are reported by body location, depth, extent, and external cause, including the agent or cause of the corrosion, as well as laterality and encounter. To code burn cases correctly, specify the site, severity, extent, and external cause.
What is the correct code for a second degree burn of the right palm initial encounter?
T23.251ABurn of second degree of right palm, initial encounter T23. 251A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you know if you have a first or second degree burn?
BurnsFirst-degree burns affect only the outer layer of the skin. They cause pain, redness, and swelling.Second-degree burns affect both the outer and underlying layer of skin. They cause pain, redness, swelling, and blistering. ... Third-degree burns affect the deep layers of skin.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for sunburn?
L55. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L55.
Can sunburns be second degree?
Skin that is red and painful and that swells up and blisters may mean that deep skin layers and nerve endings have been damaged (second-degree burn). This type of sunburn is usually more painful and takes longer to heal. It increases your chances for developing skin cancer and melanoma.
What are the degrees of sunburn?
Types of sunburnFirst-Degree Burn. The least harmful burn is the first-degree burn, also called superficial skin burn. ... Second-Degree Burn. The second-degree type of burn, also called superficial partial-thickness burn, effects the top two layers of your skin. ... Third-Degree Burn. ... Fourth-Degree Burn.
How do you code a second degree burn?
You must sequence your codes as 942.33 (3rd degree burn of the abdomen), 943.21 (2nd degree burn of the forearm), 944.11(1st degree burn of the index finger). Note: You should only code for the highest level burn when you assign multiple burns of differing degrees (severity) in the same body area.
What are the guidelines for coding burns?
Code Using the Rule of Nines ICD-10 burn codes are reported by body location, depth, extent, and external cause, including the agent or cause of the corrosion, as well as laterality and encounter. To code burn cases correctly, specify the site, severity, extent, and external cause.
What is the difference between burns and corrosions?
Burn codes apply to thermal burns (except sunburns) that come from a heat source, such as fire, hot appliance, electricity and radiation. Corrosions are burns due to chemicals.
What is the ICd code for sunburn?
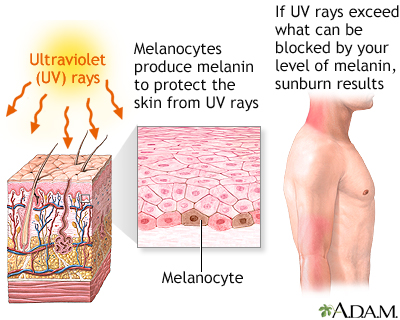
The ICD code L55 is used to code Sunburn. Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, commonly from the sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch, pain, general fatigue, and mild dizziness.
What are the symptoms of UV radiation?
Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch, pain, general fatigue, and mild dizziness. An excess of UV radiation can be life-threatening in extreme cases. Exposure of the skin to lesser amounts of UV radiation will often produce a suntan. Specialty:
What is the difference between a first degree burn and a second degree burn?
first-degree burns damage only the outer layer of skin. second-degree burns damage the outer layer and the layer underneath. third-degree burns damage or destroy the deepest layer of skin and tissues underneath. burns can cause swelling, blistering, scarring and, in serious cases, shock and even death.
What is the first degree of burn?
Injury to tissues caused by contact with dry heat, moist heat, flames, chemicals, electricity, friction or radiant and electromagnetic energy. A first degree burn is associated with redness, a second degree burn with vesication and a third degree burn with necrosis through the entire skin.
What is generic burn injury?
Generic burn injury, including that due to excessive heat, as well as cauterization, friction, electricity, radiation, sunlight, and other causes. Injuries to tissues caused by contact with heat, steam, chemicals (burns, chemical), electricity (burns, electric), or the like.
What causes burns on the skin?
Scalds from hot liquids and steam, building fires and flammable liquids and gases are the most common causes of burns. Another kind is an inhalation injury, caused by breathing smoke.there are three types of burns: first-degree burns damage only the outer layer of skin.
What is a Z18 code?
code to identify any retained foreign body, if applicable ( Z18.-) A burn is damage to your body's tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight or radiation. Scalds from hot liquids and steam, building fires and flammable liquids and gases are the most common causes of burns.
Can antibiotic creams be used for burns?
Antibiotic creams can prevent or treat infections. After a third-degree burn, you need skin or synthetic grafts to cover exposed tissue and encourage new skin to grow. First- and second-degree burns usually heal without grafts. nih: national institute of general medical sciences.
What does it mean when you have a second degree burn?
Second-degree burns indicate blistering with damage extending beyond the epidermis partially into the layer beneath it (dermis) Third-degree burns indicate full-thickness tissue loss with damage or complete destruction of both layers of skin (including hair follicles, oil glands, & sweat glands)
What is a burn?
Burn Types. A burn is tissue damage with partial or complete destruction of the skin caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight, or nuclear radiation. Proper selection of burn codes requires consideration of the location of the burn, severity, extent, and external cause in addition to laterality and encounter.
What is the difference between a burn and a corrosion?
ICD-10 makes a distinction between burns and corrosions: Burn codes apply to thermal burns (except sunburns) that come from a heat source, such as fire, hot appliance, electricity, and radiation. Corrosions are burns due to chemicals.
What is a T20 T28 code?
The descriptions of codes in the T20-T28 range are first defined by an anatomical location of the body affected by burn or corrosion.
How many hospital admissions are there for burns?
According to the American Burn Association, an estimated 486,000 hospital admissions and visits to hospital emergency departments occur annually for burn evaluation and treatment in the United States.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code 2019 for pulmonary nodule
- 2. icd-10 code for fall at home
- 3. icd 10 cm code for mid to distal humeral pain f
- 4. icd 10 code for pancreatic cystic mass
- 5. icd 10 code for pathological left hip fracture drug-induced osteoporosis
- 6. icd-10 code for tracheocutaneous fistula
- 7. icd 10 code for left hand 4th digit mass
- 8. icd 10 code for transperineal repair with perineal body reconstruction
- 9. icd 10 code for elevated a1c / blood sugar
- 10. icd 10 code for infected thyroglossal cyst