Disorder of bile acid and cholesterol metabolism, unspecified
- E78.70 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Disorder of bile acid and cholesterol metabolism, unsp
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E78.70 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E78.70 -...
What is the ICD 10 code for peptic ulcer?
Peptic ulcer, site unspecified, unspecified as acute or chronic, without hemorrhage or perforation. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. K27.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Peptic ulc, site unsp, unsp as ac or chr, w/o hemor or perf.
What is the ICD 10 code for dyspepsia?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K30. Functional dyspepsia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. K30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for E79?
E79.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E79.0 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E79.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 E79.0 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 for reflux without esophagitis?
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K21.9 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K21.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 K21.9 may differ.

What is the ICD-10 code for peptic ulcer disease?
ICD-10 code K27. 9 for Peptic ulcer, site unspecified, unspecified as acute or chronic, without hemorrhage or perforation is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD-10 code for heartburn?
ICD-10 code R12 for Heartburn is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for healed gastric ulcer?
ICD-10-CM Code for Gastric ulcer, unspecified as acute or chronic, without hemorrhage or perforation K25. 9.
Is a gastric ulcer the same as a peptic ulcer?
Ulcers. A peptic ulcer is a sore on the lining of your stomach, small intestine or esophagus. A peptic ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer. A duodenal ulcer is a peptic ulcer that develops in the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
What is the diagnosis code K21 9?
ICD-10 code: K21. 9 Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease without oesophagitis.
What is the CPT code for acid reflux?
CPT® 91034, Under Gastroesophageal Reflux Test Studies The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) code 91034 as maintained by American Medical Association, is a medical procedural code under the range - Gastroesophageal Reflux Test Studies.
What is the ICD-10 code for reflux esophagitis?
01 - Gastro-esophageal reflux disease with esophagitis, with bleeding is a sample topic from the ICD-10-CM. To view other topics, please log in or purchase a subscription. ICD-10-CM 2022 Coding Guide™ from Unbound Medicine.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of gastric ulcers?
Z87. 11 - Personal history of peptic ulcer disease. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for epigastric pain?
ICD-10 code R10. 13 for Epigastric pain is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the difference between gastritis and peptic ulcer disease?
Peptic ulcer disease and gastritis A peptic ulcer is a sore or crater in the lining of the stomach or first portion of the small intestine (duodenum). Gastritis is inflammation (redness, swelling, irritation) of the lining of the stomach.
What are the 4 types of ulcers?
The different types of ulcersarterial ulcers.venous ulcers.mouth ulcers.genital ulcers.
How many types of peptic ulcer are there?
There are two different types of peptic ulcers. They are: Gastric ulcers, which form in the lining of the stomach. Duodenal ulcers, which form in the upper small intestine.
What causes gastric ulcers?
Stomach ulcers are usually caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These can break down the stomach's defence against the acid it produces to digest food. The stomach lining then becomes damaged causing an ulcer to form.
Can gastric ulcer be cured?
With treatment, most ulcers heal in a few months. If your stomach ulcer is caused by a Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacterial infection, a course of antibiotics and a medication called a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) is recommended.
What is the difference between duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer?
Gastric and duodenal ulcers are peptic ulcers, which are open sores in the lining of the digestive tract. Gastric ulcers form in the lining of the stomach. Duodenal ulcers develop in the lining of the duodenum, which is the upper part of the small intestine.
Which ulcer is worse with food?
Stomach ulcers often are not consistent. For example, eating sometimes will make the pain worse rather than better with certain types of ulcers, such as pyloric channel ulcers, which are often associated with bloating, nausea and vomiting, symptoms of a blockage caused by swelling (edema) and scarring.
GERD
Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a digestive system disorder in which the stomach acid flows back to esophagus. This can damage the tissue lining of esophagus and makes it difficult to pass food. It is a common digestive system disorder affecting millions of people throughout the world.
Stomach- Esophagus-Reflux
After we swallow food it goes to esophagus, and the opening called sphincter (valve) opens to allow the food pass into stomach. Then the valve closes. When GERD happens, Sphincter does not close properly and this causes stomach acid and juices flow back to esophagus.
GERD ICD 10 Codes and guidelines
Location in ICD-10-CM manual – It is located in chapter 11 (Diseases of digestive system) – code range K00 to K95.
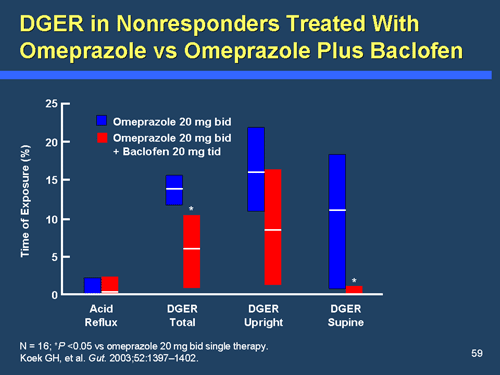
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for neurocognitive disorder
- 2. icd 10 cm code for neonatal pyoderma
- 3. icd 10 code for testosterone women children
- 4. icd 10 code for strain of muscle fascia and tendon of the posterior muscle group
- 5. icd-10 code for nausea and vomiting due to chemotherapy
- 6. what is the correct icd 10 code for left submandibular sialadenitis
- 7. what is the 2018 icd 10 code for vallecular lesion
- 8. icd-10 code for duodenal stenosis
- 9. icd 10 code for peritoneal lesion
- 10. icd 10 cm code for screening mammogram