What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is the ICD - 10 code for brain stem stroke?
ICD-10 code G46.3 for Brain stem stroke syndrome is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -Episodic and paroxysmal disorders .
What is the ICD 10 code for history of cirrhosis?
Unspecified cirrhosis of liver
- K74.60 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K74.60 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K74.60 - other international versions of ICD-10 K74.60 may differ.
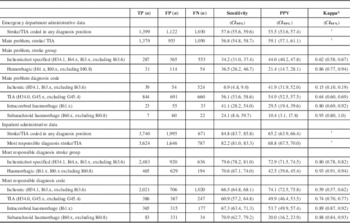
What is the ICD-10 code for acute stroke due to ischemia?
I63. 50 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I63. 50 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD code for stroke?
For ischaemic stroke, the main codes are ICD-8 433/434 and ICD-9 434 (occlusion of the cerebral arteries), and ICD-10 I63 (cerebral infarction).
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA unspecified?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cerebral infarction, unspecified I63. 9.
What are acute strokes?
Acute strokes, also known as cerebrovascular accidents, are broadly classified as either ischemic or hemorrhagic. Acute strokes result in loss of blood flow, nutrients and oxygen to a region of the brain, resulting in neuronal damage and subsequent neurological deficits.
How do you code an acute stroke?
Acute Ischemic Stroke (ICD-10 code I63.
What is ICD-10 code for history of stroke?
73 for Personal history of transient ischemic attack (TIA), and cerebral infarction without residual deficits is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the difference between stroke and acute stroke?
An acute stroke, like most forms of stroke, starts suddenly and worsens rapidly. Some strokes may be preceded by a transient ischemic attack (TIA), a temporary stroke that resolves before causing any lasting effects.
Is a stroke acute or chronic?
Long Term Outcome of Stroke: Stroke is a chronic disease with acute events - PMC.
What is the acute Stroke Unit?
The Acute Stroke Unit is an acute neurological ward providing specialist services for people who have had a new suspected stroke.
How is a stroke classified?
Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810) A stroke is a medical emergency.
What is the term for a loss of blood flow to the brain?
An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries. In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
Explicitly document findings to support diagnoses of › Stroke sequela codes (ICD-10 category I69.-) should acute stroke, stroke and subsequent sequela of be used at the time of an ambulatory care visit stroke, and personal history of stroke without sequela, oce, which is considered subsequent to any acute
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue?
stroke occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue, this leads to ischemia (deprivation of oxygen) and potentially infarction (dysfunctional scar tissue). Strokes can be either hemorrhagic, or embolic/thrombotic. Hemorrhagic strokes occur as a result of a ruptured cerebral blood vessel. Embolic/thrombic strokes occur as a result of an obstructed cerebral vessel.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
In ICD-10 CM, code category I63 should be utilized when the medical documentation indicates that an infarction or stroke has occurred. Coding of sequelae of stroke and infarction also demands a level of detail often missing in medical records. There are specific codes which indicate the cause of the infarction, such as embolism or thrombosis, as well as the specific affected arteries. The sixth digit provides additional information which designates the affected side when applicable.
What is the ICD-10 code for cerebral infarction?
The patient is admitted into hospital and diagnosed with cerebral infarction, unspecified ( ICD-10 code I63.9). At the 3-week post-discharge follow-up appointment for the cerebral infarction, the office visit note states the patient had a stroke and has a residual deficit of hemiplegia, affecting the right dominant side.
Can I60-I69 be used for a CT scan?
Codes I60-I69 should never be used to report traumatic intracranial events. Normally, do not report codes from I80-I67 with codes from I69. ...
Is unilateral weakness a symptom of stroke?
Documentation of unilateral weakness in conjunction with a stroke is considered by the ICD to be hemiparesis/hemiplegia due to the stroke and should be reported separately. Hemiparesis is not considered a normal sign or symptom of stroke and is always reported separately. If the patient’s dominant side is not documented, ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. billiable icd 10 code for spinal decompression
- 2. icd 10 code for gastroenterology
- 3. icd 9 code for gait disturbance
- 4. icd 10 code for mild shortness of breath
- 5. icd 10 code for left 3rd toe osteomyelitis
- 6. icd-10-cm pcs code for respiratory nebulizer treatment ??
- 7. icd 10 code for rheumatoid bursitis of the right foot and ankle
- 8. icd 10 code for left chest wound
- 9. icd 20 code for complication of a leg brace
- 10. the icd 10 cm code for ataxa