Vitiligo. L80 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM L80 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L80 - other international versions of ICD-10 L80 may differ.
Full Answer
What is the ICD 10 code for vitiligo of the eye?
Vitiligo. L80 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L80 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L80 - …
What is the ICD 10 code for pigmentation disorder?
When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( L80) and the excluded code together. vitiligo of eyelids (. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H02.73. Vitiligo of eyelid and periocular area. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 …
What is the 2019 version of the ICD 10 diagnosis code L80?
ICD-10-CM Code L80Vitiligo. ICD-10-CM Code. L80. Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. L80 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of vitiligo. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the ICD 10 code for primary diagnosis?
Oct 01, 2021 · ICD-10-CM Code L80 Vitiligo Billable Code L80 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Vitiligo . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . ↓ See below for any exclusions, inclusions or special notations Excludes2

How to treat vitiligo?
Using sunscreen will help protect your skin, and cosmetics can cover up the patches. Treatments for vitiligo include medicines, light therapy and surgery. Not every treatment is right for everyone. Many have side effects.
What is macular depigmentation?
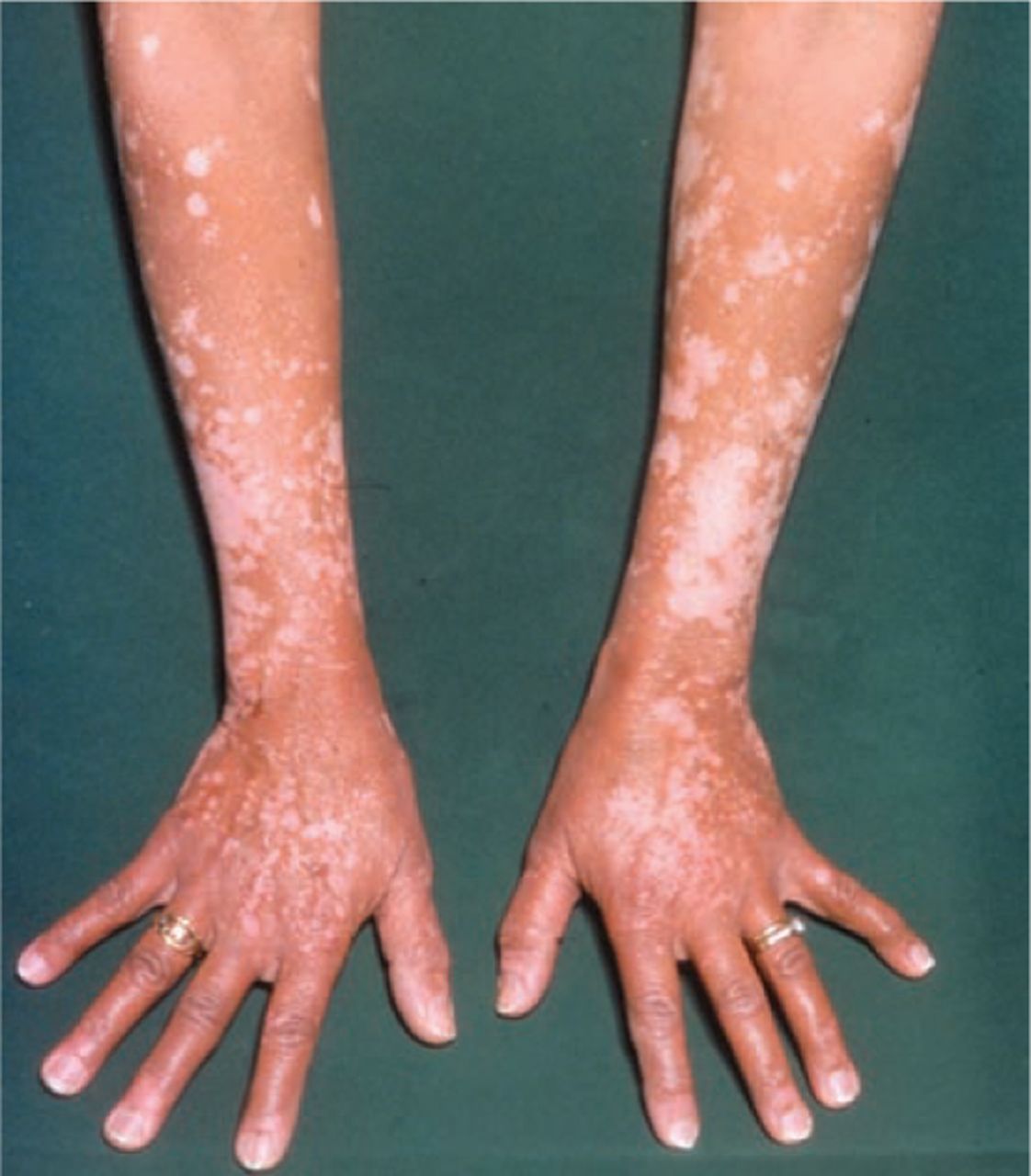
A disorder consisting of areas of macular depigmentation, commonly on extensor aspects of extremities, on the face or neck, and in skin folds. Age of onset is often in young adulthood and the condition tends to progress gradually with lesions enlarging and extending until a quiescent state is reached. Usually progressive, chronic pigmentary anomaly ...
What is a type 2 exclude note?
A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( L80) and the excluded code together.
What is the condition where the skin turns white?
A condition in which the skin turns white due to the loss of melanocytes. A disorder consisting of areas of macular depigmentation, commonly on extensor aspects of extremities, on the face or neck, and in skin folds.
What causes white patches on the face?
Usually progressive, chronic pigmentary anomaly of the skin manifested by depigmented white patches that may be surrounded by a hyperpigmented border. Vitiligo causes white patches on your skin. It can also affect your eyes, mouth and nose. It occurs when the cells that give your skin its color are destroyed.
Why does my hair turn gray?
The white patches are more common where your skin is exposed to the sun. In some cases, the patches spread. Vitiligo can cause your hair to gray early. If you have dark skin, you may lose color inside your mouth. Using sunscreen will help protect your skin, and cosmetics can cover up the patches.
What is pigmentation disorder?
Pigmentation disorders are disturbances of human skin color, either loss or reduction, which may be related to loss of melanocytes or the inability of melanocytes to produce melanin or transport melanosomes correctly.
What does "type 2 excludes" mean?
Type-2 Excludes means the excluded conditions are different, although they may appear similar. A patient may have both conditions, but one does not include the other. Excludes 2 means "not coded here."
What is tabular list?
When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the “other specified” code. This abbreviation is the equivalent of unspecified. This note further define, or give examples of, the content of the code or category.
What does "excludes2" mean?
An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together.
What is a list of terms?
List of terms is included under some codes. These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used. The terms may be synonyms of the code title, or, in the case of “other specified” codes, the terms are a list of the various conditions assigned to that code.
What does NEC not elsewhere mean?
NEC Not elsewhere classifiable#N#This abbreviation in the Tabular List represents “other specified”. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the “other specified” code.
What is vitiligo in medical terms?
Vitiligo (Medical Encyclopedia) [ Learn More in MedlinePlus ] Vitiligo Vitiligo is a condition that causes patchy loss of skin coloring (pigmentation). The average age of onset of vitiligo is in the mid-twenties, but it can appear at any age. It tends to progress over time, with larger areas of the skin losing pigment.
What is the most common form of vitiligo?
Some people with vitiligo also have patches of pigment loss affecting the hair on their scalp or body.Researchers have identified several forms of vitiligo. Generalized vitiligo (also called nonsegmental vitiligo), which is the most common form, involves loss of pigment (depigmentation) in patches of skin all over the body.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code L80:
What is a vitigigo?
VITILIGO-. a disorder consisting of areas of macular depigmentation commonly on extensor aspects of extremities on the face or neck and in skin folds. age of onset is often in young adulthood and the condition tends to progress gradually with lesions enlarging and extending until a quiescent state is reached.
What causes white spots on the face?
Vitiligo causes white patches on your skin. It can also affect your eyes, mouth, and nose. It occurs when the cells that give your skin its color are destroyed. No one knows what destroys them. It is more common in people with autoimmune diseases, and it might run in families. It usually starts before age 40.
When does vitiligo start?
It is more common in people with autoimmune diseases, and it might run in families. It usually starts before age 40. The white patches are more common where your skin is exposed to the sun. In some cases, the patches spread. Vitiligo can cause your hair to gray early.
Can vitiligo cause gray hair?
Vitiligo can cause your hair to gray early. If you have dark skin, you may lose color inside your mouth. Using sunscreen will help protect your skin, and cosmetics can cover up the patches. Treatments for vitiligo include medicines, light therapy, and surgery. Not every treatment is right for everyone.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for evaluate liver, pancreas, and gallbladder
- 2. icd 10 code for right calcaneal fracture
- 3. icd 10 code for isolation precautions
- 4. icd 10 cm code for aggression
- 5. 2019 icd 10 code for osteoarthritis of handoison ivy
- 6. icd 10 cm code for right testicle mass
- 7. icd 10 code for noncompliance unspecified
- 8. icd 10 code for bone density on someone with hodgkin's lymphoma
- 9. icd 10 code for unspecified depressive disorder with anxiety
- 10. icd 10 code for sycope