What are the common ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM CATEGORY CODE RANGE SPECIFIC CONDITION ICD-10 CODE Diseases of the Circulatory System I00 –I99 Essential hypertension I10 Unspecified atrial fibrillation I48.91 Diseases of the Respiratory System J00 –J99 Acute pharyngitis, NOS J02.9 Acute upper respiratory infection J06._ Acute bronchitis, *,unspecified J20.9 Vasomotor rhinitis J30.0
What is the longest ICD 10 code?
What is the ICD 10 code for long term use of anticoagulants? Z79.01. What is the ICD 10 code for medication monitoring? Z51.81. How do you code an eye exam with Plaquenil? Here’s the coding for a patient taking Plaquenil for RA:Report M06. 08 for RA, other, or M06. Report Z79. 899 for Plaquenil use for RA.Always report both.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
How many ICD 10 codes are there?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...

What ICD-10 code covers homocysteine?
Serum homocysteine levels will not be covered other than for suspected B12/folate deficiency, or for risk stratification for the conditions noted in the ICD-10 Codes that Support Medical Necessity section of this Billing and Coding: Homocysteine Level, Serum A56675 article.
What does elevated homocysteine mean?
If your results show high homocysteine levels, it may mean: You are not getting enough vitamin B12, B6, or folic acid in your diet. You are at a higher risk of heart disease. Homocystinuria. If high levels of homocysteine are found, more testing will be needed to rule out or confirm a diagnosis.
What does homocysteine mean?
Homocysteine is an amino acid. Vitamins B12, B6 and folate break down homocysteine to create other chemicals your body needs. High homocysteine levels may mean you have a vitamin deficiency. Without treatment, elevated homocysteine increases your risks for dementia, heart disease and stroke.
Is homocysteine the same as homocystinuria?
Homocysteine is an intermediary amino acid formed by the conversion of methionine to cysteine (figure 1). Homocystinuria is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe elevations in plasma and urine homocysteine concentrations.
What is the blood test for homocysteine called?
A homocysteine test is a blood test. It measures the amount of homocysteine, an amino acid in the body. The test is often used to diagnose vitamin B6, B9 or B12 deficiency.
What does a homocysteine test show?
Description. The homocysteine blood test helps diagnose B6 and B12 Deficiency, as well as, a Folate Deficiency. It is also used to identify patients who may be at risk for heart disease and/or strokes.
What does low homocysteine mean?
Atypical homocysteine levels may indicate that a person has a deficiency in specific vitamins. It is also associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. Most people have low homocysteine levels. This is because the body breaks down the amino acid quickly into other compounds.
What is normal homocysteine level?
The normal range of homocysteine levels are less than 15 micromoles per liter (mcmol/L). Higher levels are: Moderate (15 to 30 mcmol/L)
How is homocystinuria diagnosed?
How Is Homocystinuria Diagnosed?genetic testing to look for one of the genes involved in the disorder.an amino acid screen of the blood and urine to check for excess homocysteine.a test to determine the body's response to consuming methionine.a liver biopsy and enzyme assay to check enzymatic activity.
What are the types of homocystinuria?
Classical Homocystinuria is divided into two types; Vitamin B6 responsive and Vitamin B6 non-responsive. This will be discussed more later. The second route of Homocysteine metabolism is the Remethylation Pathway that depends on Folate, a B vitamin. This pathway converts Homocysteine back to Methionine.
What deficiency causes homocystinuria?
In most cases, homocystinuria is caused by reduced activity of an enzyme known as cystathionine beta-synthase and this results in CBS deficiency.
What is the code for alcohol or drugs in blood?
code for findings of alcohol or drugs in blood (R78.-)
What is the code for a neonatal aspiration?
Neonatal aspiration of blood co-occurrent with respiratory symptoms; Neonatal aspiration of blood with pneumonia; Neonatal aspiration of blood with pneumonitis; code to identify any secondary pulmonary hypertension, if applicable (I27.2-)
What happens when homocysteine levels go above normal?
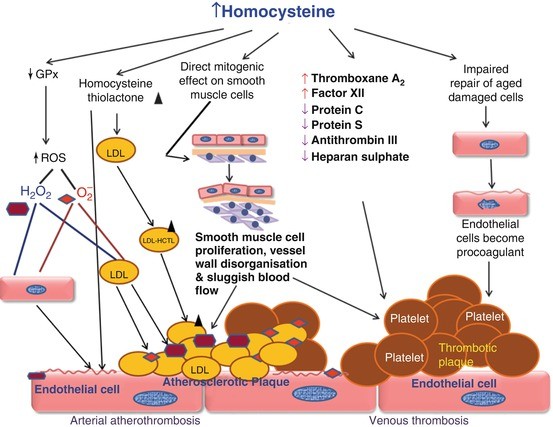
Like other health complications and disorders, Hyperhomocysteinemia is a critical vascular disorder that happens when the level of homocysteine in the human blood goes above normal values . It may react with other natural substances and create more complicated and lasting effects that are also hard to treat and recover. However, the excessive increase in the level of homocysteine will affect the vitamin-b complex family. This disorder itself does not cause any life threatening condition but it may produce some troublesome complications like increase risk of bone fractures and peripheral circulatory problems. This disorder can also lead to many vascular and cardiac issues. In general, Hyperhomocysteinemia directly influences and disturbs the arterial system and blood flow.
Why is homocysteine important?
Basically, the homocysteine is very important, fundamental and key substance for the growth of bones, muscles, tissues, vascular, and other body parts. The deficiency or increase in production of homocysteine may arise troublesome complications some which are irreversible.
What supplements are good for hyperhomocysteinemia?
The Vitamin B6, B9 & B12 supplements are the best to treat this medical condition. However, clinically there is no licensed treatment for hyperhomocysteinemia that is specifically designated for its treatment. People who have genetic predispositions towards hyperhomocysteinemia must avoid those actors that aggravate the level of homocysteine. As mentioned earlier only vitamins therapy is found to be beneficial in maintaining homocystein level so far. Many herbal alternatives are claimed to be effective in hyperhomocysteinemia but unfortunately non them is approved by US FDA.
Is homocysteine good for you?
The homocysteine is good for overall human health and this amino acid plays a key part to develop the tissues, muscles, bones and the bone mass. If there is any disturbance or deficiency, then the human body may suffer from critical problems. Similarly, if you observe the increase in amount or level of homocysteine in the blood, then more chronic infections and disorders will happen. However, there are very limited hyperhomocysteinemia symptoms which you can observe or come to know through medical checkups for the confirmation of this health condition. Some major signs of this disorder will be;
General Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2021 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
CMS National Coverage Policy
Title XVIII of the Social Security Act §1833 (e) prohibits Medicare payment for any claim which lacks the necessary information to process the claim.
Article Guidance
The information in this article contains billing, coding or other guidelines that complement the Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Homocysteine Level, Serum L34419.
ICD-10-CM Codes that Support Medical Necessity
The correct use of an ICD-10 code listed below does not assure coverage of a service. The service must be reasonable and necessary in the specific case and must meet the criteria specified in the Homocysteine Level, Serum L34419 LCD.
Bill Type Codes
Contractors may specify Bill Types to help providers identify those Bill Types typically used to report this service. Absence of a Bill Type does not guarantee that the article does not apply to that Bill Type.
Revenue Codes
Contractors may specify Revenue Codes to help providers identify those Revenue Codes typically used to report this service. In most instances Revenue Codes are purely advisory. Unless specified in the article, services reported under other Revenue Codes are equally subject to this coverage determination.
What is the CMS 410.32?
Under CMS National Coverage Policy - revised title for 42 CFR §410.32 ‘Indicates that diagnostic tests may only be ordered by the treating physician (or other treating practitioner acting within the scope of his or her license and Medicare requirements). Added title ‘Diagnostic Services Defined’ to CMS internet-only manual, Publication 100-02 Chapter 6 Section 20.4.1. Added title ‘Diagnosis Code Requirements’ to CMS internet-only manual Publication 100-08 Chapter 3 Section 3.4.1.3. Under Sources of Information and Basis for Decision – revised title of the eleventh article listed.
Does Medicare cover homocysteine?
Homocysteine levels will be covered by Medicare to confirm vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
Is homocysteine level necessary for CV?
Serum homocysteine levels for the evaluation of treatment of hyperhomocysteinemia in patients with CV risk factors will be denied as not medically necessary.
How is homocysteine formed?
Homocysteine (Hcy), a sulphur-containing amino acid, is formed from the conversion of methionine into cysteine. It is usually rapidly metabolized via 1 of 2 pathways:
What is the cause of homocystinuria?
The most common form of homocystinuria is caused by the lack of cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), a vitamin B6-dependent enzyme. Homocystinuria caused by CBS deficiency affects at least 1 in 200,000 to 335,000 people worldwide. Other forms of homocystinuria are much rarer. Moreover, the hallmarks of homocystinuria caused by CBS deficiency are developmental delay/mental retardation, ectopia lentis (dislocation of the ocular lens) and/or severe myopia, skeletal abnormalities as well as thrombo-embolism. There are two phenotypic variants of homocystinuria:
What is the name of the amino acid that is formed from the conversion of methionine into cysteine?
Excess levels in the blood are purported to increase the risk of stroke, certain types of heart disease or peripheral artery disease (PAD). Homocysteine (Hcy), a sulphur-containing amino acid, is formed from the conversion of methionine into cysteine. It is usually rapidly metabolized via 1 of 2 pathways:
Which pathway converts HCY to cysteine?
a vitamin B6-dependent trans-sulphuration pathway that converts Hcy to cysteine.
What is CPB 0536?
Assessment of borderline vitamin B12 deficiency, where the results will impact the member's management (see CPB 0536 - Vitamin B-12 Therapy ); or
Is homocysteine testing experimental?
Aetna considers homocysteine testing experimental and investigational for all other indications, including the following (not an all inclusive list) because its effectiveness for these indications has not been established: As a biomarker for the development and/or progression of erectile dysfunction.
Does HCY cause stroke?
While Hcy has been reported to exhibit atherogenic and prothrombotic properties, and histopathological hallmarks of Hcy-induced vascular injury include intimal thickening, elastic lamina disruption, smooth muscle hypertrophy, marked platelet accumulation, and the formation of platelet-enriched occlusive thrombi, its role in coronary heart disease and stroke is unclear. In randomized trials, reduction in Hcy levels has failed to lower overall risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lvertigo
- 2. 2018 icd 10 code for removal swanz ganznon-st-elevation myocardial infarction
- 3. icd 10 code for muscular calcification and ossification
- 4. icd 10 code for behavior problem in child
- 5. icd 10 code for abnormal ultrasound findings in pregnancy
- 6. icd 10 code for superficial blister on palm of right hand
- 7. the icd-10-cm code for nemaline myopathy is________.
- 8. icd 10 code for strain of muscle fascia and tendon of the posterior muscle
- 9. icd 10 code for local finger infection
- 10. icd 10 code for getd