How do I diagnose acute pulmonary embolism?
The system used most often is the Wells scoring system, which takes into account whether: 2
- Symptoms suggesting deep vein thrombosis are present
- All other possible diagnoses seem less likely than a pulmonary embolus
- Heart rate is over 100 beats per minute
- A history of recent surgery or other immobilization
- A prior history of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolus
- Presence of hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Presence of cancer
Is pulmonary embolism a deadly disease?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and potentially deadly form of venous thromboembolic disease. It is the third most common cause of cardiovascular death and is associated with multiple inherited and acquired risk factors as well as advanced age.
What is new in acute pulmonary embolism?
in combination with anticoagulation to anticoagulation alone for the treatment of acute, intermediate-high-risk pulmonary embolism (PE). Each year nearly one million patients in the US and Europe are affected by PE, a blood clot causing a blockage in one ...
Are You having symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
There are some common signs, but you also may have no symptoms beforehand. Pain, tenderness, swelling, and redness in the area where a blood clot is blocking circulation might precede a pulmonary embolism. 7 These symptoms of deep vein thrombosis should be discussed immediately with your doctor.
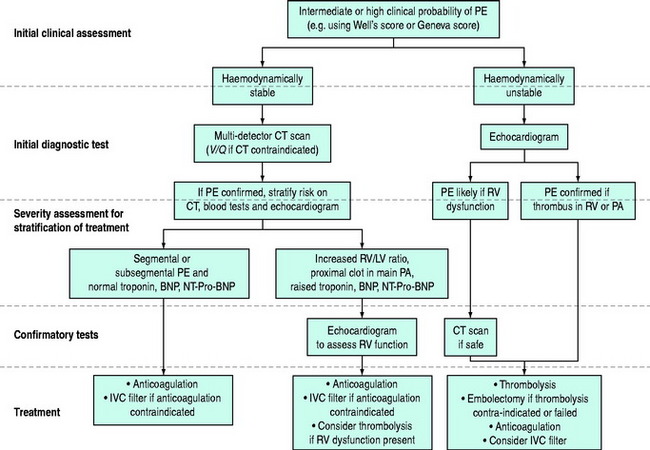
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral pulmonary embolism?
ICD-10 code I26. 9 for Pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is a bilateral pulmonary embolism?
Bilateral massive pulmonary thromboembolism is a life-threatening condition wherein patients present with circulatory and respiratory collapse. These patients require either thrombolysis or an intervention such as thrombectomy performed by a specialized cardiovascular thoracic surgeon to obtain a good outcome.
What is the ICD code for pulmonary embolism?
We used ICD-10 codes (I26. 9: pulmonary embolism without cor pulmonale, and I26. 0: pulmonary embolism with cor pulmonale) to identify patients diagnosed with PE; we refer to these identified patients as the coded PE group (Fig.
What is the cause of bilateral pulmonary embolism?
In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from deep veins in the legs or, rarely, from veins in other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis). Because the clots block blood flow to the lungs, pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening.
What are the different types of pulmonary embolism?
Based on location of the clot into pulmonary artery following terms are used A) saddle PE (large clot into main pulmonary artery), B) lobar PE (into big branch of pulmonary artery), or C) distal PE (into small branches of pulmonary artery).
What is pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale?
Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) is the prototype for acute cor pulmonale. Acute obstruction of the pulmonary vasculature may lead to acute right-sided heart failure, and at times, total cardiovascular collapse.
What is the ICD 10 code for history of pulmonary embolism?
Z86.711Personal history of pulmonary embolism Z86. 711 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z86. 711 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary embolism and infarction?
415.19 - Other Pulmonary Embolism and Infarction [Internet]. In: ICD-10-CM.
What is acute pulmonary thromboembolism?
An acute pulmonary embolism, or embolus, is a blockage of a pulmonary (lung) artery. Most often, the condition results from a blood clot that forms in the legs or another part of the body (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT) and travels to the lungs.
What is Virchow's triad?
The three factors of Virchow's triad include intravascular vessel wall damage, stasis of flow, and the presence of a hypercoagulable state.
What is the difference between embolism and thrombosis?
Thrombosis occurs when a thrombus, or blood clot, develops in a blood vessel and reduces the flow of blood through the vessel. Embolism occurs when a piece of a blood clot, foreign object, or other bodily substance becomes stuck in a blood vessel and largely obstructs the flow of blood.
What causes pulmonary embolism in lungs?
A pulmonary embolism happens when a blood vessel in your lungs becomes blocked. Most of the time, this blockage is caused by a blood clot and happens suddenly. Usually, a pulmonary embolism is caused by a blood clot travelling up from one of the deep veins in your body, usually in the leg.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is the term for the closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches?
The closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung. The obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for ulcer left toe
- 2. icd 10 code for personal history of hernia
- 3. icd 10 cm code for atrail fibrillation
- 4. icd 10 code for bleeding from tracheostomy site
- 5. icd 9 code for axillary lymphadenopathy
- 6. icd-10 code for induction of labor
- 7. icd 10 code for work note
- 8. icd 10 code for mucocele of appendix
- 9. icd 10 code for complication of epidural injection
- 10. icd 10 code for mentor