What do you need to know about uterine fibroids?
- Genetic changes. Many fibroids contain changes in genes that differ from those in typical uterine muscle cells.
- Hormones. ...
- Other growth factors. ...
- Extracellular matrix (ECM). ...
Are uterine fibroids a preexisting condition?
Fibroids or even a history of them with no current health effects were treated as a pre-existing condition. The consequence was that insurance companies either would not provide any coverage related to my uterus – including for cancer and other potential conditions completely unrelated to fibroids – or would charge me significant additional ...
How can an uterine fibroid be treated?
What Procedures Might Work?
- Fibroid embolization. Your doctor will inject polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) into the arteries that feed the fibroid. The PVA blocks the blood supply to the fibroid, which makes it shrink.
- Endometrial ablation. Myomectomy is a surgery to remove fibroids. ...
- Hysterectomy. Many women don’t need treatment that’s this drastic. ...
What are the treatments for uterine fibroids?
- Stewart E, ASRM 2020; Late-breaker abstract P-930
- Al-Hendy A, NEJM 2021; 384:630-42
- Schlaff W, NEJM 2020; 382:328-40
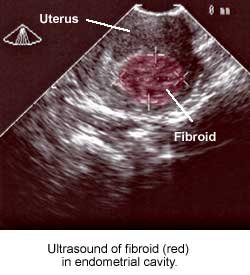
What is the ICD-10 code for enlarged fibroid uterus?
N85. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is diagnosis code D25 9?
ICD-10 code: D25. 9 Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified.
What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. Also called leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs) or myomas, uterine fibroids aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer.
What is the ICD-10 code for intramural fibroid?
1.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of fibroids?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z87. 42: Personal history of other diseases of the female genital tract.
What is an intramural fibroid?
An intramural fibroid is a noncancerous tumor that grows between the muscles of the uterus. There are several types of intramural fibroids: anterior intramural fibroid, located in the front of the uterus. posterior intramural fibroid, located in the back of the uterus.
Where are uterine fibroids?
Most fibroids grow in the wall of the uterus. Doctors put them into three groups based on where they grow: Submucosal (sub-myoo-KOH-zuhl) fibroids grow into the uterine cavity. Intramural (ihn-truh-MYOOR-uhl) fibroids grow within the wall of the uterus.
What causes uterus fibroids?
What causes fibroids? The cause of fibroids is not known. Research suggests each tumor develops from an abnormal muscle cell in the uterus and multiplies rapidly when encountering the estrogen hormone, which promotes the tumor's growth.
How are uterine fibroids diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of uterine fibroids, your doctor may order these tests: Ultrasound. If confirmation is needed, your doctor may order an ultrasound. It uses sound waves to get a picture of your uterus to confirm the diagnosis and to map and measure fibroids.
What is the ICD-10 code for myomectomy?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98. 891 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z98.
What is the ICD-10 code for enlarged uterus?
ICD-10 code N85. 2 for Hypertrophy of uterus is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What does pedunculated fibroid mean?
Pedunculated fibroids are benign (noncancerous) growths in the uterus. These fibroids are attached to the uterine wall by a stalk-like growth called a peduncle. The main difference between pedunculated fibroids and other fibroids is the peduncle. These fibroids can grow both inside and outside the uterus.
What is the code for uterine fibroids?
nih: national institute of child health and human development. Codes. D25 Leiomyoma of uterus. D25.0 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus.
What is a fibroid uterus?
uterine fibroid. uterine fibromyoma. uterine myoma. Clinical Information. A benign smooth muscle neoplasm arising from the body of the uterus. It is characterized by the presence of spindle cells with cigar-shaped nuclei, interlacing fascicles, and a whorled pattern. Uterine fibroids are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women ...
What is a fibrous tumor?
Uterine fibroids are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women of childbearing age . Fibroids are made of muscle cells and other tissues that grow in and around the wall of the uterus, or womb. The cause of fibroids is unknown. Risk factors include being african-american or being overweight.
Can fibroids cause a miscarriage?
Many women with uterine fibroids have no symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may include. heavy or painful periods or bleeding between periods. feeling "full" in the lower abdomen. reproductive problems, such as infertility, multiple miscarriages or early labor. most women with fibroids can get pregnant naturally.
What is the code for uterine fibroids?
Hysterectomy —Uterus removal is the only certain way to cure uterine fibroids. For a hysterectomy performed via the abdomen, look to code range 58150-58240. For a hysterectomy by vaginal approach, select a code from 58260-58294.
What is the ICd 9 code for fibroid?
Most fibroids grow within the uterus wall. These are known as intramural fibroids and are reported using 218.1 Intramural leiomyoma of uterus (interstitial leiomyoma of uterus). Whereas submucosal fibroids (218.0 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus) grow into the uterine cavity; and subserosal fibroids (218.2 Subserous leiomyoma of uterus) grow outside of the uterus.#N#Other fibroids grow on stalks from the uterus’ surface or in the uterus’ cavity (they might look like mushrooms). These are called pedunculated fibroids and are reported with 218.9 Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified. You should also report 218.9 if the provider does not specify the location of the uterine fibroid.
What is the procedure code for a vaginal hysterectomy?
58550 Laparoscopy, surgical, with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less; 58552 Laparoscopy, surgical, with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less; with removal of tube (s) and/or ovary (s) 58553 Laparoscopy, surgical, with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus greater than 250 g;
Where do submucosal fibroids grow?
Whereas submucosal fibroids (218.0 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus) grow into the uterine cavity; and subserosal fibroids (218.2 Subserous leiomyoma of uterus) grow outside of the uterus. Other fibroids grow on stalks from the uterus’ surface or in the uterus’ cavity (they might look like mushrooms).
What test is used to confirm fibroids?
The physician may perform imaging tests to confirm fibroids. These tests might include: Ultrasound —The ultrasound probe can be placed on the abdomen or inside the vagina. For pelvic exam, report 76856 Ultrasound, pelvic (nonobstetric), real time image documentation; complete.
Can fibroids displace fallopian tubes?
Fibroids may also displace the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Because fibroids are almost always benign, it is rare (less than one in 1,000 cases) for a cancerous fibroid (leiomyosarcoma) to occur. No one knows for sure what causes fibroids.
Can a doctor check for fibroids?
The physician may also perform hysteroscopy to confirm fibroids. The doctor passes a long, thin scope with a light through the vagina and cervix into the uterus; no incision is needed. The doctor can look inside the uterus for fibroids and other problems, such as polyps.

Popular Posts:
- 1. the icd-10-cm code(s) for atony of colon is
- 2. icd 10 code for 2nd pregnancy
- 3. icd-10 code for mssa pneumonia
- 4. icd 9 code for tinea pedis
- 5. 2015 icd 9 code for degenertative sacroiliac joint
- 6. icd 10 code for pica
- 7. icd 10 code for dependent personality disorder
- 8. icd 10 code for left ptosis
- 9. icd 10 code for right eye cataract surgery
- 10. icd 10 pcs code for brachial to basilic fistula creation