What is the ICD 10 code for resp failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute and chronic respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. J96.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Acute and chr resp failure, unsp w hypoxia or hypercapnia
What are the signs and symptoms of acute respiratory failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute and chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. J96.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.21 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the criteria for chronic respiratory failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute and chronic respiratory failure with hypercapnia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. J96.22 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.22 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the clinical indicators of acute respiratory failure?
ICD-10 code J96.2 for Acute and chronic respiratory failure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
How do you code acute on chronic respiratory failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure J96. 2.
Can you have acute and chronic respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure comes on quickly, and it's an emergency. But respiratory failure can also be chronic, a long-term problem that you'll need regular care to manage.Jan 31, 2021
What is the ICD 10 code for acute on chronic Hypercarbic respiratory failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia J96. 20.
What is the difference between acute respiratory failure and chronic respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure is a short-term condition. It occurs suddenly and is typically treated as a medical emergency. Chronic respiratory failure, however, is an ongoing condition. It gradually develops over time and requires long-term treatment.
How can you differentiate acute and chronic type 2 respiratory failure?
Acute hypercapnic respiratory failure develops over minutes to hours; therefore, pH is less than 7.3. Chronic respiratory failure develops over several days or longer, allowing time for renal compensation and an increase in bicarbonate concentration. Therefore, the pH usually is only slightly decreased.Apr 7, 2020
How do you differentiate acute and chronic respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosisAcute: Expected decrease in pH = 0.08 x (measured PaCO2 - 40)Chronic: Expected drop in pH = 0.03 x (measured PaCO2 - 40)
What is acute on chronic respiratory failure?
Acute-on-chronic respiratory failure (ACRF) occurs when relatively minor, although often multiple, insults cause acute deterioration in a patient with chronic respiratory insufficiency.
When do you code acute respiratory failure as a secondary diagnosis?
If it occurs after admission or it is present on admission but does not meet the definition of principal diagnosis, respiratory failure may be listed as a secondary diagnosis.
What is chronic respiratory failure?
Chronic respiratory failure is a condition that results in the inability to effectively exchange carbon dioxide and oxygen, and induces chronically low oxygen levels or chronically high carbon dioxide levels.
What are the two types of respiratory failure?
Examples of type I respiratory failures are carcinogenic or non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema and severe pneumonia. Type 2 (hypercapnic) respiratory failure has a PaCO2 > 50 mmHg. Hypoxemia is common, and it is due to respiratory pump failure.Nov 26, 2021
What is the nursing diagnosis for acute respiratory failure?
Commonly used NANDA-I nursing diagnoses for patients experiencing decreased oxygenation and dyspnea include Impaired Gas Exchange, Ineffective Breathing Pattern, Ineffective Airway Clearance, Decreased Cardiac Output, and Activity Intolerance.
Is acute respiratory failure the same as COPD?
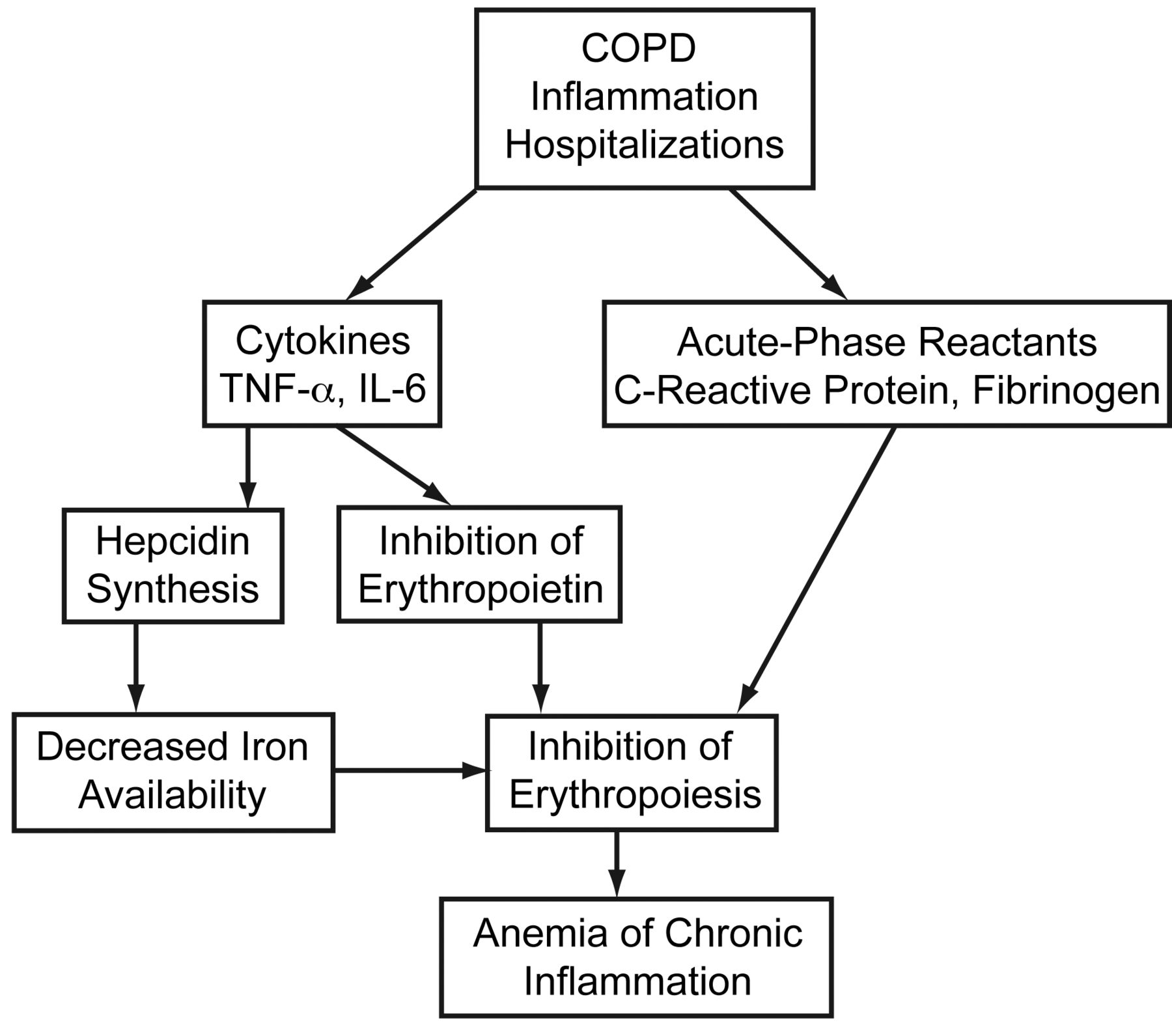
Summary. Many patients with COPD have acute exacerbations that lead to acute respiratory failure and require hospitalization. It is important to understand the pathophysiology of COPD and what leads to acute respiratory failure in these patients.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute respiratory failure?
J96.2 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
What is a 3 character code?
A 3-character code is to be used only if it is not further subdivided. A code is invalid if it has not been coded to the full number of characters required for that code, including the 7 th character, if applicable.
What is the code for acute respiratory failure?
code from subcategory J96.0, Acute respiratory failure, or subcategory J96.2, Acute and chronic respiratory failure, may be assigned as a principal diagnosis when it is the condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for occasioning the admission to the hospital, and the selection is supported by the Alphabetic Index and Tabular List. However, chapter-specific coding guidelines (such as obstetrics, poisoning, HIV, newborn) that provide sequencing direction take precedence.
What does "N" mean in a COPD code?
Assign “N” if at least one of the clinical concepts included in the code was not present on admission (e.g., COPD with acute exacerbation and the exacerbation was not present on admission; gastric ulcer that does not start bleeding until after admission; asthma patient develops status asthmaticus after admission).
What is the principal diagnosis?
The principal diagnosis is defined in the Uniform Hospital Discharge Data Set (UHDDS) as “that condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for occasioning the admission of the patient to the hospital for care.”
Is respiratory failure a secondary diagnosis?
Respiratory failure may be listed as a secondary diagnosis if it occurs after admission, or if it is present on admission, but does not meet the definition of principal diagnosis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of preeclampsia currently pregnant
- 2. icd 10 code for cognitive deficits
- 3. icd 10 code for left hallux amputation status
- 4. icd code for external cause - wilderness
- 5. 2016 icd 10 code for ventral hernia
- 6. icd 10 cm code for peripheral vascular disease
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for double lung transplant
- 8. icd 10 cm code for postoperative mrsa
- 9. icd code for graves disease
- 10. icd 10 code for individual psychotherapy