2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Q53.20 Undescended testicle, unspecified, bilateral Billable/Specific Code Male Dx POA Exempt ICD-10-CM Coding Rules Q53.20 is applicable to male patients. Approximate Synonyms Bilateral undescended testicle Bilateral undescended testicles Present On Admission Q53.20 is considered exempt from POA reporting.
Is there a cure for undescended testicle?
There is no way to prevent this condition because the exact cause is not known. Treatment. A persistent undescended testicle usually is treated between 6 months and 2 years of age. Most cases can be corrected with a surgical procedure called orchiopexy, in which the surgeon brings the testicle down into the scrotum through the normal abdominal ...
What is the treatment for an undescended testicle?
Undescended testicle
- Undescended testicle diagnosis. The doctor performs a regular examination of the fetus shortly after the birth. ...
- Undescended testicle treatment. It is better to treat cryptorchidism early in the boy’s life. ...
- Surgery. It is a commonly used method of undescended testicle treatment. ...
- Hormone treatment. ...
- Other treatment methods. ...
- Prognosis. ...
What normally causes undescended testicle?
Undescended testicle
- Undescended testicle causes. There is no specific cause of undescended testicle known these days. ...
- Undescended testicle risk factors. There are three groups of factors that increase the risk of an undescended testicle in an infant. ...
- Cryptorchidism symptoms. ...
- Complications. ...
Is surgery necessary for an undescended testicle?
Surgery is done to bring an undescended testicle into the normal position within the scrotum. Why treatment is needed. The longer a testicle remains outside the scrotum, the more likely it is that it will produce fewer sperm. An undescended testicle has a higher risk of cancer. This is true even after the testicle is brought down into the scrotum.
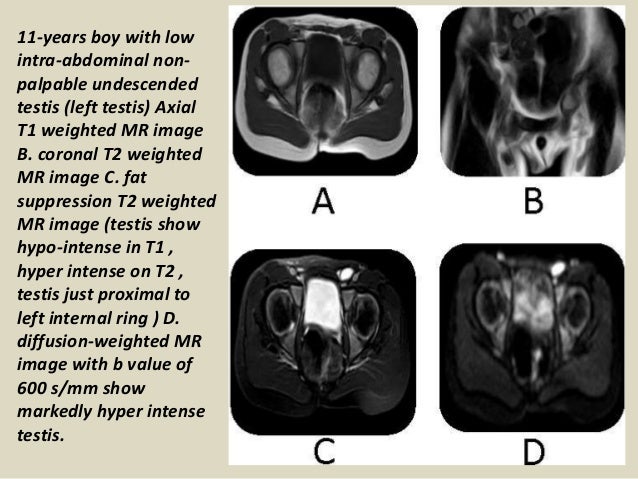
What is the medical term for an undescended testis?
Listen to pronunciation. (krip-TOR-kih-dih-zum) A condition in which one or both testicles fail to move from the abdomen, where they develop before birth, into the scrotum. Cryptorchidism may increase the risk for development of testicular cancer.
Is undescended testis a congenital disease?
Undescended testicles, also known as cryptorchidism, is a fairly common and normally painless congenital condition in which one or both of a baby's testicles (testes) have not moved into the proper position.
What is the ICD-10 code for orchiopexy?
1, 2020: 54640 (Orchiopexy, inguinal approach, with or without hernia repair) will change to 54640 (Orchiopexy, inguinal or scrotal approach).
Can a boy be born without testes?
Babies born without testes in the scrotum have congenital undescended testes. Usually doctors cannot find the cause; however, some hormone and genetic disorders can cause undescended testes.
How serious is an undescended testicle?
If the testicles don't drop into the scrotum, they may not function normally and produce healthy sperm. This can lead to infertility later in life. Males born with undescended testicles also have a higher risk of testicular cancer in adulthood.
What is the meaning of Orchiopexy?
Orchiopexy (or orchidopexy) is a surgery to move an undescended (cryptorchid) testicle into the scrotum and permanently fix it there. Orchiopexy typically also describes the surgery used to resolve testicular torsion. Urology 216.444.5600. Kidney Medicine 216.444.6771.
What is orchidopexy operation?
Orchidopexy (OR-kid-o-pex-ee) is a surgery to move a testicle that has not descended or moved down to its proper place in the scrotum.
What is the ICD 10 code for hypospadias?
Q54.9Q54. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q54.
What is an undescended testicle?
Undescended and ectopic testicle Q53-. A condition in which one or both testicles fail to move from the abdomen, where they develop before birth, into the scrotum. Undescended testicles may increase the risk for development of testicular cancer.
What is cryptorchidism subclassified by?
Cryptorchidism can be subclassified by the location of the maldescended testis. Failure of testes to descend into scrotum. The failure of one or both testes of a male fetus to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum during the late part of pregnancy.
What does "undetermined" mean in medical terms?
Clinically undetermined. Provider unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.
What is congenital anomaly?
Congenital anomaly of the genitalia is a medical term referring to any physical abnormality of the male or female internal or external genitalia present at birth. This is a broad category of conditions, some common and some rare.
Is diagnosis present at time of inpatient admission?
Diagnosis was present at time of inpatient admission. Yes. N. Diagnosis was not present at time of inpatient admission. No. U. Documentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.
What is the ICD code for undescended testicle unilateral?
To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the three child codes of Q53.1 that describes the diagnosis 'undescended testicle, unilateral' in more detail. Q53.1 Undescended testicle, unilateral.
What is the ICD code for genital anomalies?
The ICD code Q53 is used to code Congenital anomalies of the genitalia. Congenital anomaly of the genitalia is a medical term referring to any physical abnormality of the male or female internal or external genitalia present at birth. This is a broad category of conditions, some common and some rare.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code Q53.1 is a non-billable code.
What is the ICd 10 code for testicle?
Q53.9 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Undescended testicle, unspecified . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
When an excludes2 note appears under a code, is it acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code?
When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
What does "Excludes 2" mean?
A type 2 Excludes note represents 'Not included here'. An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes. It means 'NOT CODED HERE!' An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left breast nodule
- 2. icd 0 code for pressure ulcer stage 2 to left buttock
- 3. icd 10 code for right breast mass lower outer quadrant
- 4. icd-10-cm code for costen's complex
- 5. icd 9 code for high psa
- 6. icd 10 code for non valvular atrial fibrillation
- 7. icd 10 code for hurler syndrome
- 8. icd 10 code for family history of abdominal aortic aneurysm
- 9. icd 10 code for generalized body pain
- 10. icd-10-cm code for stage-1 pressure ulcer of the right hip