photochromogenic (acid-fast bacilli) (pulmonary) A31.0 nonpulmonary A31.9 Mycobacterium, mycobacterial (infection) A31.9 atypical A31.9
What is the ICD 10 code for tuberculosis of lung?
Tuberculosis of lung 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code A15.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM A15.0 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary mycobacterial infection?
Pulmonary mycobacterial infection 1 A31.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM A31.0 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of A31.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 A31.0 may differ.
What is the latest ICD 10 version for lung disorders?
Other disorders of lung. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM J98.4 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J98.4 - other international versions of ICD-10 J98.4 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for unspecified bacterial pneumonia?
Unspecified bacterial pneumonia. J15.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM J15.9 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J15.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 J15.9 may differ.
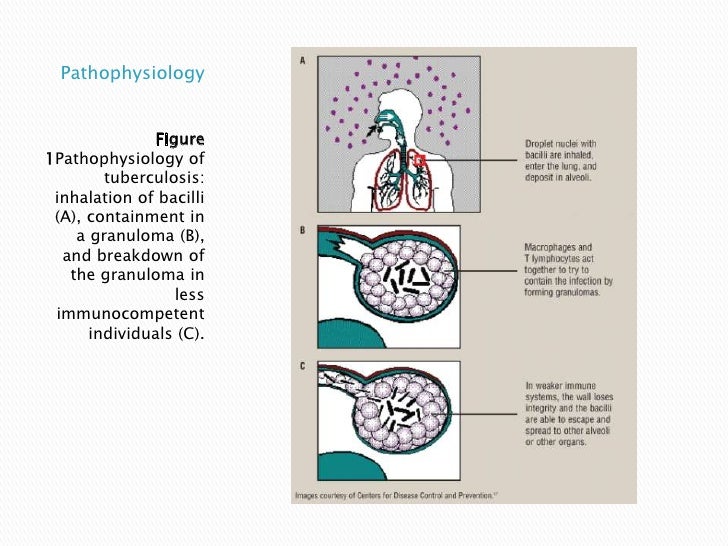
What is MAC disease of the lungs?
MAC lung disease is an infection caused a group of bacteria called Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). MAC includes two closely related species, Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare, and may also be referred to as MAI.
What is a pulmonary mycobacterial infection?
Mycobacterial lung infections are caused by a group of bacteria, mycobacteria, that includes the causative-agents of tuberculosis (TB) and leprosy. There are also nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM), ubiquitous in soil, water, food, on the surfaces of many plants and within buildings, particularly within water pipes.
What is the ICD-10 code for respiratory tuberculosis?
Z11. 1: “encounter for screening for respiratory tuberculosis now includes “encounter for screening for active tuberculosis disease.”
What is the code for nodular pulmonary tuberculosis?
A15. 0 - Tuberculosis of lung. ICD-10-CM.
What is the difference between NTM and MAC?
NTM includes a number of different species, but the most common one causing disease is MAC. MAC is not spread person to person like Mtb. MAC is not contagious. MAC lung disease seen in HIV (-) (non-AIDS) patients is a chronic lung infection and is often misdiagnosed as chronic bronchitis or recurrent pneumonia.
What is nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease?
Nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) lung disease is a general term for a group of disorders characterized by exposure to specific bacterial germs known as mycobacteria. These germs are found in the water and soil and are common throughout the environment as a whole. They usually do not cause illness.
What is I10 diagnosis?
ICD-Code I10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Essential (Primary) Hypertension.
What is the ICD-10 code for positive TB test?
ICD-10-CM Code for Nonspecific reaction to tuberculin skin test without active tuberculosis R76. 11.
How do you code a TB test?
To bill for placing the purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test for tuberculosis, use CPT®code 86580. Use this code when the nurse or medical assistant places the test on the patient's skin. The CPT®definition of the code is: Skin test, tuberculosis, intradermal.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
10 for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is Koch's infection?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs. The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from person to person through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes.
What is R76 12?
ICD-10 code R76. 12 for Nonspecific reaction to cell mediated immunity measurement of gamma interferon antigen response without active tuberculosis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Why are mycobacteria called acid fast bacilli?
Mycobacteria are called acid-fast bacilli because they are rod-shaped bacteria (bacilli) that can be seen under the microscope following a staining procedure in which the bacteria retain the color of the stain after an acid wash (acid-fast). A few different tests may be used to help identify AFB as the cause of an infection: ...
What is AFB in medical terms?
To help diagnose tuberculosis (TB) and infections caused by other Mycobacterium species, which are known as acid-fast bacilli (AFB), in people at risk of developing mycobacterial infections; to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. When To Get Tested?
What is MAC in TB?
Some examples include Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC), which can cause lung infection and disseminated disease in people with weakened immune systems. (See the article on Nontuberculous Mycobacteria for more details on different types). In addition to TB, AFB testing can help identify infections caused by these nontuberculous ...
What is AFB test?
AFB laboratory tests detect the bacteria in a person's sample and help identify an infection caused by AFB. There are several types of AFB that may be detected with this testing; however, the most common and medically important ones are members of the genus Mycobacterium.
When is sputum collected for tuberculosis?
For suspected cases of tuberculosis lung infections, usually three sputum samples are collected early in the morning on different days. If you are unable to produce sputum, a bronchoscope may be used to collect fluid during a procedure called a bronchoscopy. In children, gastric washings/aspirates may be collected.
Can TB be detected outside the lungs?
If the healthcare practitioners suspect TB is present outside of the lungs (extra pulmonary), they may test the body fluids and tissues most likely affected. For instance, one or more urine samples may be collected if the practitioner suspects TB has infected the kidneys.
Can a child have a gastric aspirate?
In children, gastric washings/aspirates may be collected. Depending on symptoms, urine, an aspirate from the site of suspected infection, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), other body fluids, or biopsied tissue samples may be collected for AFB testing.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of bone marrow transplant
- 2. icd 10 code for uti proteus mirabilis
- 3. icd 10 code for postpartum dilation and curettage
- 4. icd 10 code for left tka revision
- 5. icd 10 code for chronic intractable pain due to degenerative disc disease
- 6. icd 10 code for multilevel ddd lumbar region
- 7. icd 10 cm code for right toenail infection
- 8. icd 10 code for screening for malignant neoplasm of the ovaries
- 9. icd 10 code for attention to urostomy
- 10. icd 10 code for l shin stasis ulcer