What are the signs and symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke?
The signs of a stroke are:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden confusion
- Sudden trouble speaking
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Sudden, severe headache with no known cause
How is a hemorrhagic stroke diagnosed?
- A very severe headache that starts suddenly (Some people describe it like a "thunderclap.")
- Loss of consciousness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Inability to look at bright light
- Stiff neck
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Seizure
- Loss of consciousness
What are the ICD 10 codes for stroke?
- Code: I63.
- Code Name: ICD-10 Code for Cerebral infarction.
- Block: Cerebrovascular diseases (I60-I69)
- Excludes 1: transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes (G45.-)
- Details: Cerebral infarction.
- Includes: occlusion and stenosis of cerebral and precerebral arteries, resulting in cerebral infarction.
What is a basal ganglia hemorrhage?
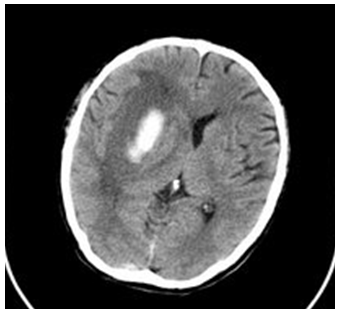
The basal ganglia hemorrhage can be defined as a form of hemorrhage that occurs inside the brain, being primarily caused by a hypertension that was poorly kept under control. The patients who suffer from this form of hemorrhage also present the signs of chronic hypertensive encephalopathy. It is important to remember that the hemorrhages caused ...

What is the ICD-10 code for basal ganglia hemorrhage?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I61. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I61.
What is basal ganglia hemorrhage?
Basal ganglia hemorrhage is a common form of intracerebral hemorrhage, and usually as a result of poorly controlled long-standing hypertension. The stigmata of chronic hypertensive encephalopathy are often present (see cerebral microhemorrhages). Other sites of hypertensive hemorrhages are the pons and the cerebellum.
Is basal ganglia hemorrhage a stroke?
The blood vessels in the basal ganglia are especially small and vulnerable to tearing or rupture. This is why basal ganglia strokes are often hemorrhagic strokes as well. About 13 percent of all strokes are hemorrhagic strokes.
What is the ICD-10 code for basal ganglia stroke?
I63. 319 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I63. 319 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What part of the brain is the basal ganglia?
The structures generally included in the basal ganglia are the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus in the cerebrum, the substantia nigra in the midbrain, and the subthalamic nucleus in the diencephalon. The word basal refers to the fact that the basal ganglia are found near the base, or bottom, of the brain.
What is acute left basal ganglia infarct?
This type of stroke occurs when blood leaks from a burst, torn, or unstable blood vessel into the tissue in the brain. The buildup of blood can create swelling, pressure, and, ultimately, brain damage.
Is a basal ganglia stroke a lacunar stroke?
A stroke in a deep area of the brain (for example, a stroke in the thalamus, the basal ganglia or pons) is called a lacunar stroke. These deeper structures receive their blood flow through a unique set of arteries.
What causes basal ganglia?
Calcium build-up in your basal ganglia can also happen because of infection, problems with your parathyroid gland, and for other reasons. When it happens this way, it is also known as basal ganglia calcification, but is different from the genetic form of the disease.
What happens when the basal ganglia is damaged?
Damage to the basal ganglia cells may cause problems controlling speech, movement, and posture. This combination of symptoms is called parkinsonism. A person with basal ganglia dysfunction may have difficulty starting, stopping, or sustaining movement.
What is basal ganglia lacunar infarct?
Lacunar infarcts are small infarcts (2–20 mm in diameter) in the deep cerebral white matter, basal ganglia, or pons, presumed to result from the occlusion of a single small perforating artery supplying the subcortical areas of the brain.
What is the ICD code for hemorrhagic stroke?
The PPV and sensitivity of the ICD-10-CM codes of I60 or I61 for identifying acute hemorrhagic stroke were 88.6% and 98.6%, respectively.
What does ICD 10 code I63 9 mean?
ICD-10 code: I63. 9 Cerebral infarction, unspecified.
The ICD code I61 is used to code Silent stroke
A silent stroke is a stroke that does not have any outward symptoms associated with stroke, and the patient is typically unaware they have suffered a stroke.
Coding Notes for I61.0 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #020-022 - Intracranial vascular procedures with pdx hemorrhage with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'I61.0 - Nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage in hemisphere, subcortical'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code I61.0. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code I61.0 and a single ICD9 code, 431 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2017 icd 10 cm code for sleep-disordered breathing
- 2. icd-10 code for diabetic gastroparesis type 1
- 3. icd 10 code for parotid cyst
- 4. icd 10 code for acute pulmonary embolus
- 5. icd 10 code for right a calcification
- 6. what icd 10 code to assign for a patient that comes for acucheck training
- 7. what is the correct icd 10 code for colotomy stricture
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for flank pain
- 9. icd 10 code for history of cancer
- 10. icd 10 cm code for grand multipara.