What is the ICD 10 code for history of pancreatitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K85.1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K85.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 K85.1 may differ. Applicable To Gallstone pancreatitis The following code (s) above K85.1 contain annotation back-references that may be applicable to K85.1 : K00-K95
How is MRCP used in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis?
Acute biliary pancreatitis; Gallstone pancreatitis; Pancreatitis (inflammation of pancreas) from gallstone; Gallstone pancreatitis ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K85.1 Biliary acute pancreatitis
What are the criteria for acute pancreatitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K85.9 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K85.9 Acute pancreatitis, unspecified 2016 2017 - Converted to Parent Code 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code K85.9 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is the ICD 10 code for pancreatic cancer?
Oct 01, 2021 · Biliary acute pancreatitis without necrosis or infection. 2017 - New Code 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. K85.10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K85.10 became effective on October 1, 2021.
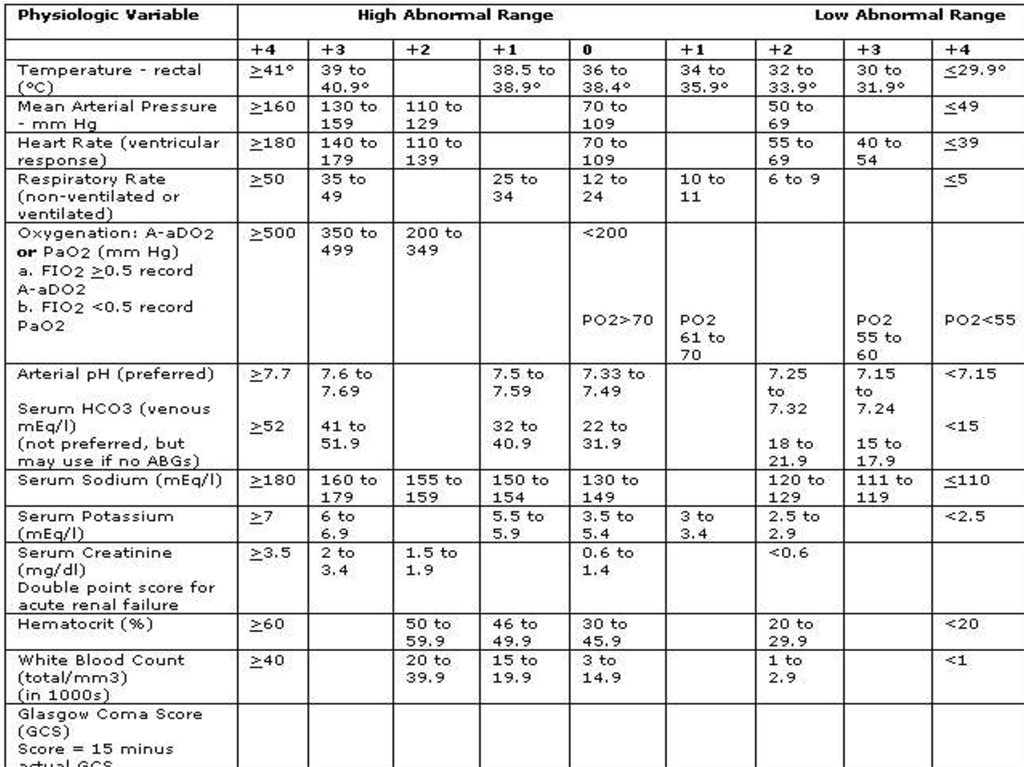
How do you code gallstones for pancreatitis?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K85. 1: Biliary acute pancreatitis.
What is acute gallstone pancreatitis?
Gallstone pancreatitis occurs when a gallstone blocks your pancreatic duct causing inflammation and pain in your pancreas. Gallstone pancreatitis causes severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, and/or jaundice. If untreated, gallstone pancreatitis can cause serious complications.
What is the ICD 10 code for Acute pancreatitis?
90 for Acute pancreatitis without necrosis or infection, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
Is gallstone pancreatitis the same as Acute pancreatitis?
This causes a backup of fluid that can travel up both the bile duct and the pancreatic duct. Gallstone pancreatitis can be very painful and life-threatening if not treated. Gallstones are the leading cause of short-term (acute) pancreatitis.
What is a gallbladder stone?
Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile that can form in your gallbladder. Bile is a digestive fluid produced in your liver and stored in your gallbladder.Aug 20, 2021
What is the pathophysiology of gallstones pancreatitis?
Gallstone-induced pancreatitis is caused by duct obstruction by gallstone migration. Obstruction is localized in the bile duct and pancreatic duct, or both. Duct obstruction promotes pancreatitis by increasing duct pressure and subsequent unregulated activation of digestive enzymes[9].
What is the ICD-10 code for gallstones?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cholelithiasis K80.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute and chronic pancreatitis?
ICD-10 code K86. 1 for Other chronic pancreatitis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the CPT code for pancreatitis?
CPT® Code 48000 in section: Placement of drains, peripancreatic, for acute pancreatitis.
Can gallbladder stones cause pancreatitis?
Gallstones are a common cause of pancreatitis. Gallstones, produced in the gallbladder, can slip out of the gallbladder and block the bile duct, stopping pancreatic enzymes from traveling to the small intestine and forcing them back into the pancreas.
How are the pancreas and gallbladder related?
Biliary and Pancreatic Ducts The small tubes that carry bile between the liver, gallbladder and small intestine are called biliary or bile ducts. The pancreatic duct connects the pancreas to the common bile duct.
Can gallstones form without a gallbladder?
About 1 in 7 people with gallstones will develop stones in the common bile duct. This is the small tube that carries bile from the gallbladder to the intestine. Risk factors include a history of gallstones. However, choledocholithiasis can occur in people who have had their gallbladder removed.
What hormones are released by the pancreas?
The pancreas also releases the hormones insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream. Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. It happens when digestive enzymes start digesting the pancreas itself. Pancreatitis can be acute or chronic. Either form is serious and can lead to complications.
What is the code for biliary acute pancreatitis?
K85.10 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of biliary acute pancreatitis without necrosis or infection. The code K85.10 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
How long does pancreatitis last?
Either form is serious and can lead to complications. Acute pancreatitis occurs suddenly and usually goes away in a few days with treatment. It is often caused by gallstones. Common symptoms are severe pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, and vomiting.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code K85.10 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
Where is the pancreas located?
Information for Patients. Pancreatitis. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the first part of the small intestine. It secretes digestive juices into the small intestine through a tube called the pancreatic duct.
Does pancreatitis heal?
Chronic pancreatitis does not heal or improve. It gets worse over time and leads to permanent damage. The most common cause is heavy alcohol use. Other causes include cystic fibrosis and other inherited disorders, high levels of calcium or fats in the blood, some medicines, and autoimmune conditions.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 procedure code for a percutaneous repair of the left knee joint?
- 2. icd 10 code for herniated disc with radiculopathy
- 3. icd 10 cm code for pain suprapubic area
- 4. icd 10 cm code for hx r ovarian germ cell tumor
- 5. icd 10 cm code for hodgkin’s sarcoma of thoracic lymph nodes
- 6. icd-10-cm code for seizures
- 7. icd 10 code for oxygen use
- 8. icd 10 cm code for forehead bruising
- 9. icd 10 code for muscle impingement
- 10. 2016 icd code for tachypnea of the newborn