Is Wolff Parkinson White a disability?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is one of the leading causes of fast heart rate disorder in newborns and young children. It is not clear what causes the additional pathway to develop inside the heart. The condition is present at birth, but genetic factors usually do not play a major role.
What are the symptoms of the Wolff Parkinson White syndrome?
Symptoms of WPW may include one or more of the following:
- Heart palpitations – a sudden pounding, fluttering or
- Racing feeling in your chest
- Dizziness – feeling lightheaded or faint
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Anxiety
- Rarely, cardiac arrest (sudden death)
Is Wolff Parkinson White syndrome misdiagnosed?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can be picked up on an ECG if a person has presented with symptoms to their GP or A&E. In most cases, it is diagnosed after symptoms of heart racing but sometimes WPW is diagnosed by accident, if a person has an electrocardiogram (ECG) as part of a general check-up for instance.
How can Wolff Parkinson White syndrome be prevented?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a type of heart condition that you are born with. It causes rapid heart rate. Medicine can help control symptoms. Cardiac ablation can cure the disease in most cases. Talk with your healthcare provider right away if you have symptoms of WPW.
What is Wolff-Parkinson-White heart Syndrome?
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a relatively common heart condition that causes the heart to beat abnormally fast for periods of time. The cause is an extra electrical connection in the heart. This problem with the heart is present at birth (congenital), although symptoms may not develop until later in life.
Is Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome a heart block?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (type A) complicated by heart block in both normal and accessory pathways.
Is Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome the same as AFIB?
In Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, antegrade conduction occurs over an accessory pathway. If atrial fibrillation, develops this is a medical emergency as very rapid ventricular rates can develop. and Atrial Fibrillation. Symptoms include palpitations and sometimes weakness, effort intolerance, dyspnea, and presyncope.
Is Wolff-Parkinson-White a heart murmur?
The case of a girl is presented with the WPW syndrome, which spontaneously intermits with a nodal rhythm and where a cardiac systolic murmur is linked only with the WPW beats. Pharmacologic tests demonstrated a close relationship between the type of ventricular excitation and the presence of the cardiac murmur.
Which of the following are associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome often occurs with other structural abnormalities of the heart or underlying heart disease. The most common heart defect associated with the condition is Ebstein anomaly, which affects the valve that allows blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle (the tricuspid valve).
How is Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome diagnosed?
WPW is usually diagnosed with a standard ECG, but specialized testing is required in some people. The electrocardiogram — The WPW pattern can be detected by an ECG even while the person is in a normal rhythm. Conduction through the accessory pathway produces a characteristic ECG pattern.
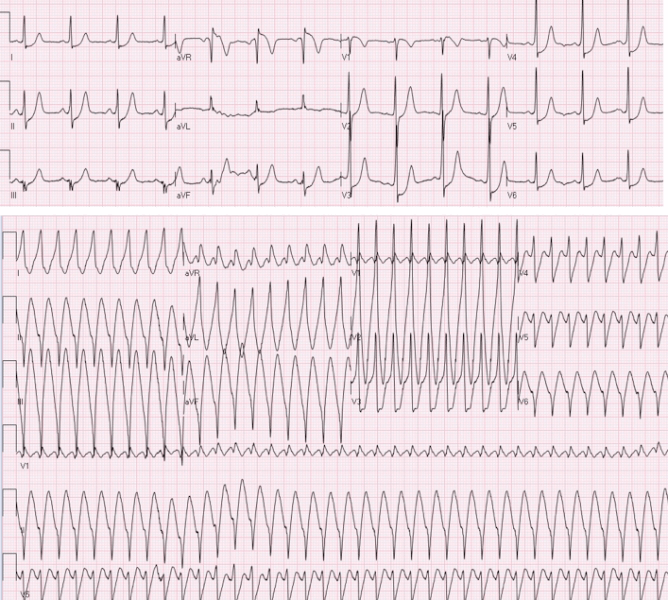
What does Wolff-Parkinson-White look like on ECG?
WPW pattern is a constellation of electrocardiographic findings, so initial evaluation relies on a surface electrocardiogram. The ECG will show a short PR interval (<120 ms), prolonged QRS complex (>120 ms), and a QRS morphology consisting of a slurred delta wave.
What does Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome look like on ECG?
Classic ECG findings that are associated with WPW syndrome include the following: Presence of a short PR interval (<120 ms) A wide QRS complex longer than 120 ms with a slurred onset of the QRS waveform, termed a delta wave, in the early part of QRS. Secondary ST-T wave changes (see the image below)
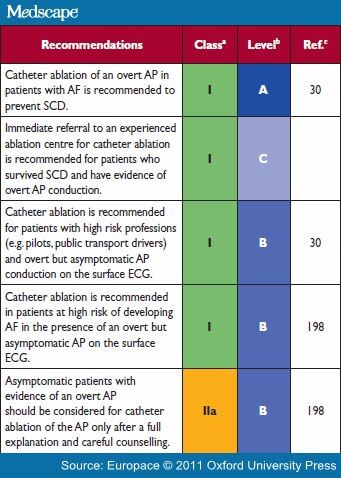
Is WPW Orthodromic or Antidromic?
Types of arrhythmias in WPW are AVRT (80%). There are two type of AVRT, orthodromic (90 to 95%) vs. antidromic (5%), other types are atrial fibrillation (AF) (10% to 30%), atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation [4-7]. The different types of arrhythmias are shown in Figure 5.
Does WPW always show up on ECG?
WPW can only be diagnosed by reviewing an ECG (electrocardiogram). A holter or ambulatory monitor and exercise testing are also helpful in evaluating patients known to have WPW. In the past, patients with WPW but without symptoms had been observed by a cardiologist for many years.
Can Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome cause high blood pressure?
This extra pathway creates a shortcut for the electrical impulses. As a result, these impulses may activate the heartbeats too early or at the wrong time. If it's left untreated, the abnormal heartbeat, arrhythmia, or tachycardia, can cause blood pressure, heart failure, and even death.
Can Wolff-Parkinson-White cause seizures?
Patients with WPW syndrome and neurologic abnormalities consistent with MELAS syndrome, such as seizures, deafness, short stature, and stroke, should be screened for the A3243G mutation.
What is Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease is a disorder that affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. In parkinson's, neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements.
How old do you have to be to get Parkinson's?
They may also have problems such as depression, sleep problems or trouble chewing, swallowing or speaking. Parkinson's usually begins around age 60, but it can start earlier.
When will the ICD-10 G20 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is progressive degenerative disorder?
Progressive, degenerative disorder of the nervous system characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, and gait abnormalities; caused by a loss of neurons and a decrease of dopamine in the basal ganglia.
What is the ICD10 code for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome? And the ICD9 code for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
My dad was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease.his symptoms were shuffling of feet,slurred speech,degradation of hand writing, horrible driving skills, right arm held at 46 degree angle, things were tough for me, but now he finally free from the disease with the help of total cure from ULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC, he now walks properly and all symptoms has reversed, he was having trouble with balance especially at night, getting into the shower and exiting it is difficult,getting into bed is also another thing he finds impossible.we had to find a better solution for his condition which really helped him a lot,the biggest helped we had was ultimate life clinic they walked him through the proper steps,i recommended this http://www.ultimatelifeclinic.com to anyone who also needs help..
Stories of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
I was born in 2014 at 26 weeks weighing 630g. I had 1 episode of SVT and diagnosed with WPW in August 2014 and have been on propranolol ever since. If anyone can help my mummy and daddy understand this disease better and what it's like living wi...
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome forum
I went to the hospital yesterday for my review of ecg, heart scan and 24 hour monitor results as in March I was admitted to a&e for being dehydrated in pregnancy. Im currently 24 weeks pregnant with my first and have now been diagnosed with this ...
What are the symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
The early stages of PD include the following signs and symptoms: Slight shaking of a finger, hand, leg, chin, or lip. Stiffness or difficulty walking. Difficulty getting out of a chair.
How many people are affected by Parkinson's disease?
As a neurodegenerative disease of the brain, which impacts an individual’s motor function, Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the most common neurological disorder, affecting approximately one million people in the United Status. It is estimated that approximately 60,000 Americans are diagnosed with PD each year, and this number does not reflect ...
What is the PD G20 code?
With PD G20 code, you will be coding associated signs and symptoms or those complications not necessarily inherent to the disease. Most of these complications will be found in Chapter 18, as signs and/or symptoms.
What are the symptoms of PD?
PD is associated with the physical symptoms of tremor and/or rigidity. These symptoms may be shown as head bobbing or other sudden involuntary jerking movements and shaking hand (s).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for intermittent monocular exotropia convergence excess
- 2. icd 10 code for cervical central canal stenosis
- 3. icd 10 code for tips procedure
- 4. 2018 icd 10 code for asbestosis
- 5. icd 10 code for s p bilateral knee replacement
- 6. icd 10 code for polymicrobial uti
- 7. billable icd 10 code for left hip fracture
- 8. icd 10 code for allergy to shellfish
- 9. icd 10 code for temporal lobe epilepsy?trackid=sp-006
- 10. icd 10 code for influenza a positive