Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
What are ICD-10 diagnostic codes?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes
| A00.0 | B99.9 | 1. Certain infectious and parasitic dise ... |
| C00.0 | D49.9 | 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) |
| D50.0 | D89.9 | 3. Diseases of the blood and blood-formi ... |
| E00.0 | E89.89 | 4. Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic ... |
| F01.50 | F99 | 5. Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopme ... |
What are ICD 10 codes?
Why ICD-10 codes are important
- The ICD-10 code system offers accurate and up-to-date procedure codes to improve health care cost and ensure fair reimbursement policies. ...
- ICD-10-CM has been adopted internationally to facilitate implementation of quality health care as well as its comparison on a global scale.
- Compared to the previous version (i.e. ...
What does ICD 10 mean?
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
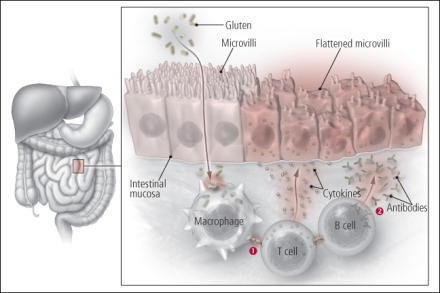
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal lab results?
ICD-10 code R79. 9 for Abnormal finding of blood chemistry, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated tTG?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R76. 0: Raised antibody titer.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for celiac disease?
ICD-10 code K90. 0 for Celiac disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the diagnosis code for antibody testing?
DIAGNOSIS CODES FOR COVID-19 ANTIBODY TESTING Report code Z01. 84, “Encounter for antibody response examination,” if the antibody test is neither to confirm a current COVID-19 infection nor for follow-up of a known infection. For a current COVID-19 infection, report U07. 1 and codes for any manifestations.
What is positive celiac serology?
In patients with positive coeliac disease serology, the diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of characteristic small intestinal mucosal changes. The key diagnostic features are: intestinal histology showing raised intraepithelial lymphocytes (>25 per 100 enterocytes), crypt hyperplasia and villous atrophy (Figure 1)
What does code Z12 11 mean?
A screening colonoscopy should be reported with the following International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition (ICD-10) codes: Z12. 11: Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of the colon. Z80. 0: Family history of malignant neoplasm of digestive organs.
What is the blood test for celiac disease called?
tTG-IgA and tTG-IgG tests The tTG-IgA test is the preferred celiac disease serologic test for most patients. Research suggests that the tTG-IgA test has a sensitivity of 78% to 100% and a specificity of 90% to 100%.
What is the ICD-10 code for family history of celiac disease?
Family history of other diseases of the digestive system Z83. 79 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z83. 79 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for gluten sensitivity?
K90. 41 - Non-celiac gluten sensitivity | ICD-10-CM.
What is code 87635?
87635 Infectious agent detection by nucleic acid (DNA or RNA); severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (Coronavirus disease [COVID-19]), amplified probe technique.
What is the ICD-10 code for screening for Covid antibodies?
There are three codes for COVID-19 testing: 87635 is designed to detect the COVID-19 virus and effective March 13, 2020, and 86328 and 86769 will be used to identify the presence of antibodies to the COVID-19 virus and are effective April 10, 2020.
What is the CPT code for COVID-19 antibody test?
86769 — Antibody; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (Coronavirus disease [COVID-19]). Code 86328 should be used for antibody tests with a single-step method immunoassay — typically a strip with all the necessary components for the assay, appropriate for a point-of-care testing platform.
How does celiac disease affect the body?
Celiac disease affects each person differently. Symptoms may occur in the digestive system, or in other parts of the body. One person might have diarrhea and abdominal pain, while another person may be irritable or depressed. Irritability is one of the most common symptoms in children.
Is irritability a genetic disease?
Irritability is one of the most common symptoms in children. Some people have no symptoms.celiac disease is genetic. Blood tests can help your doctor diagnose the disease. Your doctor may also need to examine a small piece of tissue from your small intestine.
Can celiac disease cause malnutrition?
A person with celiac disease may become malnourished no matter how much food is consumed. A malabsorption syndrome that is precipitated by the ingestion of foods containing gluten, such as wheat, rye, and barley.
Does gluten affect the immune system?
If you have celiac disease and eat foods with gluten, your immune system responds by damaging the small intestine. Gluten is a protein in wheat, rye and barley. It is found mainly in foods but may also be in other products like medicines, vitamins and even the glue on stamps and envelopes.
What are the symptoms of celiac disease?
Physicians know a lot more about the disease than they used to, but diagnosis remains difficult. Stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, heartburn … these are common symptoms for a host of conditions, including celiac disease.
Where is gluten found?
Specifically, gluten is a protein found naturally in the grain of wheat, rye, oats, and barley. Gluten comes in many forms and is identified by any number of names. Patients diagnosed with celiac disease benefit from dietetic counseling to learn how to read labels and identify ingredients they cannot consume. Author.
Can celiac disease be treated without a cure?
Treatment for celiac disease is both simple and difficult. It’s simple because all patients have to do is abstain from all gluten to start feeling better. It’s difficult because gluten exists in practically every processed food.
Is gluten free a household word?
Today, it’s practically a household word — along with the term “gluten free.”. The disease is so prevalent, food manufacturers now label their applicable products “Gluten Free,” and a completely new category of gluten-free food products has entered the market.
Is celiac disease an autoimmune disease?
We now know celiac disease is an autoimmune disease characterized by an abnormal proximal small intestinal mucosa. It is associated with a permanent intolerance to gluten, and can present itself at any time in a person’s life. Symptoms may include those already mentioned, in addition to: bloating, weight loss, anxiety, anemia, skin rash, and dizziness.
What is a celiac test?
As a preliminary diagnostic test for persons with symptoms suggestive of celiac disease; or. To monitor response to a gluten-free diet; or. To screen first-degree relatives of individuals with celiac disease; or. To screen persons with type 1 diabetes for celiac disease.
What is serological testing?
Serological testing can be used to identify symptomatic individuals that need a confirmatory biopsy, to screen at-risk populations or to monitor diet compliance in patients previously diagnosed with CD. Thus, interpretation of serological testing requires consideration of the full clinical scenario.
Is a small intestinal biopsy required for CD?
Accepted guidelines indicate that small intestinal biopsy is still mandatory. Treatment of CD consists of excluding wheat, rye, barley, and oats from the diet for life. In the short-term, clinical studies have shown that this will permit normal growth, with achievement of the child's full growth potential.
Does gluten cause CD?
The toxic effects of gluten most likely result from an immunologic mechanism. Circulating antibodies to wheat fractions and other dietary proteins have been detected in the sera of patients with CD. Increased density of the intraepithelial lymphocytes in the small intestinal mucosa is a hallmark of the disease.
Is gluten a disease?
It is a lifelong disorder and affects both children and adults. It may present for the first time in either childhood or adult life. Gluten, which is the protein responsible for CD, is found in the grain of wheat, rye, oats, and barley. The toxic effects of gluten most likely result from an immunologic mechanism.
Can antibodies be used for CD?
Antibodies directed against native gliadin are not recommended for the primary detection of CD. AGA guidelines state that, combining several tests for CD in lieu of TTG IgA alone may marginally increase the sensitivity for CD but reduces specificity and therefore are not recommended in low-risk populations.
What is the first step in diagnosing celiac disease?
National guidelines and position statements agree that serologic testing is the first step in diagnosing celiac disease and that the IgA antibody to human recombinant tissue transglutaminase (tTG) test is recommended. (3-5) They all state that the IgA antibody to antiendomysium antibody (EMA) test has similar sensitivity and specificity to the tTG IgA test, but two of the national organizations mention that the EMA test is more prone to interpretation error. For individuals with known selective IgA deficiency, testing with tTG IgG and/or EMA IgG is recommended. The national organizations also agree that when test results are indeterminate, testing for the genetic markers HLA (human leukocyte antigen) -DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 is recommended. None of these guidelines and statements mentioned the newer deamidated gliadin peptide (DGP) antibody tests.
What is the best test for celiac disease?
Regarding serologic testing, they concluded that, in the primary care setting, the transglutaminase IgA antibody test is the most efficient single serologic test for diagnosing celiac disease. They state that the antiendomysial antibodies (EMA) IgA test is more time-consuming and operator dependent than the tTG. If IgA deficiency is strongly suspected, testing with IgG EMA and/or tTG IgG antibody test is recommended. If serologic test results are negative and celiac disease is still strongly suspected, providers can test for the presence of the disease-associated HLA alleles and, if present, perform small intestinal mucosal biopsy. Alternatively, if signs and symptoms suggest that small intestinal biopsy is appropriate, patients can proceed to biopsy without testing for HLA alleles. (4)
How common is celiac disease?
Celiac disease, which is also referred to as celiac sprue or gluten-sensitive enteropathy, is a relatively common disorder with variable clinical expression. Population-based screening surveys suggest a prevalence of 1 in 250–500 in most countries, including the U.S. However, this prevalence may vary widely depending on how the disease is defined, i.e., whether only clinically apparent cases are considered, as opposed to including all individuals with any serologic or histologic evidence of disease.
Does inclusion of a procedure, diagnosis or device code(s) constitute or imply member coverage or provider reimbursement?
Inclusion or exclusion of a procedure, diagnosis or device code(s) does not constitute or imply member coverage or provider reimbursement. Please refer to the member's contract benefits in effect at the time of service to determine coverage or non-coverage of these services as it applies to an individual member.

Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for adenomyosis of uterus
- 2. icd 10 cm code for mdd recurrent moderate
- 3. icd 10 code for liver metastatic unspecified
- 4. icd 10 cm code for rectal bleeding.
- 5. icd 10 code for periorbital contusion
- 6. icd 9 code for dens c2 fracture
- 7. icd 10 code for prophylasic fo phst herpatic neralgia
- 8. icd-10 code for externl cause jamming finger
- 9. icd 10 code for dyspepsia syndrome
- 10. icd 10 code for right rib fracture