What are the causes of acute respiratory failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. J96.02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.02 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the signs and symptoms of acute respiratory failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute and chronic respiratory failure with hypercapnia. J96.22 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.22 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the criteria for chronic respiratory failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · J96.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Acute respiratory failure, unsp w hypoxia or hypercapnia. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What are the complications of respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia (J96.02) J96.01 J96.02 J96.1 ICD-10-CM Code for Acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia J96.02 ICD-10 code J96.02 for Acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
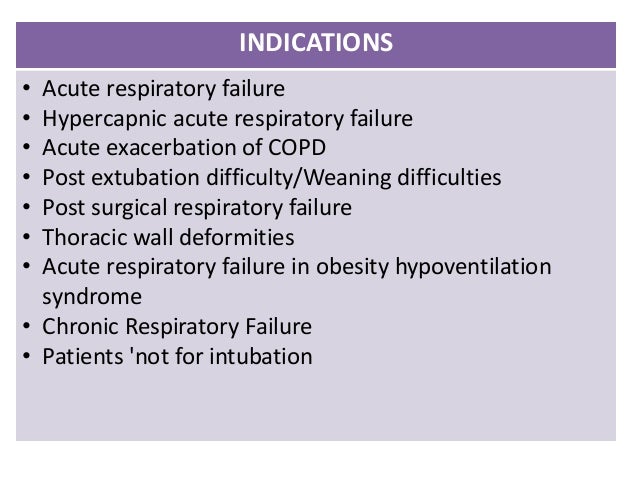
What is hypercapnic respiratory failure?
Hypercapnic respiratory failure means that there's too much carbon dioxide in your blood, and near normal or not enough oxygen in your blood. Get our weekly COPD newsletter. To help meet the challenges of living with COPD, we'll send support and advice for both patients and caregivers.
What is the ICD 10 code for Acute on chronic hypoxic hypercapnic respiratory failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia J96. 21.
Can you have respiratory failure with hypoxia and hypercapnia?
Types of Respiratory Failure If you aren't getting enough oxygen into your blood, your doctor will call this hypoxemic or type 1 respiratory failure. If you have too much carbon dioxide, it's called hypercapnic, hypercarbic, or type 2 respiratory failure.Jan 31, 2021
What is hypercapnic respiratory failure type II?
Type 2 Respiratory Failure (hypercapnic): occurs when alveolar ventilation is insufficient to excrete the carbon dioxide being produced. Inadequate ventilation is due to reduced ventilatory effort or inability to overcome increased resistance to ventilation.
How do you code acute on chronic respiratory failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure J96. 2.
Is hypercarbia and hypercapnia the same thing?
Hypercapnia (from the Greek hyper = "above" or "too much" and kapnos = "smoke"), also known as hypercarbia and CO2 retention, is a condition of abnormally elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood.
Is hypercapnia respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis results from hypoventilation and subsequent hypercapnia. Pulmonary and extrapulmonary disorders can cause hypoventilation.
What is hypercapnic?
Hypercapnia is a buildup of carbon dioxide in your bloodstream. It affects people who have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Oct 29, 2021
What is acute hypoxia respiratory failure?
Acute hypoxemic respiratory failure is severe arterial hypoxemia that is refractory to supplemental oxygen.
What causes acute hypercapnic respiratory failure?
Acute hypercapnic respiratory failure is usually caused by defects in the central nervous system, impairment of neuromuscular transmission, mechanical defect of the ribcage and fatigue of the respiratory muscles. The pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for chronic carbon dioxide retention are not yet clear.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute hypoxemic respiratory failure?
J96.01Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia J96. 01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Which of the following are causes of hypercapnic respiratory?
Common causes of type II (hypercapnic) respiratory failure include the following:COPD.Severe asthma.Drug overdose.Poisonings.Myasthenia gravis.Polyneuropathy.Poliomyelitis.Primary muscle disorders.More items...•Apr 7, 2020
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for abnormal left internal carotid artery on cta
- 2. icd 10 code for gardnerella vaganalis
- 3. icd 10 code for bipolar affective diorder
- 4. icd 10 code for postoperative edema periportal
- 5. icd 10 code for septic right hip
- 6. icd 10 cm code for labor and delivery complicated by prolapse of cord → poa no.
- 7. icd 10 code for sinus tachy
- 8. icd 10 code for hallux valgus right foot
- 9. icd 10 code for v1 zoster
- 10. icd code for gas