What does anxiety F41 1 mean?
Anxiety that is generalized and persistent but not restricted to, or even strongly predominating in, any particular environmental circumstances (i.e. it is "free-floating").
How do you code generalized anxiety disorder with panic attacks?
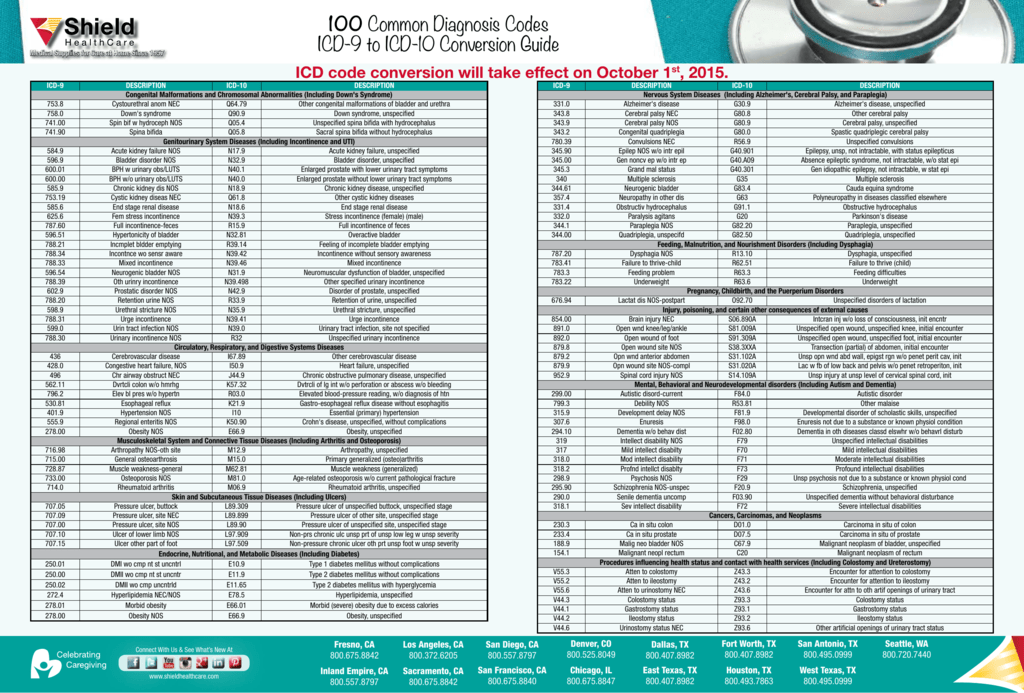
Generalized anxiety disorder (300.02) — involves six months of persistent, excessive, and unrealistic worry. Panic disorder (300.01) — may have a sudden onset causing apprehension, fear, or terror.
How do you code situational anxiety?
Wiki Need help with Situational Anxiety diagnosisCode: F41.8.Code Name: ICD-10 Code for Other specified anxiety disorders.Block: Anxiety, dissociative, stress-related, somatoform and other nonpsychotic mental disorders (F40-F48)Details: Other specified anxiety disorders.More items...•
Can Z76 89 be used as a primary diagnosis?
The patient's primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient's primary diagnostic code is Z76. 89, look in the list below to see which MDC's "Assignment of Diagnosis Codes" is first.
What is ICD-10 code for generalized anxiety disorder?
Code F41. 1 is the diagnosis code used for Generalized Anxiety Disorder. It is an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational worry, that is, apprehensive expectation about events or activities. This excessive worry often interferes with daily functioning.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for panic attacks?
ICD-10 code F41. 0 for Panic disorder [episodic paroxysmal anxiety] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
Is situational anxiety a diagnosis?
Situational anxiety is not recognized as a distinct condition in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the clinical manual that doctors utilize to diagnose mental health conditions.
What is the ICD-10 code for situational depression?
Code F43. 23 is the diagnosis code used for Adjustment Disorder (AD) with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood. It is sometimes known as situational depression. It occurs when an individual is unable to adjust to or cope with a particular stress or a major life event.
What is the ICD-10 code for adjustment disorder with anxiety?
22 Adjustment disorder with anxiety (about ICD-10!)
ICD-10 Equivalent of 300.02
As of October 2015, ICD-9 codes are no longer used for medical coding. Instead, use this equivalent ICD-10-CM code, which is an exact match to ICD-9 code 300.02:
Historical Information for ICD-9 Code 300.02
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
Not Valid for Submission
300.02 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 300.02 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Fear and anxiety are part of life. You may feel anxious before you take a test or walk down a dark street. This kind of anxiety is useful - it can make you more alert or careful. It usually ends soon after you are out of the situation that caused it.
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
Introduction
While it is not unusual for anyone to occasionally worry about things such as family problems, health or money, people with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) find themselves extremely worried about these sorts of things, as well as many other issues, even when there may be little or no reason to worry.
Symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
People with GAD experience chronic, constant and often unsubstantiated worry. Some of the more common topics or worries include work, family, health or money. Such worries can continue throughout the day, in some cases every day, disrupting social activities, family, work or school.
Diagnostic Criteria
All of the below features must be present in order to make a proper diagnosis of GAD:
Prevalence
Surveys of the general population suggest that during a person’s lifetime, somewhere between 4 to 6% of people will experience GAD. Women seem to be more susceptible to GAD then men, occurring approximately twice as frequently in females.
Comorbidities
GAD tends to coexist with a number of other psychiatric disorders, including, but not limited to major depression, bipolar disorder, other anxieties and substance abuse problems. So many similarities exist between depression and GAD that many experts have even suggested re-categorizing GAD as a mood disorder.
Treatment for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD is typically treated using either psychotherapy, medication or a combination of both. In terms of psychotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) tends to be especially useful in the treatment of GAD. This approach works by teaching different ways of thinking, behaving and reacting to certain situations.
Strategies for living with GAD
If a patient feels that they suffer anxiety, the initial step is to consult with their general practitioner. Such professionals have the training to determine if the symptoms observed might be due to an anxiety disorder or be the result of a medical condition, or both.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for abdominal aortic aneurysm
- 2. icd 10 cm code encounter for anti neoplastic chemotherapy
- 3. icd 10 code for follow up healed non-pressure ulceration
- 4. icd 10 code for pain in rib
- 5. icd-10-cm code for aids
- 6. icd 10 code for rotator cuff repair
- 7. icd 10 code for c reactive protein screening
- 8. icd 9 code for suicidal ideation
- 9. icd-10-cm code for obstructed ventriculoperitoneal shunt
- 10. icd-10 code for pelvic congestion syndrome