What is the ICD 10 code for hyperparathyroidism?
Hyperparathyroidism, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. E21.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM E21.3 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is secondary hyperparathyroidism?
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is increased pth secretion in response to hypocalcemia, usually caused by chronic kidney diseases. A disorder characterized by an increase in production of parathyroid hormone by the parathyroid glands. This results in hypercalcemia (abnormally high levels of calcium in the blood).
What are the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism?
Hyperparathyroidism, unspecified. This causes a loss of calcium from the bones and an increased level of calcium in the blood. Symptoms include bone pain and kidney problems. A condition of abnormally elevated output of parathyroid hormone (or pth) triggering responses that increase blood calcium.
What is hyperparathyroidism and osteogenic synovitis?
Hyperparathyroidism, unspecified. In osteogenic synovitis there is softening and collapse of subchondral bone. Eventually the cartilage overlying this area erodes and is replaced by an irregular fibrocartilage. Eventually the articular surface of the joint is destroyed and secondary degenerative arthritis may develop.
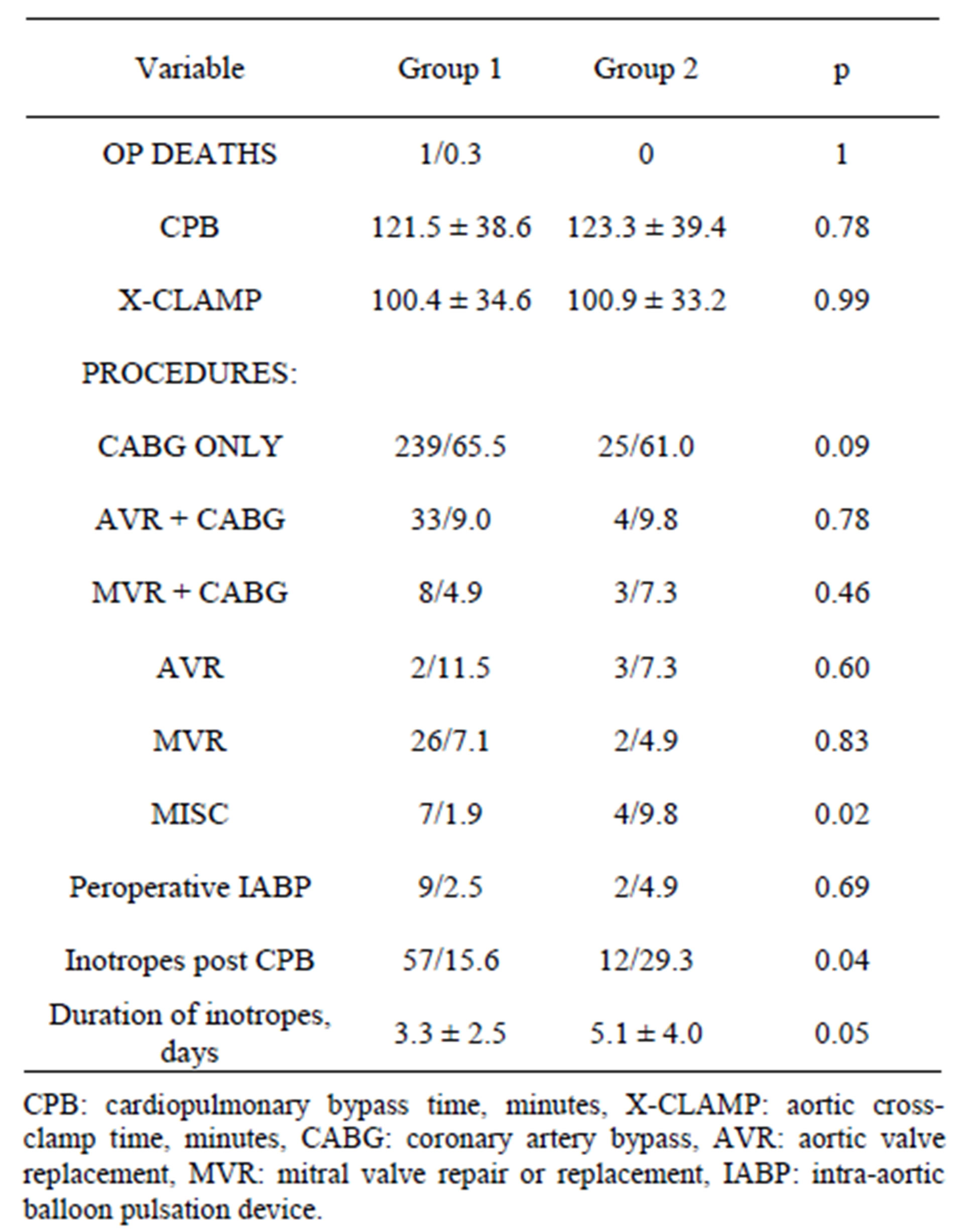
What is secondary hyperparathyroidism?
Secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs when the parathyroid glands become enlarged and release too much PTH, causing a high blood level of PTH. There are several reasons why this happens in patients with kidney disease: Higher blood phosphorus levels. The kidneys cannot make active vitamin D (needed to absorb calcium)
What does code E21 3 mean?
3: Hyperparathyroidism, unspecified.
What is E83 52?
ICD-10 code E83. 52 for Hypercalcemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is hyperparathyroidism unspecified?
A condition in which the parathyroid gland (one of four pea-sized organs found on the thyroid) makes too much parathyroid hormone. This causes a loss of calcium from the bones and an increased level of calcium in the blood.
What is primary hyperparathyroidism?
In primary hyperparathyroidism, an enlargement of one or more of the parathyroid glands causes overproduction of parathyroid hormone. This causes high calcium levels in the blood, which can cause a variety of health problems. Surgery is the most common treatment for primary hyperparathyroidism.
Why does secondary hyperparathyroidism cause hypocalcemia?
Failing kidneys do not convert enough vitamin D to its active form, and they do not adequately excrete phosphate. When this happens, insoluble calcium phosphate forms in the body and removes calcium from the circulation. Both processes lead to hypocalcemia and hence secondary hyperparathyroidism.
What K57 92?
ICD-10 code: K57. 92 Diverticulitis of intestine, part unspecified, without perforation, abscess or bleeding.
What is the ICD-10 code for primary hyperparathyroidism?
E21. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E21.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypothyroidism?
9 – Hypothyroidism, Unspecified. ICD-Code E03. 9 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Hypothyroidism, Unspecified.
What is the difference between primary secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism?
The increase may be due to a) primary hyperparathyroidism which is caused by adenoma of one or more parathyroid glands or hyperplasia of all four glands, b) secondary hyperparathyroidism, which may be caused by deficiency in vitamin D or uremia, and 3) tertiary hyperparathyroidism, which most often is the result of a ...
What are the 3 types of hyperparathyroidism?
There are three types of hyperparathyroidism: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
What are the symptoms of secondary hyperparathyroidism?
Symptoms of SHPT include:Weak or broken bones (osteoporosis)Bone and joint pain.Kidney stones.Urinating (peeing) more often than normal.Belly pain.Feeling weak or tired easily.Feeling sick to your stomach or throwing up.Feeling less hungry than usual (loss of appetite)
What is hyperparathyroidism?
Hyperparathyroidism (high parathyroid hormone level) Clinical Information. A condition in which the parathyroid gland (one of four pea-sized organs found on the thyroid) makes too much parathyroid hormone. This causes a loss of calcium from the bones and an increased level of calcium in the blood.
What is the condition of abnormally elevated output of parathyroid hormone (or pth) triggering responses that
A condition of abnormally elevated output of parathyroid hormone (or pth) triggering responses that increase blood calcium. It is characterized by hypercalcemia and bone resorption, eventually leading to bone diseases. Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by parathyroid hyperplasia or parathyroid neoplasms.
What is the ICd 10 code for secondary hyperparathyroidism?
E21.1 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Secondary hyperparathyroidism, not elsewhere classified . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Hyperparathyroidism E21.3. secondary (renal) N25.81.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for crush injury left middle finger
- 2. icd 10 code for mild pulmonary hypertension
- 3. icd 10 code for moderate acromioclaviclar osteoarthritis
- 4. icd 10 code for chronic urinary incontinence
- 5. icd 10 code for rt knee pain'
- 6. icd 10 code for screening for chlmydia and gonorrhea
- 7. icd 10 code for aftercare following surgery of circulatory system
- 8. icd 10 code for dementia with anxiety
- 9. icd 10 code for amenor
- 10. what is billable icd 10 code for senile dementia