What is the ICD 10 code for chronic ear infection?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H65.20 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Chronic serous otitis media, unspecified ear. Chronic serous otitis media; Otitis media (middle ear infection), chronic serous; Otitis media, chronic serosanguinous; Serosanguineous chronic otitis media. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H65.20.
How is acute otitis media diagnosed?
What a diagnosis means
- Acute otitis media. The diagnosis of "ear infection" is generally shorthand for acute otitis media. ...
- Otitis media with effusion. If the diagnosis is otitis media with effusion, the doctor has found evidence of fluid in the middle ear, but there are presently no signs or ...
- Chronic suppurative otitis media. ...
Is acute otitis media contagious?
Acute otitis media is an acute general inflammatory disease of the middle ear mucosa, caused primarily by acute bacterial infection, and is generally not contagious. If the above is useful to you, please feel free to support us with a donation.
Can acute otitis media be prevented?
Recurrent acute otitis media may be prevented by the insertion of drainage tubes (tympanostomy tubes). Most people with acute otitis media get better without treatment. However, because it is hard to predict whose symptoms will not lessen, some doctors treat all people with antibiotics, such as amoxicillin.
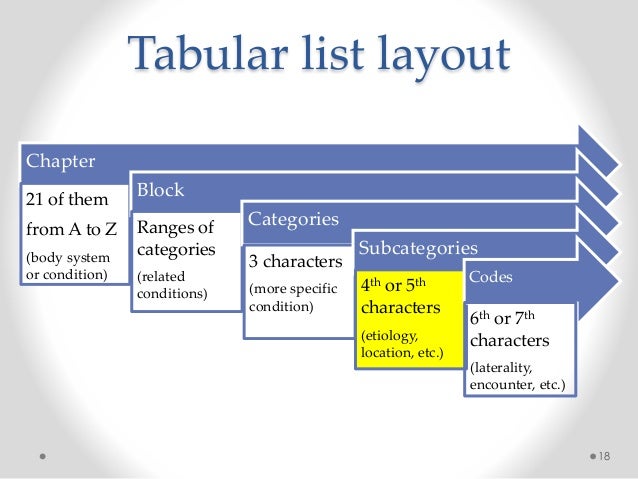
What is left acute otitis media?
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a painful type of ear infection. It occurs when the area behind the eardrum called the middle ear becomes inflamed and infected. The following behaviors in children often mean they have AOM: fits of fussiness and intense crying (in infants)
What is the difference between otitis media and acute otitis media?
Otitis media with effusion (OME) and acute otitis media (AOM) are two main types of otitis media (OM). OME describes the symptoms of middle ear effusion (MEE) without infection, and AOM is an acute infection of the middle ear and caused by bacteria in about 70% of cases (1).
What is the ICD-10 code for external otitis left ear?
ICD-10 Code for Unspecified otitis externa, left ear- H60. 92- Codify by AAPC.
What are the 4 types of otitis media?
What are the different types of otitis media?Acute otitis media. This middle ear infection occurs abruptly causing swelling and redness. ... Otitis media with effusion. Fluid (effusion) and mucus continue to accumulate in the middle ear after an initial infection subsides. ... Chronic otitis media with effusion.
What is the ICD 10 code for otitis media?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66. 9.
What does acute otitis media look like?
The classic findings of acute otitis media, such as fever and earache, are sometimes absent even in cases confirmed by tympanocentesis. A bulging, red, immobile tympanic membrane is highly associated with acute otitis media. However, many physicians rely on redness of the eardrum as the main diagnostic clue.
What is acute otitis externa?
Acute otitis externa is a common condition involving inflammation of the ear canal. The acute form is caused primarily by bacterial infection, with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus the most common pathogens.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
Is otitis media a disease?
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep.
What is acute otitis media with effusion?
What is otitis media with effusion (OME)? Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear space. It is also called serous or secretory otitis media (SOM). This fluid may accumulate in the middle ear as a result of a cold, sore throat or upper respiratory infection.
What are the two types of otitis media?
Serous otitis media (SOM) or Otitis media with effusion (OME) SOM typically follows an episode of AOM. The buildup of fluid that is secreted from the inflamed mucous membrane can be temporary with no signs of infection. Serous otitis media is a common childhood condition that is often known as “glue ear”.
How is otitis media diagnosis?
Otitis media is diagnosed clinically via objective findings on physical exam (otoscopy) combined with the patient's history and presenting signs and symptoms. Several diagnostic tools are available such as a pneumatic otoscope, tympanometry, and acoustic reflectometry to aid in the diagnosis of otitis media.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for exogenous obesity
- 2. what is the icd-10 code for b12
- 3. icd 10 code for iga
- 4. icd 10 code for pharyngeal edema
- 5. icd 10 code for cyst on left face
- 6. icd code for hashimoto thyroiditis
- 7. 2015 icd 10 code for internal fixation of the distal left humerus fracture fracture
- 8. icd 10 code for right index finger wound
- 9. icd 10 code for cesarean delivery
- 10. icd 10 code for pneumonitis, interstitial