What is the ICD 10 code for T85 Xa?
T85.09XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T85.09XA became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T85.09XA - other international versions of ICD-10 T85.09XA may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for shunt infection?
Infection and inflammatory reaction due to ventricular intracranial (communicating) shunt, sequela. T85.730S is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM T85.730S became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the principal diagnosis for O80 encounter for delivery?
If multiple conditions prompted the admission, the condition most related to the delivery is the principal diagnosis (ICD-10-CM Coding Guideline I.C.15.b.4). Code O80 Encounter for full term uncomplicated delivery is assigned as the principal diagnosis for delivery admissions that meet the following criteria (ICD-10-CM Coding Guideline I.C.15.n):
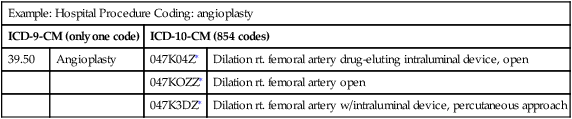
What is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10?
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code V45.2 was previously used, Z98.2 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.

What is the ICD-10-CM code for VP shunt?
ICD-10 code T85. 09XA for Other mechanical complication of ventricular intracranial (communicating) shunt, initial encounter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is a VP shunt for hydrocephalus?
A ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is a cerebral shunt that drains excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) when there is an obstruction in the normal outflow or there is a decreased absorption of the fluid. Cerebral shunts are used to treat hydrocephalus.
What is a VP shunt?
A ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is a thin plastic tube that helps drain extra cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain. CSF is the saltwater that surrounds and cushions the brain and spinal cord.
Where is a VP shunt placed?
It is sent down the neck and chest, and usually into the belly area. Sometimes, it stops at the chest area. In the belly, the catheter is often placed using an endoscope. The doctor may also make a few more small cuts, for instance in the neck or near the collarbone, to help pass the catheter under the skin.
What is a VPS in medical terms?
A ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) is a surgical treatment for hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus is a neurological disease literally meaning water on the brain and can be very disabling.
Is an EVD the same as a shunt?
EVDs are a short-term solution to hydrocephalus, and if the underlying hydrocephalus does not eventually resolve, it may be necessary to convert the EVD to a cerebral shunt, which is a fully internalized, long-term treatment for hydrocephalus.
What is a VP shunt made of?
Ventriculoperitoneal shunts consist of a valve and two tubes, called catheters, which drain the fluid. One catheter drains fluid from the brain out of a small hole the doctor makes in the skull. This is called the inflow catheter. The other runs under the skin, taking the fluid to a drainage site elsewhere in the body.
What are the different types of shunts?
What are the most common shunt systems?Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunts. This type of shunt diverts CSF from the ventricles of the brain into the peritoneal cavity, the space in the abdomen where the digestive organs are located. ... Ventriculoatrial (VA) shunts. ... Ventriculopleural (VPL) shunts. ... Lumboperitoneal (LP) shunts.
How do you know if a VP shunt is clinically performed?
By injecting a small volume of contrast dye or a radiotracer into the shunt reservoir, the flow of CSF through the catheters and valve can be measured. Shunt Tap is a diagnostic test to screen for infection and confirm that the shunt is still functioning.
What is the most common complication of VP shunt?
Obstruction is the most common cause of ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) malfunction. Infection is the second most common cause of VPS malfunction, which is more common in children. Pseudocyst is a late complication of VPS, which may present as abdominal pain and a palpable mass.
How do you examine a VP shunt?
Tap the shuntPalpate for the location of the shunt reservoir.Use strict aseptic technique.Ideally, attach a 25 gauge needle to a 3 way stopcock to allow for manometer attachment. ... Insert the needle at approximately 45 degrees towards the centre of the reservoir.More items...•
Is a shunt considered brain surgery?
Shunt surgery is done by a specialist in brain and nervous system surgery (neurosurgeon). It's done under a general anaesthetic and usually takes 1 to 2 hours. You may need to stay in hospital for a few days after the operation to recover.
What is the ICd 10 code for a ventricular shunt?
Infection and inflammatory reaction due to ventricular intracranial (communicating) shunt, sequela 1 T85.730S is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: I/I react d/t ventricular intracranial shunt, sequela 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM T85.730S became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T85.730S - other international versions of ICD-10 T85.730S may differ.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
What is the O80 code?
Code O80 Encounter for full term uncomplicated delivery is assigned as the principal diagnosis for delivery admissions that meet the following criteria (ICD-10-CM Coding Guideline I.C.15.n): 1 Vaginal delivery at full term 2 No accompanying instrumentation (episiotomy is ok) 3 Single, healthy infant 4 No unresolved antepartum complications 5 No complications of labor or delivery 6 No postpartum complications during the delivery admission
How many codes are needed for vaginal delivery?
Coding of vaginal deliveries requires a minimum of 3 codes; a principal diagnosis code, an outcome of delivery code and a weeks of gestation code. Fortunately, there are guidelines and notes to provide direction in properly assigning these codes.
What is the code for weeks of gestation?
The notes at the beginning of Chapter 15 Pregnancy, Childbirth and the Puerperium indicate that in addition to the Chapter 15 codes, the coder should assign a code from category Z3A, Weeks of gestation, to identify the specific week of the pregnancy, if known. The guidelines provide further direction, ...
What is the principal diagnosis for delivery?
For delivery admissions, the principal diagnosis is the condition that prompted the admission. If multiple conditions prompted the admission, the condition most related to the delivery is the principal diagnosis (ICD-10-CM Coding Guideline I.C.15.b.4).
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) requires medical coders to indicate whether or not a condition was present at the time of admission, in order to properly assign MS-DRG codes.
Is a diagnosis present at time of inpatient admission?
Diagnosis was present at time of inpatient admission. Yes. N. Diagnosis was not present at time of inpatient admission. No. U. Documentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. No.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 diagnosis code for hypoxemia
- 2. icd 10 code for delirium
- 3. icd 10 code for cerebral toxoplasmosis
- 4. icd 10 code for adenoma colon
- 5. icd 10 code for recovering heroin adict
- 6. icd 9 code for open wound arm
- 7. icd 10 code for acute embolism and thrombosis of deep veins of lower extremity
- 8. icd 10 code for dog bite right arm
- 9. icd 10 cm code for rheumatoid arthritis unspecified
- 10. icd 10 code for l olecranon bursitis